Question
In the intra-AS routing algorithm based on Belman-Ford, the distance vector of any vertex contains the shortest distances between it and any other vertex in
In the intra-AS routing algorithm based on Belman-Ford, the distance vector of any vertex contains the shortest distances between it and any other vertex in the network. For example, the final distance vector for vertex z in the following grid drawing is (0,1,1,4,5,7,8) for (z,x,y,v,w,u,t) respectively.
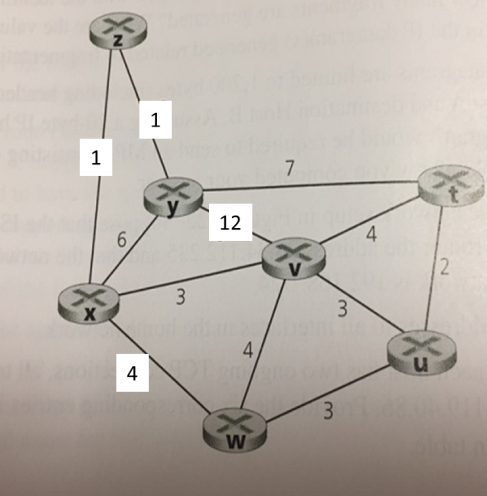
A. What is the formula used by each router running the distance vector algorithm to build this routing table? Use c(x,y) to denote link bandwidth for directly connected x,y, and D(x,y) to describe the distance between x and y.
B. In the initial routing table of node z, z knows only the immediate distance to its neighbors. Therefore its initial vector is:
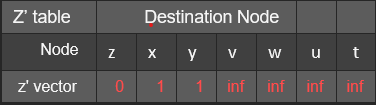
Assume that the nodes are synchronized and in each round each node sends its distance vector to its neighbors and simultaneously receives their vectors. We have updated the following table of z following the first round. We have updated the vectors that his neighbors received in the first round and his vector following the use of the formula you mentioned in section B. Show the calculation

C. Is the vector obtained for z after section b the vector with the shortest distances? If the vector of z was not calculated in the next round

d. Is the vector obtained for z after section c the vector with the shortest distances? What is the final vector of z Explain the answer. Is the vector of y the most finite? If not how many additional rounds are required to obtain this information?
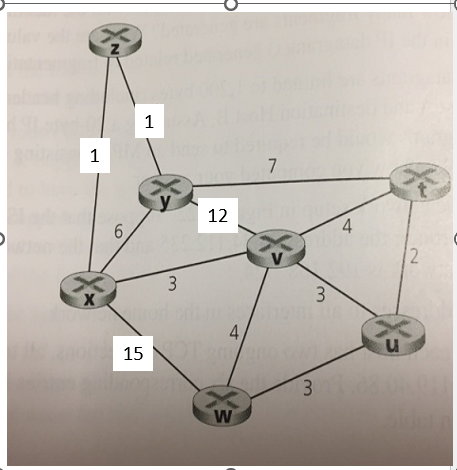
e. Explain how the movement will go from z to W if the weight between x and w suddenly becomes 15 instead of 4? What is the problem that can arise and how can it be solved?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


