Question
In Java import java.util.Scanner; public class LabProgram { // Read and return an array of integers. // The first integer read is number of integers
In Java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LabProgram { // Read and return an array of integers. // The first integer read is number of integers that follow. private static int[] readNums() { Scanner scnr = new Scanner(System.in); int size = scnr.nextInt(); // Read array size int[] numbers = new int[size]; // Create array for (int i = 0; i
// Print the numbers in the array, separated by spaces // (No space or newline before the first number or after the last.) private static void printNums(int[] nums) { for (int i = 0; i
// Exchange nums[j] and nums[k]. private static void swap(int[] nums, int j, int k) { int temp = nums[j]; nums[j] = nums[k]; nums[k] = temp; }
// Sort numbers /* TODO: Count comparisons and swaps. Output the array at the end of each iteration. */ public static void insertionSort(int[] numbers) { int i; int j;
for (i = 1; i 0 && numbers[j]
public static void main(String[] args) { // Step 1: Read numbers into an array int[] numbers = readNums();
// Step 2: Output the numbers array printNums(numbers); System.out.println();
// Step 3: Sort the numbers array insertionSort(numbers); System.out.println();
// step 4 /* TODO: Output the number of comparisons and swaps performed */ } }
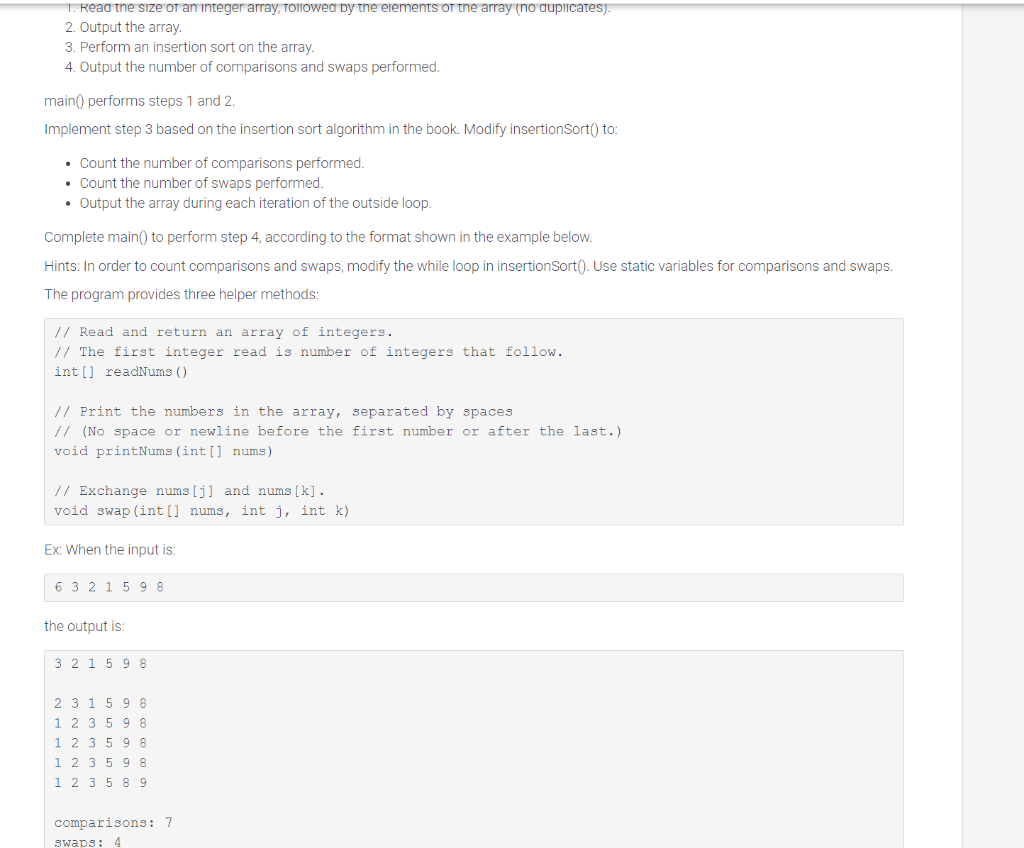
1. Read the size an integer array, ollowed by the elements or the array (no duplicates). 2. Output the array. 3. Perform an insertion sort on the array. 4. Output the number of comparisons and swaps performed. main() performs steps 1 and 2. Implement step 3 based on the insertion sort algorithm in the book. Modify insertionSort() to: - Count the number of comparisons performed. - Count the number of swaps performed. - Output the array during each iteration of the outside loop. Complete main() to perform step 4, according to the format shown in the example below. Hints: In order to count comparisons and swaps, modify the while loop in insertionSort(). Use static variables for comparisons and swaps. The program provides three helper methods: // Read and return an array of integers. // The first integer read is number of integers that follow. int [] readNums() // Print the numbers in the array, separated by spaces // (No space or newline before the first number or after the last.) void printNums (int[] nums) // Exchange nums[j] and nums[k]. void swap (int[] nums, int j, int k) Ex: When the input is: 6321598 the output is: 321111comparisons:7232222113333555555999998888889Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


