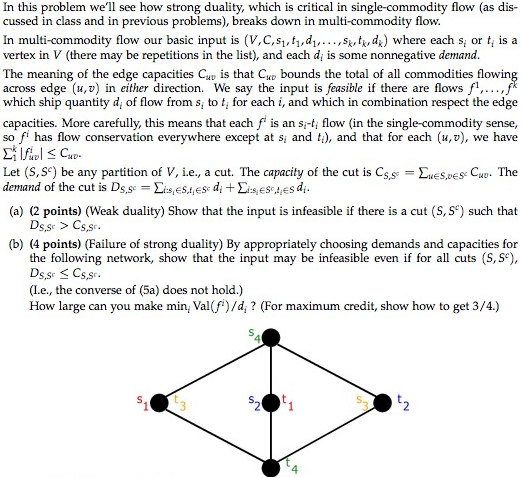
In this problem we'll see how strong duality, which is critical in single-commodity flow (as discussed in class and in previous problems), breaks down in multi-commodity flow. In multi-commodity flow our basic input is (V, C, s_1, _1, d_1, .., s_k, t_k, d_k) where each s_1 or t_i is a vertex in V (there may be repetitions in the list), and each d_i is some nonnegative demand. The meaning of the edge capacities C_u upsilon, is that C_u upsilon bounds the total of all commodities flowing across edge (u, upsilon) in either direction. We say the input is feasible if there are flows f^1, .., f^k which ship quantity d_i of flow from s_i to t_i for each i, and which in combination respect the edge capacities. More carefully, this means that each f^i is an s_i - t_i flow (in the single-commodity sense, so f^i has flow conservation everywhere except at s_i and t_i), and that for each (u, upsilon), we have sigma ^k _1 |f^i _u upsilon | lessthanorequalto C_u upsilon. Let (S, S^c) be any partition of V, i.e., a cut. The capacity of the cut is C_S, S^c = sigma_u Element S, upsilon Element S^c C_u upsilon. The demand of the cut is D_S, S^c = sigma _i: s_i Element S, t_i Element S^c d_i + sigma _i: s_t Element S^c, t_i Element S d_i. (a) (Weak duality) Show that the input is infeasible if there is a cut (S, S^c) such that D_S, S^c > C_S, s^c. (b) (Failure of strong duality) By appropriately choosing demands and capacities for the following network, show that the input may be infeasible even if for all cuts (S, S^c), D_S, S^c lessthanorequalto C_S, S^c. (I.e., the converse of (5a) does not hold.) How large can you make min_i Val (f^i)/d_i ? (For maximum credit, show how to get 3/4.) In this problem we'll see how strong duality, which is critical in single-commodity flow (as discussed in class and in previous problems), breaks down in multi-commodity flow. In multi-commodity flow our basic input is (V, C, s_1, _1, d_1, .., s_k, t_k, d_k) where each s_1 or t_i is a vertex in V (there may be repetitions in the list), and each d_i is some nonnegative demand. The meaning of the edge capacities C_u upsilon, is that C_u upsilon bounds the total of all commodities flowing across edge (u, upsilon) in either direction. We say the input is feasible if there are flows f^1, .., f^k which ship quantity d_i of flow from s_i to t_i for each i, and which in combination respect the edge capacities. More carefully, this means that each f^i is an s_i - t_i flow (in the single-commodity sense, so f^i has flow conservation everywhere except at s_i and t_i), and that for each (u, upsilon), we have sigma ^k _1 |f^i _u upsilon | lessthanorequalto C_u upsilon. Let (S, S^c) be any partition of V, i.e., a cut. The capacity of the cut is C_S, S^c = sigma_u Element S, upsilon Element S^c C_u upsilon. The demand of the cut is D_S, S^c = sigma _i: s_i Element S, t_i Element S^c d_i + sigma _i: s_t Element S^c, t_i Element S d_i. (a) (Weak duality) Show that the input is infeasible if there is a cut (S, S^c) such that D_S, S^c > C_S, s^c. (b) (Failure of strong duality) By appropriately choosing demands and capacities for the following network, show that the input may be infeasible even if for all cuts (S, S^c), D_S, S^c lessthanorequalto C_S, S^c. (I.e., the converse of (5a) does not hold.) How large can you make min_i Val (f^i)/d_i ? (For maximum credit, show how to get 3/4.)







