In the image is the entire problem with all the correct answers, but I am wondering how to calculate only two parts of one question (in the red square in the image). I put the whole question so you can see the whole process, but the part of the question I am wondering is how they calculated the $4,900 as well as the $704 in the following questions: The person in charge of purchasing (overspent, saved money) by purchasing materials $0.50 per pound (above, below) standard cost. However, (less, more) material was used. The net effect was a(n) (unfavorable, favorable) variance of $4,900. There was (a savings, an excess cost) on labor because the average wage rate was (below, higher than) standard. However, (less, more) than the standard amount of labor was used. The net effect was a(n) (unfavorable, favorable) variance of $704. 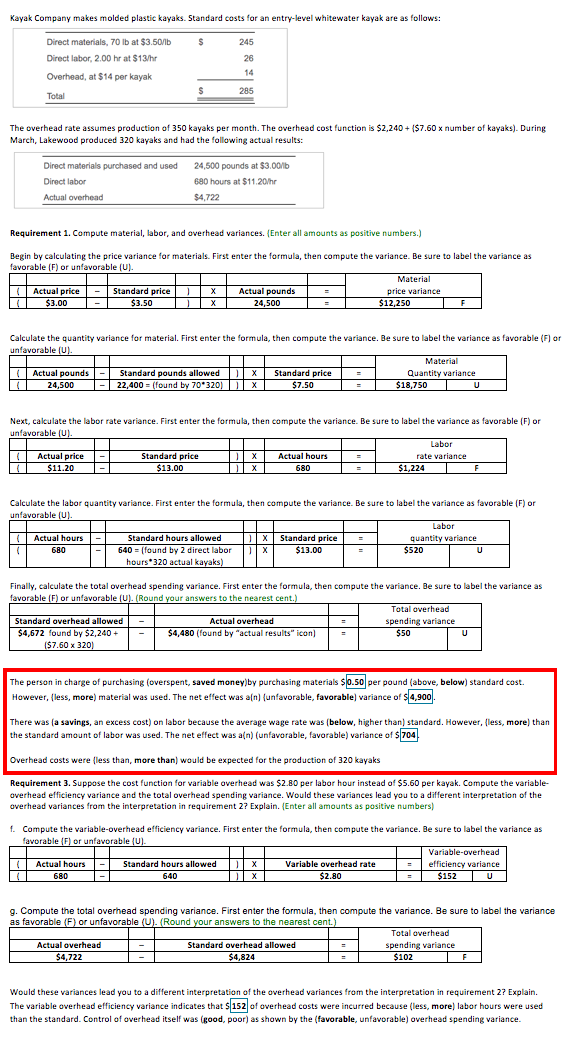
Kayak Company makes molded plastic kayaks. Standard costs for an entry-level whitewater kayak are as follows: Direct materials, 70 lb at $3.50/1b S 245 Direct labor, 2.00 hr at $13/hr $/ 26 14 Overhead, at $14 per kayak 285 Total The overhead rate assumes production of 350 kayaks per month. The overhead cost function is $2,240 + ($7.60 x number of kayaks). During March, Lakewood produced 320 kayaks and had the following actual results: Direct materials purchased and used 24,500 pounds at $3.00/b Direct labor 680 hours at $11.20/hr Actual overhead $4,722 Requirement 1. Compute material, labor, and overhead variances. Enter all amounts as positive numbers.) Begin by calculating the price variance for materials. First enter the formula, then compute the variance. Be sure to label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). Material Actual price - Standard price X $3.00 $3.50 Actual pounds 24,500 price variance $12,250 F Calculate the quantity variance for material. First enter the formula, then compute the variance. Be sure to label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (u) Material Actual pounds Standard pounds allowed 1 X Standard price Quantity variance 10 24,500 -22,400 = (found by 70*320) X X $7.50 $18,750 U Next, calculate the labor rate variance. First enter the formula, then compute the variance. Be sure to label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). Labor Actual hours Actual price $11.20 Standard price $13.00 1 x rate variance $1,224 680 Calculate the labor quantity variance. First enter the formula, then compute the variance. Be sure to label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). Labor ( Actual hours Standard hours allowed 1 x Standard price quantity variance 680 640 = {found by 2 direct labor $13.00 $520 U hours 320 actual kayaks) Finally, calculate the total overhead spending variance. First enter the formula, then compute the variance. Be sure to label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Round your answers to the nearest cent.) Total overhead Standard overhead allowed Actual overhead spending variance $4,672 found by $2,240 + $4,480 (found by "actual results" icon) $50 U 1$7.50 x 320) The person in charge of purchasing (overspent, saved money) by purchasing materials $0.50 per pound (above, below) standard cost. However, (less, more) material was used. The net effect was an unfavorable, favorable) variance of $4,900. There was (a savings, an excess cost) on labor because the average wage rate was (below, higher than) standard. However, less, more than the standard amount of labor was used. The net effect was a(n) (unfavorable, favorable) variance of $ 704 Overhead costs were less than, more than) would be expected for the production of 320 kayaks Requirement 3. Suppose the cost function for variable overhead was $2.80 per labor hour instead of $5.50 per kayak. Compute the variable- overhead efficiency variance and the total overhead spending variance. Would these variances lead you to a different interpretation of the overhead variances from the interpretation in requirement 2? Explain. {Enter all amounts as positive numbers) f. Compute the variable-overhead efficiency variance. First enter the formula, then compute the variance. Be sure to label the variance as favorable) or unfavorable (U). Variable-overhead Actual hours - Standard hours allowed ) XT Variable overhead rate efficiency variance 680 640 $2.80 $152U 9. Compute the total overhead spending variance. First enter the formula, then compute the variance. Be sure to label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Round your answers to the nearest cent.) Total overhead Actual overhead Standard overhead allowed spending variance $4,722 $4,824 $102 F Would these variances lead you to a different interpretation of the overhead variances from the interpretation in requirement 2? Explain. The variable overhead efficiency variance indicates that s 152 of overhead costs were incurred because (less, more) labor hours were used than the standard. Control of overhead itself was good, poor) as shown by the (favorable, unfavorable) overhead spending variance







