In the case study from The Foreign Exchange Market The Venezuelan Bolivar Black Market, illustrate with clarity how firms can emerge stronger from similar crisis. (250 words)


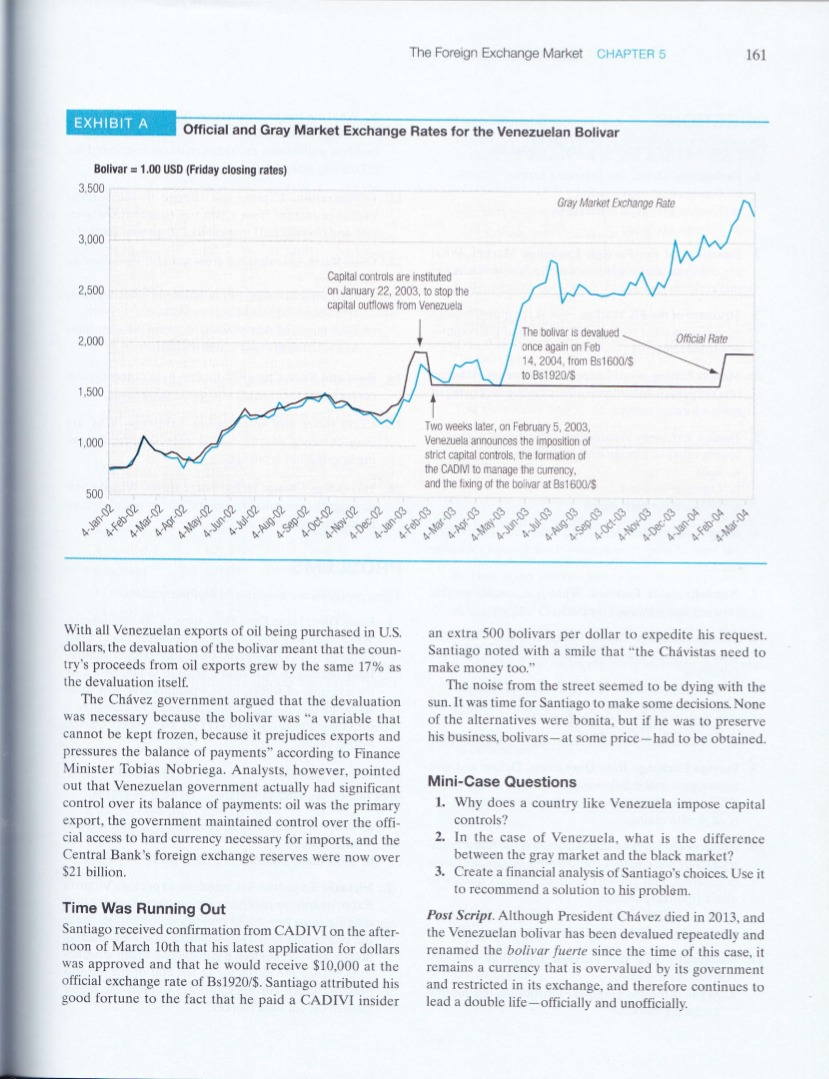
The Foreign Exchange Market CHAPTER 5 159 MINI-CASE Santiago), the escalating capital flight caused the black mar- ket value of the bolivar to plummet to Bs2500/$ in weeks. As markets collapsed and exchange values fell, the Venezuelan inflation rate soared to more than 30% per annum. Capital Controls and CADIVI To combat the downward pressures on the bolivar, the Venezuelan government announced on February 5th, 2003, the passage of the 2003 Exchange Regulations Decree. The Decree took the following actions: The Venezuelan Bolivar Black Market It's late afternoon on March 10th, 2004, and Santiago opens the window of his office in Caracas, Venezuela. Immedi- ately he is hit with the sounds rising from the plaza-cars honking, protesters banging their pots and pans, street ven- dors hawking their goods. Since the imposition of a new set of economic policies by President Hugo Chvez in 2002, such sights and sounds had become a fixture of city life in Caracas. Santiago sighed as he yearned for the simplicity of life in the old Caracas. Santiago's once-thriving pharmaceutical distribution business had hit hard times. Since capital controls were implemented in February of 2003, dollars had been hard to come by. He had been forced to pursue various methods- methods that were more expensive and not always legal - to obtain dollars, causing his margins to decrease by 50%. Adding to the strain, the Venezuelan currency, the boli var (Bs), had been recently devalued (repeatedly). This had instantly squeezed his margins as his costs had risen directly with the exchange rate. He could not find anyone to sell him dollars. His customers needed supplies and they needed them quickly, but how was he going to come up with the $30,000 - the hard currency - to pay for his most recent order? 1. Set the official exchange rate at Bs1596/$ for purchase (bid) and Bs1600/$ for sale (ask): 2. Established the Comisin de Administracin de Divi- sas (CADIVI) to control the distribution of foreign exchange; and 3. Implemented strict price controls to stem inflation trig- gered by the weaker bolivar and the exchange control- induced contraction of imports. Political Chaos Hugo Chvez's tenure as President of Venezuela had been tumultuous at best since his election in 1998. After repeated recalls, resignations, coups, and reappointments, the politi- cal turmoil had taken its toll on the Venezuelan economy as a whole, and its currency in particular. The short-lived suc. cess of the anti-Chvez coup in 2001, and his nearly imme. diate return to office, had set the stage for a retrenchment of his isolationist economic and financial policies. On January 21st, 2003, the bolivar closed at a record low- Bs1853/$. The next day President Hugo Chvez suspended the sale of dollars for two weeks. Nearly instantaneously, an unofficial or black market for the exchange of Venezu- elan bolivars for foreign currencies (primarily U.S. dollars) sprouted. As investors of all kinds sought ways to exit the Ven- ezuelan market, or simply obtain the hard-currency needed to continue to conduct their businesses (as was the case for CADIVI was both the official means and the cheap- est means by which Venezuelan citizens could obtain for- eign currency. In order to receive an authorization from CADIVI to obtain dollars, an applicant was required to complete a series of forms. The applicant was then required to prove that they had paid taxes the previous three years, provide proof of business and asset ownership and lease agreements for company property, and document the cur- rent payment of Social Security. Unofficially, however, there was an additional unstated requirement for permission to obtain foreign currency: authorizations would be reserved for Chvez support ers. In August 2003 an anti-Chvez petition had gained widespread circulation. One million signatures had been collected. Although the government ruled that the peti- tion was invalid, it had used the list of signatures to cre- ate a database of names and social security numbers that CADIVI utilized to cross-check identities on hard currency requests. President Chvez was quoted as saying "Not one more dollar for the putschits; the bolivars belong to the people." Copyright 2004 Thunderbird School of Global Management. All rights reserved. This case was prepared by Nina Camera, Thanh Nguyen, and Jay Ward under the direction of Professor Michael H. Moffett for the purpose of classroom discussion only and not to indi- cate either effective or ineffective management. Names of principals involved in the case have been changed to preserve confidentiality, Venezuela Girds for Exchange Controls." The Wall Street Journal (Eastern edition), February 5, 2003, p. A14. 160 CHAPTER 5 The Foreign Exchange Market Caracas. The implied gray market exchange rate was then calculated as follows: Implicit Gray 7 x Bs7945/Share Bs2952/$ Market Rate $18.84/ADR The official exchange rate on that same day was Bs1598/$. This meant that the gray market rate was quoting the bolivar about 46% weaker against the dollar than what the Venezuelan government officially declared its currency to be worth. Exhibit A illustrates both the official exchange rate and the gray market rate (calculated using CANTV shares) for the January 2002 to March 2004 period. The divergence between the official and gray market rates beginning in February 2003 coincided with the imposition of capital controls Santiago's Alternatives Santiago had little luck obtaining dollars via CADIVI to pay for his imports. Because he had signed the petition call- ing for President Chvez's removal, he had been listed in the CADIVI database as anti-Chvez, and now could not obtain permission to exchange bolivar for dollars. The transaction in question was an invoice for $30,000 in pharmaceutical products from his U.S.-based supplier. Santiago intended to resell these products to a large Ven- ezuelan customer who would distribute the products. This transaction was not the first time that Santiago had been forced to search out alternative sources for meeting his U.S. dollar obligations. Since the imposition of capital con trols, his search for dollars had become a weekly activity for Santiago. In addition to the official process -- through CADIVI-he could also obtain dollars through the gray or black markets. The Gray Market: CANTV Shares In May 2003, three months following the implementation of the exchange controls, a window of opportunity had opened up for Venezuelans-an opportunity that allowed investors in the Caracas stock exchange to avoid the tight foreign exchange curbs. This loophole circumvented the government-imposed restrictions by allowing investors to purchase local shares of the leading telecommunications company CANTV on the Caracas' bourse, and to then convert those shares into dollar-denominated American Depositary Receipts (ADRs) traded on the NYSE. The sponsor for CANTV ADRs on the NYSE was the Bank of New York, the leader in ADR sponsorship and management in the U.S. The Bank of New York had sus- pended trading in CANTV ADRs in February after the passage of the Decree, wishing to determine the legality of trading under the new Venezuelan currency controls. On May 26th, after concluding that trading was indeed legal under the Decree, trading resumed in CANTV shares. CANTV's share price and trading volume both soared in the following week. The share price of CANTV quickly became the primary method of calculating the implicit gray market exchange rate. For example, CANTV shares closed at Bs7945/share on the Caracas bourse on February 6, 2004. That same day, CANTV ADRs closed in New York at $18.84/ADR. Each New York ADR was equal to seven shares of CANTV in The Black Market A third method of obtaining hard currency by Venezuelans was through the rapidly expanding black market. The black market was, as is the case with black markets all over the world, essentially unseen and illegal. It was, however, quite sophisticated, using the services of a stockbroker or banker in Venezuela who simultaneously held U.S. dollar accounts offshore. The choice of a black market broker was a critical one; in the event of a failure to complete the transaction properly there was no legal recourse. If Santiago wished to purchase dollars on the black mar- ket, he would deposit bolivars in his broker's account in Venezuela. The agreed upon black market exchange rate was determined on the day of the deposit, and usually was within a 20% band of the gray market rate derived from the CANTV share price. Santiago would then be given access to a dollar-denominated bank account outside of Venezu- ela in the agreed amount. The transaction took, on average, two business days to settle. The unofficial black market rate was Bs3300/$. In early 2004 President Chvez had asked Venezuela's Central Bank to give him "a little billion" - millardito-of its $21 billion in foreign exchange reserves. Chvez argued that the money was actually the people's, and he wished to invest some of it in the agricultural sector. The Central Bank refused. Not to be thwarted in its search for funds, the Chvez government announced on February 9, 2004, another devaluation. The bolivar was devalued 17%, falling in official value from Bs1600/$ to Bs1920/$ (see Exhibit A). 'In fact CANTV's share price continued to rise over the 2002 to 2004 period as a result of its use as an exchange rate mechanism. The use of CANTV ADRs as a method of obtaining dollars by Venezuelan individuals and organizations was typically described as "not illegal." "Morgan Stanley Capital International (MSCI) announced on November 26, 2003, that it would change its standard spot rate for the Venezuelan bolivar to the notional rate based on the relationship between the price of CANTV Telefonos de Venezuela D in the local market in bolivars and the price of its ADR in U.S. dollars. The Foreign Exchange Market CHAPTER 5 161 EXHIBITA Official and Gray Market Exchange Rates for the Venezuelan Bolivar Bolivar = 1.00 USD (Friday closing rates) 3,500 Gray Market Exchange Rate 3,000 2,500 Capital controls are instituted on January 22, 2003, to stop the capital outflows from Venezuela 2,000 Official Rate The bolivar is devalued once again on Feb 14, 2004, from Bs1600/$ to Bs1920/$ 1,500 1,000 Two weeks later, on February 5, 2003, Venezuela announces the imposition of strict capital controls, the formation of the CAD to manage the currency and the fixing of the bolivar at Bs1600/$ 500 4-Apr-02 4-May-02 4-Jun-02 4-Feb-02 4-Mar-02 20-in-t 4-Sep-02 4-Dec-02 4-Jan-03 4-Feb-03 4-Jul-03 4-Aug-03 4-Jun-03 4-Apr-03 4-May-03 4-Sep-03 4-Oct-03 4-Dec-03 4-Jan-04 4-Mar-04 4-Jan-02 4-Aug-02 4-Oct-02 4-Nov-02 4-Mar-03 4-Nov-03 4-Feb-04 an extra 500 bolivars per dollar to expedite his request. Santiago noted with a smile that "the Chvistas need to make money too." The noise from the street seemed to be dying with the sun. It was time for Santiago to make some decisions. None of the alternatives were bonita, but if he was to preserve his business, bolivars--at some price-had to be obtained. With all Venezuelan exports of oil being purchased in U.S. dollars, the devaluation of the bolivar meant that the coun- try's proceeds from oil exports grew by the same 17% as the devaluation itself. The Chvez government argued that the devaluation was necessary because the bolivar was "a variable that cannot be kept frozen, because it prejudices exports and pressures the balance of payments according to Finance Minister Tobias Nobriega. Analysts, however, pointed out that Venezuelan government actually had significant control over its balance of payments: oil was the primary export, the government maintained control over the offi- cial access to hard currency necessary for imports, and the Central Bank's foreign exchange reserves were now over $21 billion. Mini-Case Questions 1. Why does a country like Venezuela impose capital controls? 2. In the case of Venezuela, what is the difference between the gray market and the black market? 3. Create a financial analysis of Santiago's choices. Use it to recommend a solution to his problem. Post Script. Although President Chvez died in 2013, and the Venezuelan bolivar has been devalued repeatedly and renamed the bolivar fuerte since the time of this case, it remains a currency that is overvalued by its government and restricted in its exchange, and therefore continues to lead a double life-officially and unofficially. Time Was Running Out Santiago received confirmation from CADIVI on the after- noon of March 10th that his latest application for dollars was approved and that he would receive $10,000 at the official exchange rate of Bs1920/$. Santiago attributed his good fortune to the fact that he paid a CADIVI insider The Foreign Exchange Market CHAPTER 5 159 MINI-CASE Santiago), the escalating capital flight caused the black mar- ket value of the bolivar to plummet to Bs2500/$ in weeks. As markets collapsed and exchange values fell, the Venezuelan inflation rate soared to more than 30% per annum. Capital Controls and CADIVI To combat the downward pressures on the bolivar, the Venezuelan government announced on February 5th, 2003, the passage of the 2003 Exchange Regulations Decree. The Decree took the following actions: The Venezuelan Bolivar Black Market It's late afternoon on March 10th, 2004, and Santiago opens the window of his office in Caracas, Venezuela. Immedi- ately he is hit with the sounds rising from the plaza-cars honking, protesters banging their pots and pans, street ven- dors hawking their goods. Since the imposition of a new set of economic policies by President Hugo Chvez in 2002, such sights and sounds had become a fixture of city life in Caracas. Santiago sighed as he yearned for the simplicity of life in the old Caracas. Santiago's once-thriving pharmaceutical distribution business had hit hard times. Since capital controls were implemented in February of 2003, dollars had been hard to come by. He had been forced to pursue various methods- methods that were more expensive and not always legal - to obtain dollars, causing his margins to decrease by 50%. Adding to the strain, the Venezuelan currency, the boli var (Bs), had been recently devalued (repeatedly). This had instantly squeezed his margins as his costs had risen directly with the exchange rate. He could not find anyone to sell him dollars. His customers needed supplies and they needed them quickly, but how was he going to come up with the $30,000 - the hard currency - to pay for his most recent order? 1. Set the official exchange rate at Bs1596/$ for purchase (bid) and Bs1600/$ for sale (ask): 2. Established the Comisin de Administracin de Divi- sas (CADIVI) to control the distribution of foreign exchange; and 3. Implemented strict price controls to stem inflation trig- gered by the weaker bolivar and the exchange control- induced contraction of imports. Political Chaos Hugo Chvez's tenure as President of Venezuela had been tumultuous at best since his election in 1998. After repeated recalls, resignations, coups, and reappointments, the politi- cal turmoil had taken its toll on the Venezuelan economy as a whole, and its currency in particular. The short-lived suc. cess of the anti-Chvez coup in 2001, and his nearly imme. diate return to office, had set the stage for a retrenchment of his isolationist economic and financial policies. On January 21st, 2003, the bolivar closed at a record low- Bs1853/$. The next day President Hugo Chvez suspended the sale of dollars for two weeks. Nearly instantaneously, an unofficial or black market for the exchange of Venezu- elan bolivars for foreign currencies (primarily U.S. dollars) sprouted. As investors of all kinds sought ways to exit the Ven- ezuelan market, or simply obtain the hard-currency needed to continue to conduct their businesses (as was the case for CADIVI was both the official means and the cheap- est means by which Venezuelan citizens could obtain for- eign currency. In order to receive an authorization from CADIVI to obtain dollars, an applicant was required to complete a series of forms. The applicant was then required to prove that they had paid taxes the previous three years, provide proof of business and asset ownership and lease agreements for company property, and document the cur- rent payment of Social Security. Unofficially, however, there was an additional unstated requirement for permission to obtain foreign currency: authorizations would be reserved for Chvez support ers. In August 2003 an anti-Chvez petition had gained widespread circulation. One million signatures had been collected. Although the government ruled that the peti- tion was invalid, it had used the list of signatures to cre- ate a database of names and social security numbers that CADIVI utilized to cross-check identities on hard currency requests. President Chvez was quoted as saying "Not one more dollar for the putschits; the bolivars belong to the people." Copyright 2004 Thunderbird School of Global Management. All rights reserved. This case was prepared by Nina Camera, Thanh Nguyen, and Jay Ward under the direction of Professor Michael H. Moffett for the purpose of classroom discussion only and not to indi- cate either effective or ineffective management. Names of principals involved in the case have been changed to preserve confidentiality, Venezuela Girds for Exchange Controls." The Wall Street Journal (Eastern edition), February 5, 2003, p. A14. 160 CHAPTER 5 The Foreign Exchange Market Caracas. The implied gray market exchange rate was then calculated as follows: Implicit Gray 7 x Bs7945/Share Bs2952/$ Market Rate $18.84/ADR The official exchange rate on that same day was Bs1598/$. This meant that the gray market rate was quoting the bolivar about 46% weaker against the dollar than what the Venezuelan government officially declared its currency to be worth. Exhibit A illustrates both the official exchange rate and the gray market rate (calculated using CANTV shares) for the January 2002 to March 2004 period. The divergence between the official and gray market rates beginning in February 2003 coincided with the imposition of capital controls Santiago's Alternatives Santiago had little luck obtaining dollars via CADIVI to pay for his imports. Because he had signed the petition call- ing for President Chvez's removal, he had been listed in the CADIVI database as anti-Chvez, and now could not obtain permission to exchange bolivar for dollars. The transaction in question was an invoice for $30,000 in pharmaceutical products from his U.S.-based supplier. Santiago intended to resell these products to a large Ven- ezuelan customer who would distribute the products. This transaction was not the first time that Santiago had been forced to search out alternative sources for meeting his U.S. dollar obligations. Since the imposition of capital con trols, his search for dollars had become a weekly activity for Santiago. In addition to the official process -- through CADIVI-he could also obtain dollars through the gray or black markets. The Gray Market: CANTV Shares In May 2003, three months following the implementation of the exchange controls, a window of opportunity had opened up for Venezuelans-an opportunity that allowed investors in the Caracas stock exchange to avoid the tight foreign exchange curbs. This loophole circumvented the government-imposed restrictions by allowing investors to purchase local shares of the leading telecommunications company CANTV on the Caracas' bourse, and to then convert those shares into dollar-denominated American Depositary Receipts (ADRs) traded on the NYSE. The sponsor for CANTV ADRs on the NYSE was the Bank of New York, the leader in ADR sponsorship and management in the U.S. The Bank of New York had sus- pended trading in CANTV ADRs in February after the passage of the Decree, wishing to determine the legality of trading under the new Venezuelan currency controls. On May 26th, after concluding that trading was indeed legal under the Decree, trading resumed in CANTV shares. CANTV's share price and trading volume both soared in the following week. The share price of CANTV quickly became the primary method of calculating the implicit gray market exchange rate. For example, CANTV shares closed at Bs7945/share on the Caracas bourse on February 6, 2004. That same day, CANTV ADRs closed in New York at $18.84/ADR. Each New York ADR was equal to seven shares of CANTV in The Black Market A third method of obtaining hard currency by Venezuelans was through the rapidly expanding black market. The black market was, as is the case with black markets all over the world, essentially unseen and illegal. It was, however, quite sophisticated, using the services of a stockbroker or banker in Venezuela who simultaneously held U.S. dollar accounts offshore. The choice of a black market broker was a critical one; in the event of a failure to complete the transaction properly there was no legal recourse. If Santiago wished to purchase dollars on the black mar- ket, he would deposit bolivars in his broker's account in Venezuela. The agreed upon black market exchange rate was determined on the day of the deposit, and usually was within a 20% band of the gray market rate derived from the CANTV share price. Santiago would then be given access to a dollar-denominated bank account outside of Venezu- ela in the agreed amount. The transaction took, on average, two business days to settle. The unofficial black market rate was Bs3300/$. In early 2004 President Chvez had asked Venezuela's Central Bank to give him "a little billion" - millardito-of its $21 billion in foreign exchange reserves. Chvez argued that the money was actually the people's, and he wished to invest some of it in the agricultural sector. The Central Bank refused. Not to be thwarted in its search for funds, the Chvez government announced on February 9, 2004, another devaluation. The bolivar was devalued 17%, falling in official value from Bs1600/$ to Bs1920/$ (see Exhibit A). 'In fact CANTV's share price continued to rise over the 2002 to 2004 period as a result of its use as an exchange rate mechanism. The use of CANTV ADRs as a method of obtaining dollars by Venezuelan individuals and organizations was typically described as "not illegal." "Morgan Stanley Capital International (MSCI) announced on November 26, 2003, that it would change its standard spot rate for the Venezuelan bolivar to the notional rate based on the relationship between the price of CANTV Telefonos de Venezuela D in the local market in bolivars and the price of its ADR in U.S. dollars. The Foreign Exchange Market CHAPTER 5 161 EXHIBITA Official and Gray Market Exchange Rates for the Venezuelan Bolivar Bolivar = 1.00 USD (Friday closing rates) 3,500 Gray Market Exchange Rate 3,000 2,500 Capital controls are instituted on January 22, 2003, to stop the capital outflows from Venezuela 2,000 Official Rate The bolivar is devalued once again on Feb 14, 2004, from Bs1600/$ to Bs1920/$ 1,500 1,000 Two weeks later, on February 5, 2003, Venezuela announces the imposition of strict capital controls, the formation of the CAD to manage the currency and the fixing of the bolivar at Bs1600/$ 500 4-Apr-02 4-May-02 4-Jun-02 4-Feb-02 4-Mar-02 20-in-t 4-Sep-02 4-Dec-02 4-Jan-03 4-Feb-03 4-Jul-03 4-Aug-03 4-Jun-03 4-Apr-03 4-May-03 4-Sep-03 4-Oct-03 4-Dec-03 4-Jan-04 4-Mar-04 4-Jan-02 4-Aug-02 4-Oct-02 4-Nov-02 4-Mar-03 4-Nov-03 4-Feb-04 an extra 500 bolivars per dollar to expedite his request. Santiago noted with a smile that "the Chvistas need to make money too." The noise from the street seemed to be dying with the sun. It was time for Santiago to make some decisions. None of the alternatives were bonita, but if he was to preserve his business, bolivars--at some price-had to be obtained. With all Venezuelan exports of oil being purchased in U.S. dollars, the devaluation of the bolivar meant that the coun- try's proceeds from oil exports grew by the same 17% as the devaluation itself. The Chvez government argued that the devaluation was necessary because the bolivar was "a variable that cannot be kept frozen, because it prejudices exports and pressures the balance of payments according to Finance Minister Tobias Nobriega. Analysts, however, pointed out that Venezuelan government actually had significant control over its balance of payments: oil was the primary export, the government maintained control over the offi- cial access to hard currency necessary for imports, and the Central Bank's foreign exchange reserves were now over $21 billion. Mini-Case Questions 1. Why does a country like Venezuela impose capital controls? 2. In the case of Venezuela, what is the difference between the gray market and the black market? 3. Create a financial analysis of Santiago's choices. Use it to recommend a solution to his problem. Post Script. Although President Chvez died in 2013, and the Venezuelan bolivar has been devalued repeatedly and renamed the bolivar fuerte since the time of this case, it remains a currency that is overvalued by its government and restricted in its exchange, and therefore continues to lead a double life-officially and unofficially. Time Was Running Out Santiago received confirmation from CADIVI on the after- noon of March 10th that his latest application for dollars was approved and that he would receive $10,000 at the official exchange rate of Bs1920/$. Santiago attributed his good fortune to the fact that he paid a CADIVI insider









