Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
In Exercises 1 through 4, describe the associated sample space. 1. A coin is tossed three times and the sequence of heads and tails



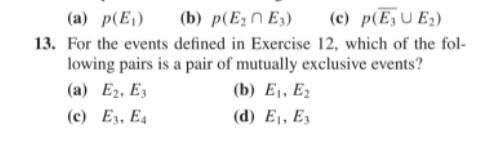


In Exercises 1 through 4, describe the associated sample space. 1. A coin is tossed three times and the sequence of heads and tails is recorded. 2. Two letters are selected simultaneously at random from the letters a, b, c, d. 3. A silver urn and a copper urn contain blue, red, and green balls. An urn is chosen at random and then a ball is se- lected at random from this urn. 4. A box contains 12 items, four of which are defective. An item is chosen at random and not replaced. This is contin- ued until all four defective items have been selected. The total number of items selected is recorded. 5. (a) Suppose that the sample space of an experiment is {1, 2, 3). Determine all possible events. (b) Let S be a sample space containing n elements. How many events are there for the associated experiment? In Exercises 6 through 8, use the following assumptions. A card is selected at random from a standard deck. Let E, F, and G be the following events. E: The card is black. F: The card is a diamond. G: The card is an ace. Describe the following events in complete sentences. 6. (a) EUG 7. (a) EnG (b) EnG (b) EUFUG 8. (a) EUFUG (b) (FOG)UE 11. A die is tossed and the number showing on the top face is recorded. Let E, F, and G be the following events. E: The number is at least 3. F: The number is at most 3. G: The number is divisible by 2. (a) Are E and F mutually exclusive? Justify your an- swer. (b) Are F and G mutually exclusive? Justify your an- swer. (c) Is EUF the certain event? Justify your answer. (d) Is EF the impossible event? Justify your answer. 12. A card is chosen from a standard deck of 52 cards. Con- sider the following events. E: The card drawn is a face card. E2: The card drawn is a heart. Ex: The card drawn has an even number on it. E4: The card drawn is a red card. Compute each of the following. (a) p(E) (b) p(E2E3) (c) p(EU E) 13. For the events defined in Exercise 12, which of the fol- lowing pairs is a pair of mutually exclusive events? (a) E2. Ex (c) E3, E4 (b) E1, E2 (d) E, E 14. Let E be an event for an experiment with sample space A. Show that (a) EUE is the certain event. (b) EnE is the impossible event. 15. A medical team classifies people according to the follow- ing characteristics. Drinking habits: drinks (d), abstains (a) Income level: low (1), middle (m), upper (u) Smoking habits: smoker (s), nonsmoker (n) Let E, F, and G be the following events. E: A person drinks. F: A person's income level is low. G: A person smokes. List the elements in each of the following events. (a) EUF (b) EnF (c) (EUG)NF In Exercises 16 and 17, let S = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) be the sample space of an experiment and let E (1,3,4,5), F(2, 3), G= (4). 16. Compute the events EUF, En F, and F. 17. Compute the following events: EUF and FOG. In Exercises 18 and 19, list the elementary events for the given experiments. 18. A vowel is selected at random from the set of all vowels a, e, i, o, u. 19. A card is selected at random from a standard deck and it is recorded whether the card is a club, spade, diamond, or heart. 20. (a) What is the probability of correctly guessing a per- son's four-digit PIN? (b) People often use the four digits of their birthday (MM-DD) to create a PIN. What is the probability of correctly guessing a PIN created this way, if the birthday is known?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


