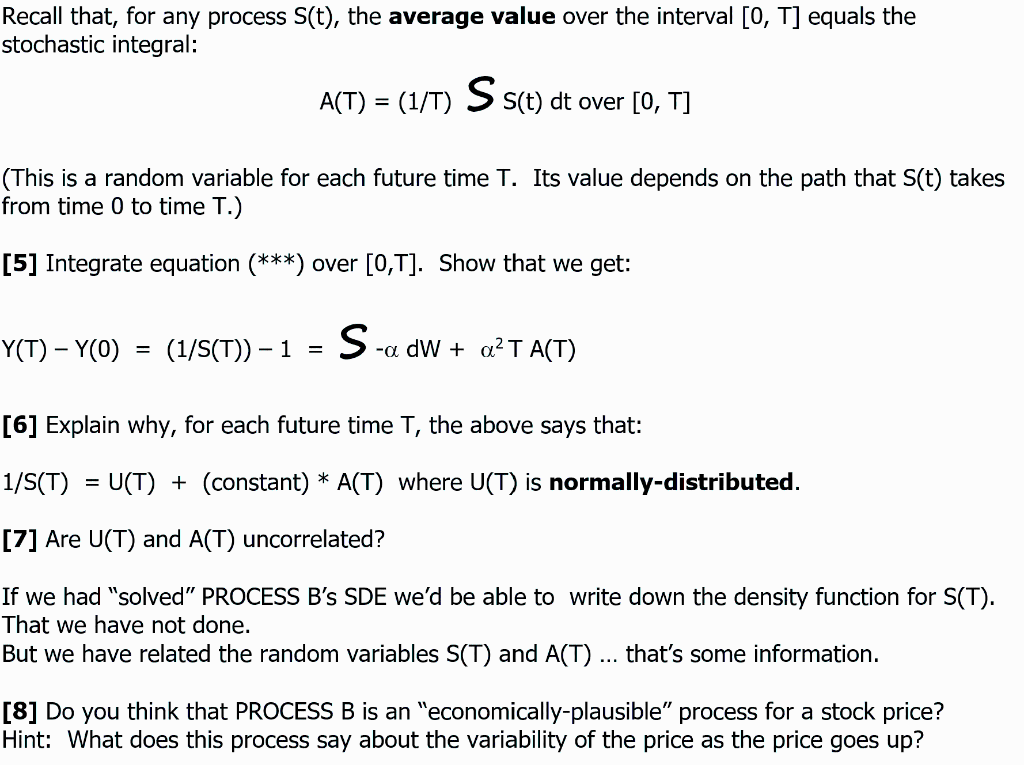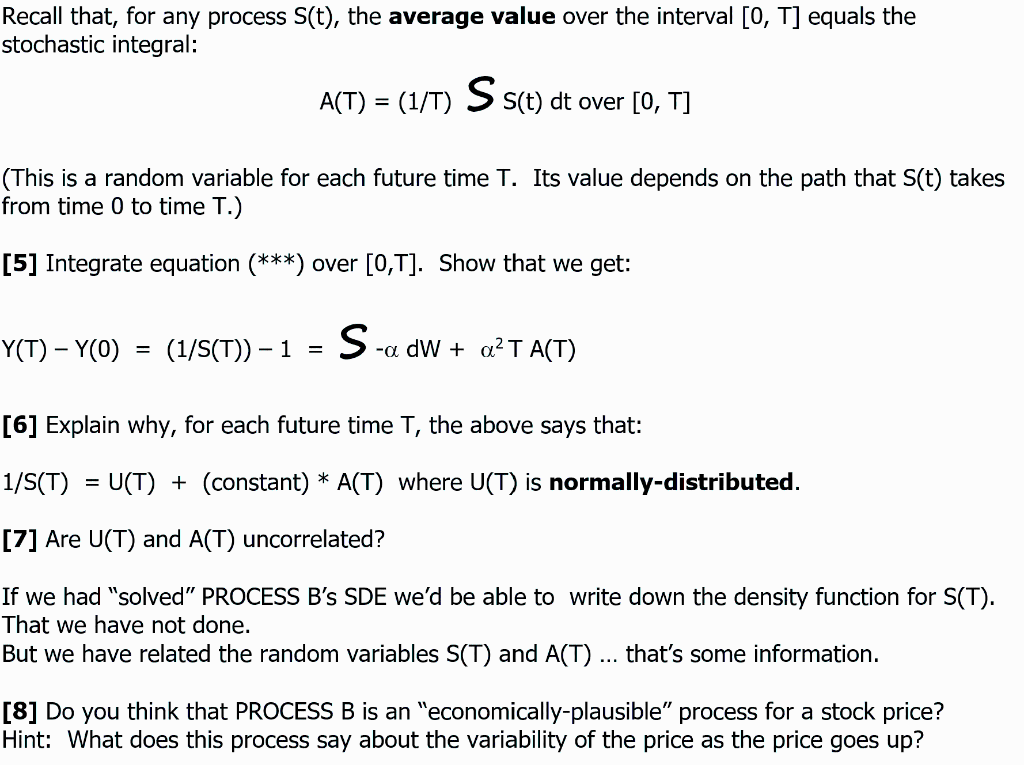
In this problem we examine two stochastic processes for a stock price: PROCESS A: "Driftless" geometric Brownian motion (GBM). "Driftless" means no "dt term. So it's our familiar process: dS = o S dw with S(0) = 1. o is the volatility. this PC PROCESS B: dS = a S2 dw for some constant a, with S(0) = 1 As we've said in class, for any process the instantaneous return is the random variable: dS/S = (S(t + dt) - S(t))/S(t) [1] Explain why, for PROCESS A, the variance of this instantaneous return (VAR[dS/S]) is constant (per unit time). Hint: What's the variance of dW? The rest of this problem involves PROCESS B. [2] For PROCESS B, the statement in [1] is not true. Explain why PROCESS B's variance of the instantaneous return (per unit time) depends on the value S(t). Let's manipulate PROCESS B using a change of variable (and Ito's Formula) to see what we come up with. Worth a try. Let Y(t) = 1/s(t). [3] Apply Ito directly and show that we obtain: dY = (-1/S2)dS + (1/2)(2/5) (dS)? [4] Can you reframe this and obtain: dY = -a dw + a2S dt (***) Recall that, for any process S(t), the average value over the interval [O, T] equals the stochastic integral: A(T) = (1/T) S s(t) dt over [0, T] (This is a random variable for each future time T. Its value depends on the path that S(t) takes from time 0 to time T.) [5] Integrate equation (***) over [0,T]. Show that we get: Y(T) - YO) = (1/S(T)) - 1 S-adW + a2T A(T) = [6] Explain why, for each future time T, the above says that: 1/S(T) = U(T) + (constant) * A(T) where U(T) is normally-distributed. [7] Are U(T) and A(T) uncorrelated? If we had "solved" PROCESS B's SDE we'd be able to write down the density function for S(T). That we have not done. But we have related the random variables S(T) and A(T) ... that's some information. [8] Do you think that PROCESS B is an "economically-plausible process for a stock price? Hint: What does this process say about the variability of the price as the price goes up? In this problem we examine two stochastic processes for a stock price: PROCESS A: "Driftless" geometric Brownian motion (GBM). "Driftless" means no "dt term. So it's our familiar process: dS = o S dw with S(0) = 1. o is the volatility. this PC PROCESS B: dS = a S2 dw for some constant a, with S(0) = 1 As we've said in class, for any process the instantaneous return is the random variable: dS/S = (S(t + dt) - S(t))/S(t) [1] Explain why, for PROCESS A, the variance of this instantaneous return (VAR[dS/S]) is constant (per unit time). Hint: What's the variance of dW? The rest of this problem involves PROCESS B. [2] For PROCESS B, the statement in [1] is not true. Explain why PROCESS B's variance of the instantaneous return (per unit time) depends on the value S(t). Let's manipulate PROCESS B using a change of variable (and Ito's Formula) to see what we come up with. Worth a try. Let Y(t) = 1/s(t). [3] Apply Ito directly and show that we obtain: dY = (-1/S2)dS + (1/2)(2/5) (dS)? [4] Can you reframe this and obtain: dY = -a dw + a2S dt (***) Recall that, for any process S(t), the average value over the interval [O, T] equals the stochastic integral: A(T) = (1/T) S s(t) dt over [0, T] (This is a random variable for each future time T. Its value depends on the path that S(t) takes from time 0 to time T.) [5] Integrate equation (***) over [0,T]. Show that we get: Y(T) - YO) = (1/S(T)) - 1 S-adW + a2T A(T) = [6] Explain why, for each future time T, the above says that: 1/S(T) = U(T) + (constant) * A(T) where U(T) is normally-distributed. [7] Are U(T) and A(T) uncorrelated? If we had "solved" PROCESS B's SDE we'd be able to write down the density function for S(T). That we have not done. But we have related the random variables S(T) and A(T) ... that's some information. [8] Do you think that PROCESS B is an "economically-plausible process for a stock price? Hint: What does this process say about the variability of the price as the price goes up