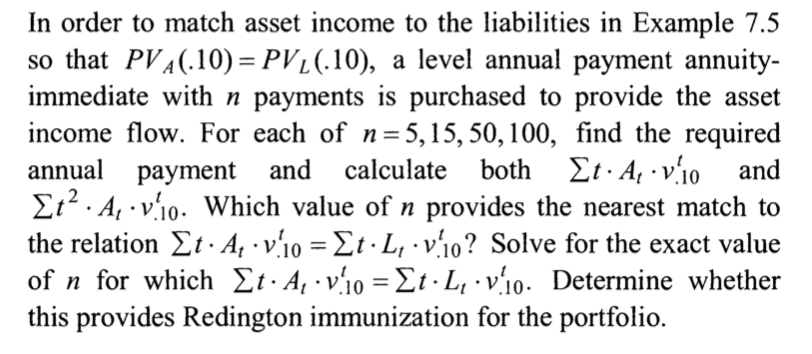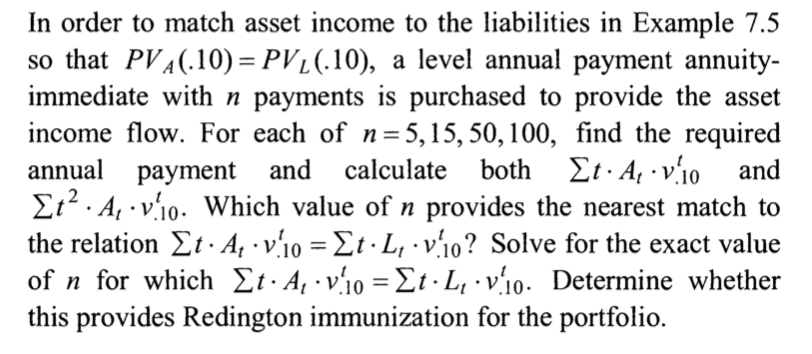


In order to match asset income to the liabilities in Example 7.5 so that PVA(.10)- PVi(10), a level annual payment annuity immediate with n payments is purchased to provide the asset income flow. For each of n-5,15,50, 100, find the required annual payment and calculate both ..v.0 and 2.2 . Al . Vtio. Which value of n provides the nearest match to the relation . At . Vt10 . L, . v110? Solve for the exact value of n for which . Al. Vtl 0.L1.Vt10. Determine whether this provides Redington immunization for the portfolio t A, v,Io EXAMPLE 7.5(Exact matching of assets and liabilities) A small company terminating its operations has decided to provide each of its three employees with a severance package that pays 10,000 per year (at the end of each year) up to and including at age 65, plus a lump sum payment of 100,000 at age 65. In case of death of an employee before age 65, the payments continue until that employee would have been 65. The three employees are now exact ages 50, 53 and 55. The company determines that the payments due under this package can be met by the income and maturities generated by three bonds, each with a face amount of 100,000 and an annual coupon rate of 10% and with maturities of 10, 12, and 15 years. Determine the cost to the company to fund the severance package if the bonds have (effective annual) yield rates of 10% for the 10 year bond. 1 1% for the 12-year bond and 12% for the 15-year bond Applying any of the bond price formulas from Chapter 4 gives prices of 100,000 for the 10-year bond, 93,507.64 for the 12-year bond and 86,378.27 for the 15-year bond, for a total cost of 279,885.91. With the purchase of these bonds, the company's liabilities to the three employees are exactly matched. As a variation on Example 7.5, suppose there are bonds available with a variety of coupon rates and maturity dates (including, perhaps, zero coupon bonds). The company might have several alternative combinations of investments whose asset income flows match the liabilities. Linear pro- gramming can be used to find the minimum cost combination of investments which matches asset flow to liability flow (see Exercise 7.2.1) In Example 7.5, once the company purchases the bonds, the payments to the employees are guaranteed at the exact amounts on the exact dates needed. It may not always be possible to obtain an exact match between projected asset income and liabilities due. Example 7.6 below considers alternative ways of setting up asset cashflows in an attempt to match the liabilities that do not involve exact matching. A simpler illustration of the risk involved in asset-liability matching is presented in the following example. In order to match asset income to the liabilities in Example 7.5 so that PVA(.10)- PVi(10), a level annual payment annuity immediate with n payments is purchased to provide the asset income flow. For each of n-5,15,50, 100, find the required annual payment and calculate both ..v.0 and 2.2 . Al . Vtio. Which value of n provides the nearest match to the relation . At . Vt10 . L, . v110? Solve for the exact value of n for which . Al. Vtl 0.L1.Vt10. Determine whether this provides Redington immunization for the portfolio t A, v,Io EXAMPLE 7.5(Exact matching of assets and liabilities) A small company terminating its operations has decided to provide each of its three employees with a severance package that pays 10,000 per year (at the end of each year) up to and including at age 65, plus a lump sum payment of 100,000 at age 65. In case of death of an employee before age 65, the payments continue until that employee would have been 65. The three employees are now exact ages 50, 53 and 55. The company determines that the payments due under this package can be met by the income and maturities generated by three bonds, each with a face amount of 100,000 and an annual coupon rate of 10% and with maturities of 10, 12, and 15 years. Determine the cost to the company to fund the severance package if the bonds have (effective annual) yield rates of 10% for the 10 year bond. 1 1% for the 12-year bond and 12% for the 15-year bond Applying any of the bond price formulas from Chapter 4 gives prices of 100,000 for the 10-year bond, 93,507.64 for the 12-year bond and 86,378.27 for the 15-year bond, for a total cost of 279,885.91. With the purchase of these bonds, the company's liabilities to the three employees are exactly matched. As a variation on Example 7.5, suppose there are bonds available with a variety of coupon rates and maturity dates (including, perhaps, zero coupon bonds). The company might have several alternative combinations of investments whose asset income flows match the liabilities. Linear pro- gramming can be used to find the minimum cost combination of investments which matches asset flow to liability flow (see Exercise 7.2.1) In Example 7.5, once the company purchases the bonds, the payments to the employees are guaranteed at the exact amounts on the exact dates needed. It may not always be possible to obtain an exact match between projected asset income and liabilities due. Example 7.6 below considers alternative ways of setting up asset cashflows in an attempt to match the liabilities that do not involve exact matching. A simpler illustration of the risk involved in asset-liability matching is presented in the following example