in Java please! someone did pa1 !
can you please do pa2 too!
The Problem This is an extension of the first assignment. We extend the problem as below. The museum stores not just paintings, but also sculptures and old, precious documents. Sculptures are put in rooms and documents are stored in show cases. Add new classes to represent these additions: Sculpture, Document, and Showcase. Other changes include the following. 1) Add the following class: Exhibit with fields name, artist (both String type) and year (int). Have a constructor to store these values and getters and setters for all fields. 2) Make Painting, Document, and Sculpture extend Exhibit. 3) Change the Entity class to an interface with two ntethods. public String getName(); public List
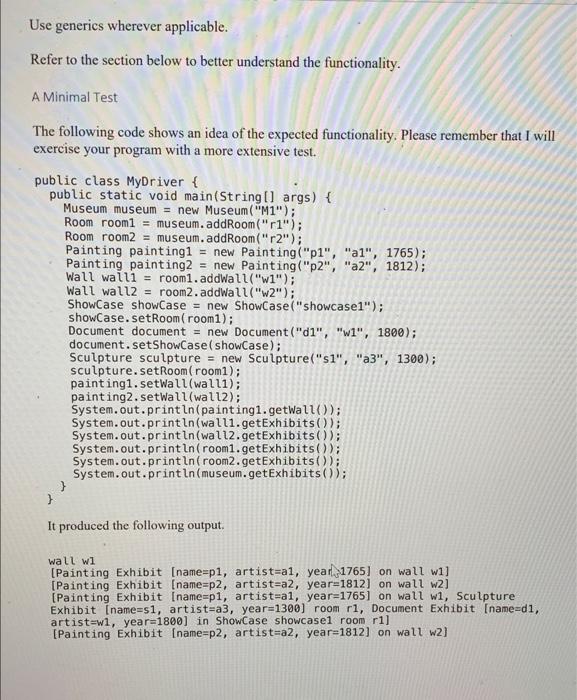
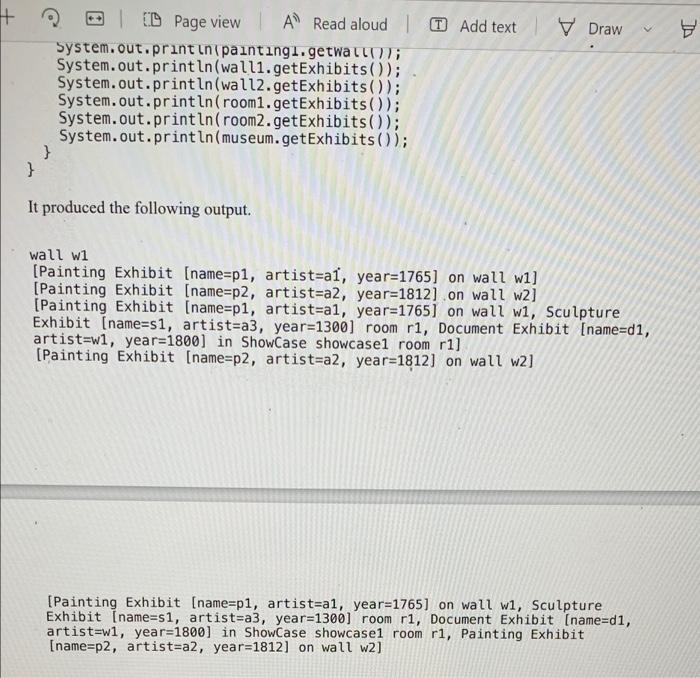
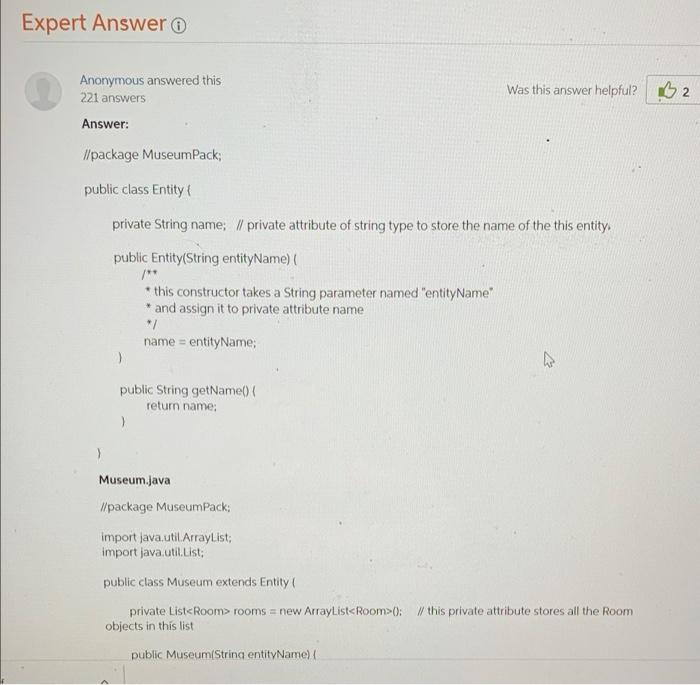
getExhibits(); 4) Implement the Entity interface in an abstract class named MuseumEntity. The class has a constructor that has a single parameter: the name, which is stored in a field. The class implements getName(), but not getExhibits(). 5) The concrete classes Museum, Room, and Wall extend MuseumEntity. Obviously, they have to implement the getExhibits() method. There is no getPaintings() methods in these classes anymore 6) Room and Wall have the method addExhibit(Exhibit exhibit). There is no addPainting(Painting painting) method anymore. 7) Make adjustments necessary to be able to compute the Exhibit objects in Room You will have to override toString() appropriately, throughout. Use generics wherever applicable. Refer to the section below to better understand the functionality. A Minimal Test The following code shows an idea of the expected functionality. Please remember that I will exercise your program with a more extensive test. public class MyDriver { public static void main(String[] args) { Museum museum = new Museum ("M1"); Room room1 = museum.addRoom("r1"); Room room2 = museum.addRoom("r2"); Painting painting1 = new Painting("p1", "al", 1765); Painting painting2 = new Painting("p2", "a2", 1812); Wall waiti = room1.addWall("w1"); Wall wall2 = room2. addWall("w2"); Showcase showCase = new ShowCase("showcasel"); showcase.setRoom(room1); Document document = new Document("di", "w1", 1800); document.setShowCase ( showCase); Sculpture sculpture = new Sculpture("s1", "a3", 1300); sculpture.setRoom(rooml); painting1. setWall(wall1); painting2.setwall(wall2); System.out.println(painting1.getWall()); System.out.println(walli.getExhibits()); System.out.println(wall2.getExhibits(); System.out.println(room1.getExhibits()); System.out.println( room2.getExhibits()); System.out.println(museum.getExhibits()); } } It produced the following output. wall wl (Painting Exhibit [name=p1, artist=a1, yearl 1765] on wall w1] [Painting Exhibit [name=p2, artist=a2, year=1812) on wall w21 (Painting Exhibit name=p1, artist=al, year=1765] on wall wi, Sculpture Exhibit (name=si, artist-a3, year=1300) room ri, Document Exhibit [name=d1, artist=wi, year=1800] in Showcase showcasel room ri] [Painting Exhibit (name=p2, artist-a2, year=1812] on wall w2] V Draw > T + E D Page view A Read aloud | D Add text System.out.print in painting1.getwa ; System.out.println(walli.getExhibits()); System.out.println(wall2.getExhibits()); System.out.println(room1.getExhibits()); System.out.println(room2.getExhibits()); System.out.println(museum.getExhibits()); } } It produced the following output. wall wi [Painting Exhibit (name=p1, artist=al, year=1765] on wall w1] [Painting Exhibit [name=p2, artist=a2, year=1812).on wall w2] [Painting Exhibit (name=p1, artist=al, year=1765] on wall wi, Sculpture Exhibit (name=s1, artist=a3, year=1300) room ri, Document Exhibit (name=d1, artist=w1, year=1800] in Showcase showcasel room r1] [Painting Exhibit [name=p2, artist=a2, year=1812) on wall w2] [Painting Exhibit [name=p1, artist=a1, year=1765] on wall wi, Sculpture Exhibit [name=si, artist=a3, year=1300) room ri, Document Exhibit [name=d1, artist=w1, year=1800] in Showcase showcase1 room ri, Painting Exhibit [name=p2, artist=a2, year=1812] on wall w2] Expert Answer Was this answer helpful? B2 Anonymous answered this 221 answers Answer: // package Museum Pack; public class Entity private String name; // private attribute of string type to store the name of the this entity public Entity(String entityName) /** * this constructor takes a String parameter named "entityName" * and assign it to private attribute name name = entity Name: ) public String getName return name; ) Museum.java //package MuseumPack: import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List: public class Museum extends Entity private List rooms = new ArrayList0: W this private attribute stores all the Room objects in this list public Museum(String entityName)