In the model of section 5.6, assume that the firm needs to have minimum cash balance of 25 at the end of each year. Introduce this constraint into the model.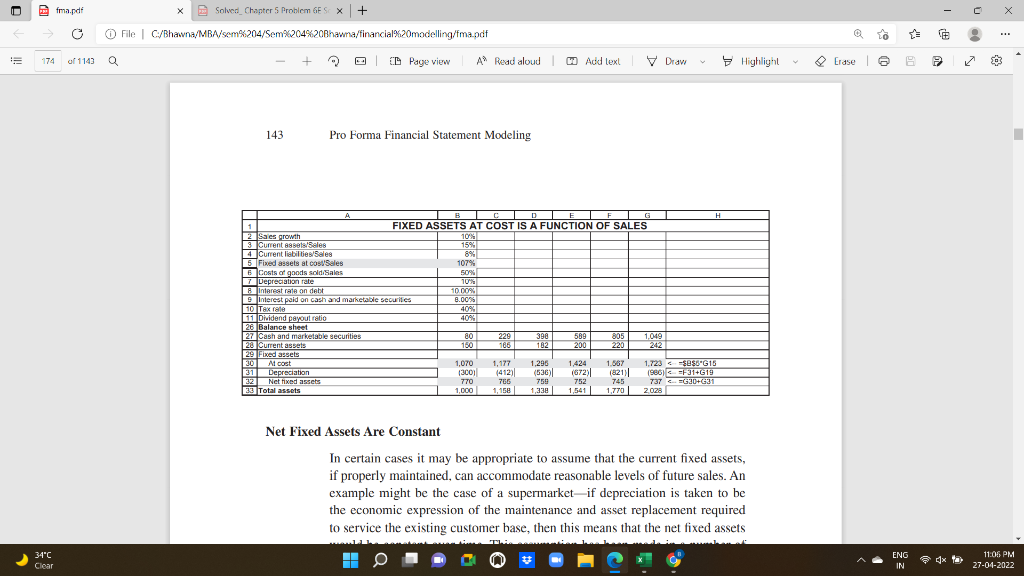
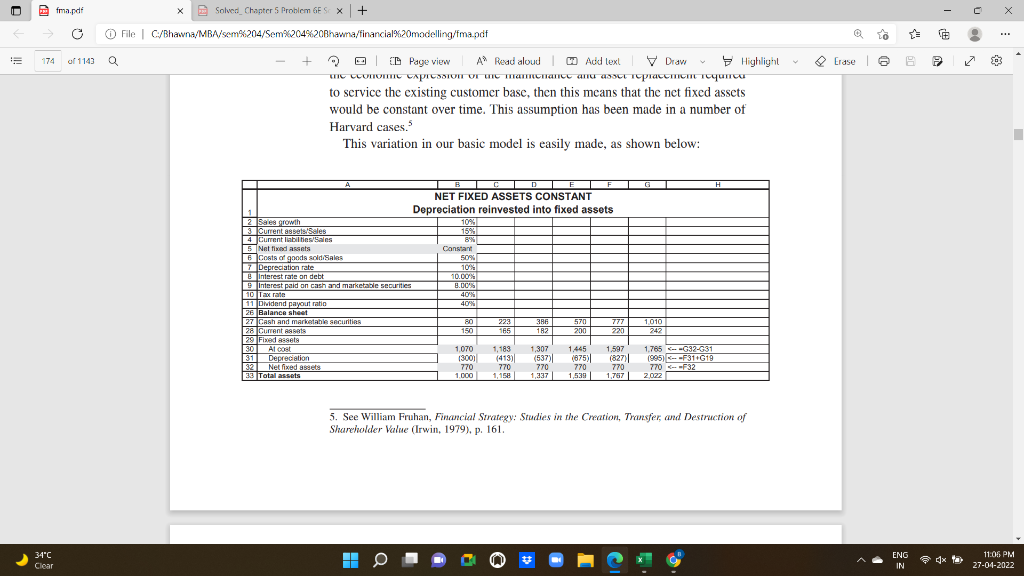
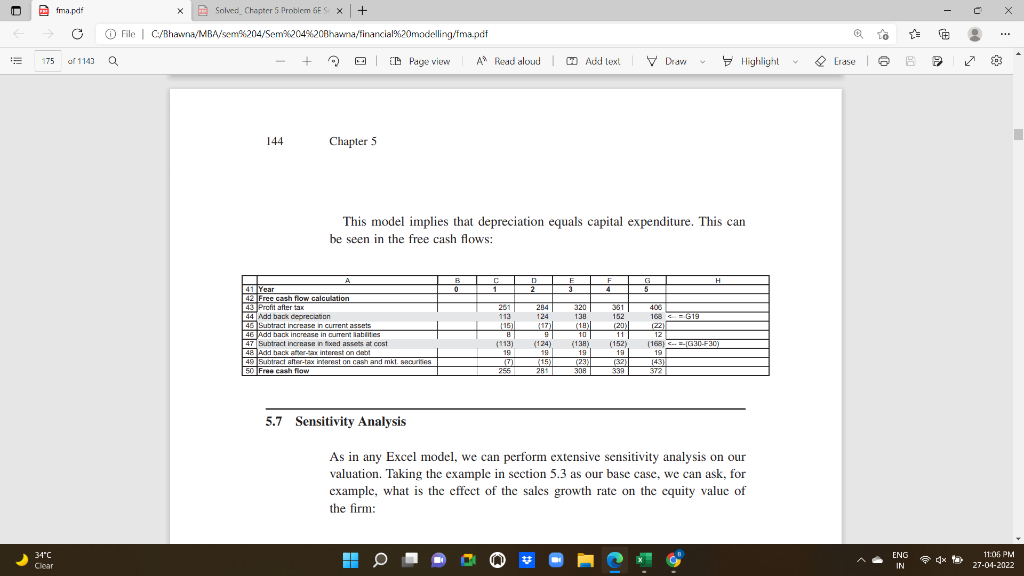
Pfma.pdf C X X Solved_Chapter 5 Problem GES X + O File C/Bhawna/MBA/sem%204/Sem%204%20Bhawna/financial%20modelling/fma.pdf o 174 of 1143 Q | ID Page view A A Read aloud Add lexl V Draw Highlight Erase 2 03 143 Pro Forma Financial Statement Modeling A BI CI DI E F G H FIXED ASSETS AT COST IS A FUNCTION OF SALES A 2 Saes growth % 10% 3 Current assets/Sales 15% 4 Current liabilities/Sales 8% 5 Fixed assets al costales 107% 6 Costs of goods sold Sales B 50% 2 Depreciation rate % 100% 8 Interest rate on debt 10.00 9 Interest paid on cash and marketable securities 8.00 10 Tax rate 40% 11 Dividend payout ratio 40% 26 Balance sheet 27 Cash and marketable securities 80 229 398 589 805 1,049 28 Current ass 150 186 182 200 220 29 Fixed assets 30 Al cost 1,070 1,177 1,296 1,424 1.567 1.723 $0$6"G15 31 Depreciation 13001 1412 ( (530) (672) (821) 1986) FF31+G1 32 Net fixed assets 770 765 759 752 745 737 CG30+G31 33 Total assets 1,000 1,158 1,541 1,770 2028 1338 Net Fixed Assets Are Constant In certain cases it may be appropriate to assume that the current fixed assets, if properly maintained, can accommodate reasonable levels of future sales. An example might be the case of a supermarketif depreciation is taken to be the economic expression of the maintenance and asset replacement required to service the existing customer base, then this means that the net fixed assets ENG 34C Clear 4x 11:06 PM 27-04-2022 IN Pfma.pdf C X To 174 of 1143 Erase e 03 X Solved Chapter 5 Problem 6ES X + O File C/Bhavna/MBA/sem%204/Sem%204%20Bhawna/financial%20modelling/fma.pdf Q + Q | D Page view CD A Read aloud Aud lexl V Draw Highlight to service the existing customer base, then this means that the nct fixed assets would be constant over time. This assumption has been made in a number of Harvard cases. This variation in our basic model is easily made, as shown below: als 1B1C1D1E1F1G1 H NET FIXED ASSETS CONSTANT Depreciation reinvested into fixed assets 25 prowth 10% 3 Current assets/Sales 15% 4 Current liabilities/Sales 8% 5 Net find assets Constant 6 Coats of goods soldi Sales 50% 7 Depreciation rate % 10% B Interest rate on debt 10.00 9 Interest paid on cash and marketable securities 8.00% 10 Tax rate 40% 11 Dividend payout ratio 40% 26 Balance sheet 27 Cash and marketable securities 80 223 RE 386 570 777 1070 28 Current Assets 150 165 182 200 220 242 29 Fixed assets 30 Al cost 1070 1,183 1,307 1.445 1.597 1.765 32-31 31 Depreciation 1300) (413) (537) (875) () (827) (995) --F314619 32 Netfixed assets 770 770 770 770 770 770 F32 33 Total assets 1.000 1,158 1,337 1,539 1,767 2022 5. See William Fruhan, Financial Strategy: Studies in the Creation, Transfer, and Destruction of Shareholder Value (Irwin, 1979). p. 161 ENG 34C Clear H 4x 11:06 PM 27-04-2022 IN Pfma.pdf C X X Solved_Chapter 5 Problem GES X | + File C/Bhavna/MBA/sem%204/Sem%204%20Bhawna/financial%20modelling/fma.pdf o 175 of 1143 Q E D Page view A Read aloud Add text V Draw Highlight Erase | 6 03 144 Chapter 5 This model implies that depreciation equals capital expenditure. This can be seen in the free cash flows: G B 0 CT DE 1 2 3 F 4 H A Baile 41 l Year | 42 Free cash flow calculation 43 Profit after tax 44 Add back depreciation 46 Subtract increase in current assets 46 lada back increase in current labaites 47 Subtract increase in fixed assets at cost 48 Add hack ater-tax interest on debt 49 Subtract Altertax interest on cash and mkt gernes 50 Free cash flow 207 113 (15) 294 124 (17) 320 138 (18) 10 (138) 19 381 152 (20) 11 (152) 19 406 168 CG19 122) 12 (168) CF-16.30-F30) ) --G30- 19 (43) 372 (113) 19 (7) 255 (124) 19 14 (15) 281 308 339 5.7 Sensitivity Analysis As in any Excel model, we can perform extensive sensitivity analysis on our valuation. Taking the example in section 5.3 as our base case, we can ask, for example, what is the effect of the sales growth rate on the cquity value of the firm: ENG 34C Clear H 4x 11:06 PM 27-04-2022 IN Pfma.pdf C X X Solved_Chapter 5 Problem GES X + O File C/Bhawna/MBA/sem%204/Sem%204%20Bhawna/financial%20modelling/fma.pdf o 174 of 1143 Q | ID Page view A A Read aloud Add lexl V Draw Highlight Erase 2 03 143 Pro Forma Financial Statement Modeling A BI CI DI E F G H FIXED ASSETS AT COST IS A FUNCTION OF SALES A 2 Saes growth % 10% 3 Current assets/Sales 15% 4 Current liabilities/Sales 8% 5 Fixed assets al costales 107% 6 Costs of goods sold Sales B 50% 2 Depreciation rate % 100% 8 Interest rate on debt 10.00 9 Interest paid on cash and marketable securities 8.00 10 Tax rate 40% 11 Dividend payout ratio 40% 26 Balance sheet 27 Cash and marketable securities 80 229 398 589 805 1,049 28 Current ass 150 186 182 200 220 29 Fixed assets 30 Al cost 1,070 1,177 1,296 1,424 1.567 1.723 $0$6"G15 31 Depreciation 13001 1412 ( (530) (672) (821) 1986) FF31+G1 32 Net fixed assets 770 765 759 752 745 737 CG30+G31 33 Total assets 1,000 1,158 1,541 1,770 2028 1338 Net Fixed Assets Are Constant In certain cases it may be appropriate to assume that the current fixed assets, if properly maintained, can accommodate reasonable levels of future sales. An example might be the case of a supermarketif depreciation is taken to be the economic expression of the maintenance and asset replacement required to service the existing customer base, then this means that the net fixed assets ENG 34C Clear 4x 11:06 PM 27-04-2022 IN Pfma.pdf C X To 174 of 1143 Erase e 03 X Solved Chapter 5 Problem 6ES X + O File C/Bhavna/MBA/sem%204/Sem%204%20Bhawna/financial%20modelling/fma.pdf Q + Q | D Page view CD A Read aloud Aud lexl V Draw Highlight to service the existing customer base, then this means that the nct fixed assets would be constant over time. This assumption has been made in a number of Harvard cases. This variation in our basic model is easily made, as shown below: als 1B1C1D1E1F1G1 H NET FIXED ASSETS CONSTANT Depreciation reinvested into fixed assets 25 prowth 10% 3 Current assets/Sales 15% 4 Current liabilities/Sales 8% 5 Net find assets Constant 6 Coats of goods soldi Sales 50% 7 Depreciation rate % 10% B Interest rate on debt 10.00 9 Interest paid on cash and marketable securities 8.00% 10 Tax rate 40% 11 Dividend payout ratio 40% 26 Balance sheet 27 Cash and marketable securities 80 223 RE 386 570 777 1070 28 Current Assets 150 165 182 200 220 242 29 Fixed assets 30 Al cost 1070 1,183 1,307 1.445 1.597 1.765 32-31 31 Depreciation 1300) (413) (537) (875) () (827) (995) --F314619 32 Netfixed assets 770 770 770 770 770 770 F32 33 Total assets 1.000 1,158 1,337 1,539 1,767 2022 5. See William Fruhan, Financial Strategy: Studies in the Creation, Transfer, and Destruction of Shareholder Value (Irwin, 1979). p. 161 ENG 34C Clear H 4x 11:06 PM 27-04-2022 IN Pfma.pdf C X X Solved_Chapter 5 Problem GES X | + File C/Bhavna/MBA/sem%204/Sem%204%20Bhawna/financial%20modelling/fma.pdf o 175 of 1143 Q E D Page view A Read aloud Add text V Draw Highlight Erase | 6 03 144 Chapter 5 This model implies that depreciation equals capital expenditure. This can be seen in the free cash flows: G B 0 CT DE 1 2 3 F 4 H A Baile 41 l Year | 42 Free cash flow calculation 43 Profit after tax 44 Add back depreciation 46 Subtract increase in current assets 46 lada back increase in current labaites 47 Subtract increase in fixed assets at cost 48 Add hack ater-tax interest on debt 49 Subtract Altertax interest on cash and mkt gernes 50 Free cash flow 207 113 (15) 294 124 (17) 320 138 (18) 10 (138) 19 381 152 (20) 11 (152) 19 406 168 CG19 122) 12 (168) CF-16.30-F30) ) --G30- 19 (43) 372 (113) 19 (7) 255 (124) 19 14 (15) 281 308 339 5.7 Sensitivity Analysis As in any Excel model, we can perform extensive sensitivity analysis on our valuation. Taking the example in section 5.3 as our base case, we can ask, for example, what is the effect of the sales growth rate on the cquity value of the firm: ENG 34C Clear H 4x 11:06 PM 27-04-2022 IN









