Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
In the case where I have answers filled in please double check the answer. Thank you. 3. 6: The Cost of Capital: Weighted Average Cost





In the case where I have answers filled in please double check the answer.
Thank you.
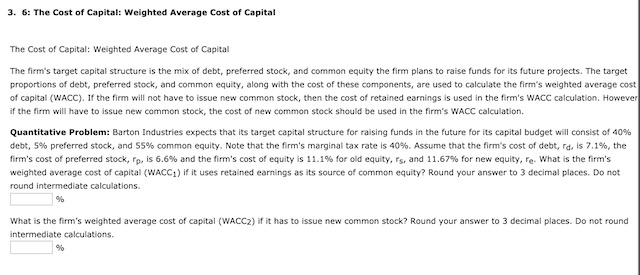
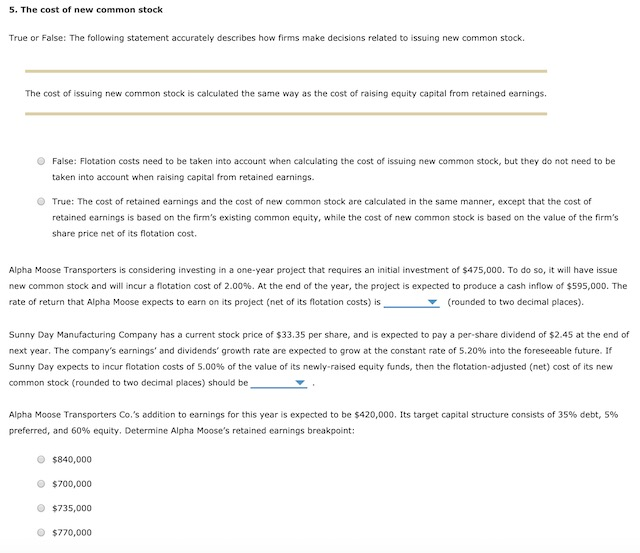
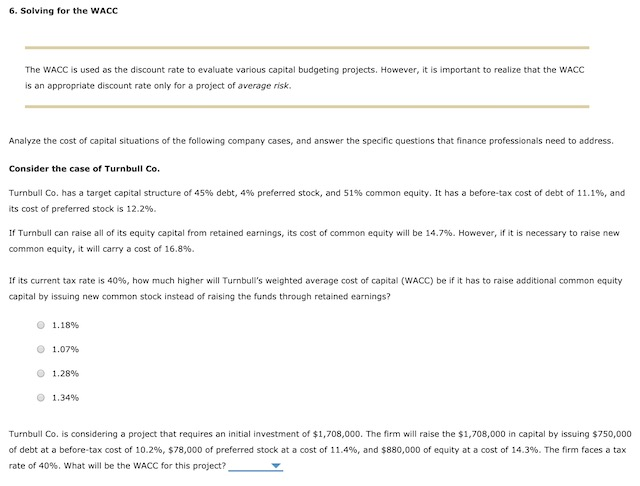
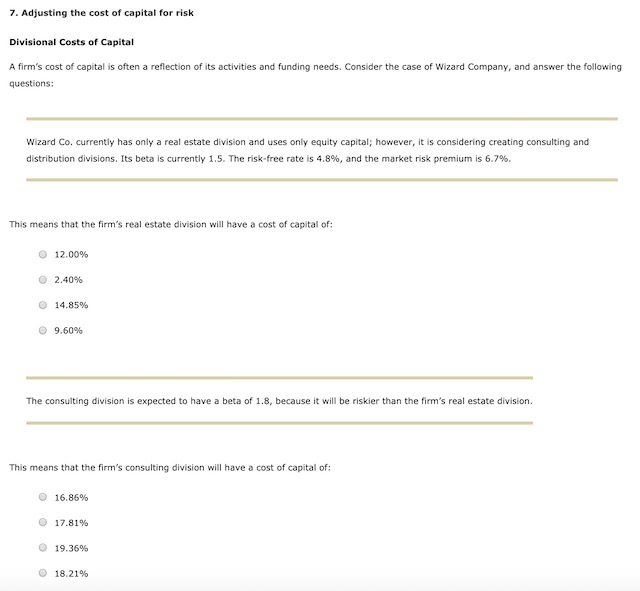
3. 6: The Cost of Capital: Weighted Average Cost of Capital The Cost of Capital: Weighted Average Cost of Capital The firm's target capital structure is the mix of debt, preferred stock, and common equity the firm plans to raise funds for its future projects. The target proportions of debt, preferred stock, and common equity, along with the cost of these components, are used to calculate the firm's weighted average cost of capital (WACC). If the firm will not have to issue new common stock, then the cost of retained earnings is used in the firm's WACC calculation. However if the firm will have to issue new common stock, the cost of new common stock should be used in the firm's WACC calculation. Quantitative Problem: Barton Industries expects that its target capital structure for raising funds in the future for its capital budget will consist of 40% debt, 5% preferred stock, and 55% common equity. Note that the firm's marginal tax rate is 40%. Assume that the firm's cost of debt, rd, is 7.1%, the firm's cost of preferred stock, fp, is 6.6% and the firm's cost of equity is 11.1% for old equity, rs, and 11.67% for new equity, re. What is the firm's weighted average cost of capital (WACC) if it uses retained earnings as its source of common equity? Round your answer to 3 decimal places. Do not round intermediate calculations What is the firm's weighted average cost of capital (WACC2) if it has to issue new common stock? Round your answer to 3 decimal places. Do not round intermediate calculations. 2. An overview of a firm's cost of debt To calculate the after-tax cost of debt, multiply the before-tax cost of debt by (1-1) Andalusian Limited (AL) can borrow funds at an interest rate of 9.70% for a period of five years. Its marginal federal-plus-state tax rate is 40%. AL'S after-tax cost of debt is 5.82% (rounded to two decimal places). At the present time, Andalusian Limited (AL) has 10-year noncallable bonds with a face value of $1,000 that are outstanding. These bonds have a current market price of $1,092.79 per bond, carry a coupon rate of 11%, and distribute annual coupon payments. The company incurs a federal-plus- state tax rate of 40%. If AL wants to issue new debt, what would be a reasonable estimate for its after-tax cost of debt (rounded to two decimal places)? 5.14% 6.85% 4.57% 5.71% 4. The cost of retained earnings True or False: It is free for a company to raise money through retained earnings, because retained earnings represent money that is left over after dividends are paid out to shareholders. True False The cost of equity using the CAPM approach The current risk-free rate of return (TP) is 4.23%, while the market risk premium is 5.75%, the Wilson Company has a beta of 0.92. Using the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) approach, Wilson's cost of equity is The cost of equity using the bond yield plus risk premium approach The Hoover Company is closely held and, therefore, cannot generate reliable inputs with which to use the CAPM method for estimating a company's cost of internal equity. Hoover's bonds yield 10.28%, and the firm's analysts estimate that the firm's risk premium on its stock over its bonds is 4.95%. Based on the bond-yield-plus-risk-premium approach, Hoover's cost of internal equity is: 16.75% 19.04% 15.23% 14.47% The cost of equity using the discounted cashflow (or dividend growth) approach Tucker Enterprises's stock is currently selling for $25.67 per share, and the firm expects its per share dividend to be $1.38 in one year. Analysts project the firm's growth rate to be constant at 5.72%. Using the cost of equity using the discounted cashflow (or dividend growth) approach, what is Tucker's cost of internal equity? 11.66% 10.55% 11.10% 14.99% Estimating growth rates It is often difficult to estimate the expected future dividend growth rate for use in estimating the cost of existing equity using the DCF or DG approach. In general, there are three available methods to generate such an estimate: Carry forward a historical realized growth rate, and apply it to the future. Locate and apply an expected future growth rate prepared and published by security analysts. Use the retention growth model. Suppose Tucker is currently distributing 70.00 of its earnings in the form of cash dividends. It has also historically generated an average return on equity (ROE) of 22.00. Tucker's estimated growth rate is 5. The cost of new common stock True or False: The following statement accurately describes how firms make decisions related to issuing new common stock. The cost of issuing new common stock is calculated the same way as the cost of raising equity capital from retained earnings. False: Flotation costs need to be taken into account when calculating the cost of issuing new common stock, but they do not need to be taken into account when raising capital from retained earnings. True: The cost of retained earnings and the cost of new common stock are calculated in the same manner, except that the cost of retained earnings is based on the firm's existing common equity, while the cost of new common stock is based on the value of the firm's share price net of its flotation cost. Alpha Moose Transporters is considering investing in a one-year project that requires an initial investment of $475,000. To do so, it will have issue new common stock and will incur a flotation cost of 2.00%. At the end of the year, the project is expected to produce a cash inflow of $595,000. The rate of return that Alpha Moose expects to earn on its project (net of its flotation costs) is (rounded to two decimal places). Sunny Day Manufacturing Company has a current stock price of $33.35 per share, and is expected to pay a per-share dividend of $2.45 at the end of next year. The company's earnings and dividends' growth rate are expected to grow at the constant rate of 5.20% into the foreseeable future. If Sunny Day expects to incur flotation costs of 5.00% of the value of its newly-raised equity funds, then the flotation-adjusted (net) cost of its new common stock (rounded to two decimal places) should be Alpha Moose Transporters Co.'s addition to earnings for this year is expected to be $420,000. Its target capital structure consists of 35% debt, 5% preferred, and 60% equity. Determine Alpha Moose's retained earnings breakpoint: $840,000 $700,000 $735,000 $770,000 6. Solving for the WACC The WACC is used as the discount rate to evaluate various capital budgeting projects. However, it is important to realize that the WACC is an appropriate discount rate only for a project of average risk Analyze the cost of capital situations of the following company cases, and answer the specific questions that finance professionals need to address Consider the case of Turnbull Co. Turnbull Co. has a target capital structure of 45% debt, 4% preferred stock, and 51% common equity. It has a before-tax cost of debt of 11.1%, and its cost of preferred stock is 12.2%. If Turnbull can raise all of its equity capital from retained earnings, its cost of common equity will be 14.7%. However, if it is necessary to raise new common equity, it will carry a cost of 16.8%. If its current tax rate is 40%, how much higher will Turnbull's weighted average cost of capital (WACC) be if it has to raise additional common equity capital by issuing new common stock instead of raising the funds through retained earnings? 1.18% 1.07% 1.28% 1.34% Turnbull Co. is considering a project that requires an initial investment of $1,708,000. The firm will raise the $1,708,000 in capital by issuing $750,000 of debt at a before-tax cost of 10.2%, $78,000 of preferred stock at a cost of 11.4%, and $880,000 of equity at a cost of 14.3%. The firm faces a tax rate of 40%. What will be the WACC for this project? Consider the case of Kuhn Co. Kuhn Co. is considering a new project that will require an initial investment of $45 million. It has a target capital structure of 45% debt, 4% preferred stock, and 51% common equity. Kuhn has noncallable bonds outstanding that mature in 15 years with a face value of $1,000, an annual coupon rate of 11%, and a market price of $1,555.38. The yield on the company's current bonds is a good approximation of the yield on any new bonds that it issues. The company can sell shares of preferred stock that pay an annual dividend of $8 at a price of $92.25 per share. Kuhn does not have any retained earnings available to finance this project, so the firm will have to issue new common stock to help fund it. Its common stock is currently selling for $22.35 per share, and it is expected to pay a dividend of $1.36 at the end of next year. Flotation costs will represent 3% of the funds raised by issuing new common stock. The company is projected to grow at a constant rate of 8.7%, and they face a tax rate of 40%. Determine what Kuhn Company's WACC will be for this project. 7. Adjusting the cost of capital for risk Divisional Costs of Capital A firm's cost of capital is often a reflection of its activities and funding needs. Consider the case of Wizard Company, and answer the following questions: Wizard Co. currently has only a real estate division and uses only equity capital; however, it is considering creating consulting and distribution divisions. Its beta is currently 1.5. The risk-free rate is 4.8%, and the market risk premium is 6.7%. This means that the firm's real estate division will have a cost of capital of: 12.00% 2.40% O 14.85% 9.60% The consulting division is expected to have a beta of 1.8, because it will be riskier than the firm's real estate division. This means that the firm's consulting division will have a cost of capital of: 16.86% 17.81% 19.36% 18.21% The distribution division will have less risk than the firm's real estate division, so its beta is expected to be 0.5. This means that the distribution division's cost of capital will be: O 17.61% 8.15% 18.91% 18.81% Wizard Co. expects 75% of its total value to end up in the real estate division, 10% in the consulting division, and 15% in the distribution division. Based on this information, what rate of return should its investors require once it opens the new divisions? (Note: Round your intermediate calculations to two decimal places.) 14.05% 16.90% 18.80% 15.35%Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


