Question
In this Project, you will write a C program to create a simple version of the Game of the Goose using 24 spaces and a
In this Project, you will write a C program to create a simple version of the Game of the Goose using 24 spaces and a two-player game mode. Player 1 will be the human player, player 2 will be the computer.
When running the program, the user will be asked to enter an integer number, which will be used as a seed for the generation of random numbers when rolling the dice. Then, your program prints a welcome menu displaying two options: 1) Press 'P' or 'p' to play or 2) Press 'Q' or 'q' to quit.
If the selected option is to play the game, the players should roll the dice (press enter) to determine which player should go first. The player who gets the highest value will go first in the game. Here is an example:
HUMAN PLAYER, Press to roll the dice
6 and 2 for a 8
COMPUTER PLAYER, Press to roll the dice
3 and 2 for a 5
HUMAN PLAYER goes first
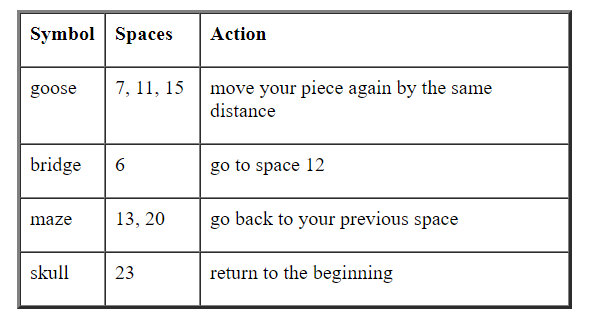
If there is a tie determining who goes first (i.e. both the Human and Computer roll the same value), a message is printed stating so, and the process is repeated until two different values are rolled. The highest roll then goes first. After determining which player goes first, 24 spaces are displayed in two lines, each represented by a number enclosed in square brackets (12 numbers in each line) and separated by tabs. The only exception is the last space which doesn't use bracket but instead is displayed as . A character before a number indicate that it is a special space. A goose is represented by '+', the bridge by '*', a maze by '-' and the skull by '!'. The following table indicates the special spaces:
The characters '$' and '%' are used to represent the pieces of human and computer player, respectively. When a player lands on a space, the space number is NOT displayed but only the player instead. If both players are in the same space, human's character is always shown first. Playing the game: After selecting play in the main menu the goose board is displayed with both players' pieces in the start position.
Below the board, a message is displayed indicating which player will next roll the dice (assuming a player didn't win the previous roll). This information should be shown in a manner similar to: (HUMAN/COMPUTER] PLAYER'S TURN, (current space] ... Press to roll the dice
After the player presses (the human player should also "roll for the computer) the value of each die along with the sum of both dice is shown. The next line shows a summary of the main movements performed in that roll. If more than one movement is carried out, a comma separates each movement. The main possible movements are:
go to space #
come back to space #
return to start
After the main movements are performed, the new board status is shown
If the new board status shows that the player won during the roll, a message is displayed indicating that the game is over, and stating which player (Human or Computer) wins:
"-GAME OVER-" Player # won!
Then the following message is displayed, allowing the user to return to the main menu:
Press to return to the main menu
Implementation: You must create at least two functions (in addition to main() for this project. If desired you can create additional functions as you see fit. Make sure that your code and the number of lines per function follows the CS 262 Style Guide.
Rolling the dice A "roll" function will be used to roll the dice. It will return an int value and contain no parameters. This function will declare two integer variables (each represents a single die). Use a random number generator for each variable, so that the possible values range from one to six. The function will print the result of each dice and the sum of both. Example: "5 and 2 for a 7" It will then return the sum.
Print board You will implement a function to print and show the status of the board. It will have two parameters (the positions of both players) and will display the board with the symbols of the special spaces and the spaces where are the players. The function will not have a return value (i.e. it will be a void function). Other considerations The board size and positions of special spaces will be denoted using global constants and symbolic constants (#define). Because all of the various symbols could potentially be placed on one or more spaces on the game board, you should make symbolic constants to reflect the number of each type of symbol, and a global array of constants for each symbol type denoting the space that those symbols are found. Using the Goose spaces as an example:
#define NUM_GOOSE_SPACES 3
const int gooseSpaces [NUM_GOOSE_SPACES] = {7, 11, 15};
The idea is that your program can be modified to create different board sizes (such as the original 63 spaces), and number of and positions of special spaces merely by changing values at the top of the program (and perhaps some modification to the display board function) and recompiling. It is acceptable to declare an array containing a single element (which you would need to do for the bridge and the skull). You will not actually make such modifications for this project (i.e. generate programs with different board sizes), but you need to write your code so that it is easy to do if it was desired to do so in the future. Don't forget to comment your code (including the standard information at the top of the file name, section, etc.).
Example Output: This is an example of some of the output that might be displayed on the screen based on the inputs and result of the dice sum:
Enter a seed for the random number generator: 10
Welcome to the game of goose, please select an option:
Press 'p' or 'p' to play
Press 'Q' or 'q' to quit
P
HUMAN PLAYER, Press
6 and 2 for a 8
COMPUTER PLAYER, Press
3 and 2 for a 5
HUMAN PLAYER goes first
[$%] [2] [3] [4] [5] * [6] + [7] [8] [9] [10] +[11] [12]
-[13] [14] +[15] [16] [17] [18] [19] - [20] [21] [22] ![23]
HUMAN PLAYER'S TURN, [1]... Press
go to space 10
[%] [2] [3] [4] [5] *[6] + [7] [8] [9] [$] + [11] [12]
-[13] [14] +[15] [16] [17] [18] [19] - [20] [21] [22] ! [23]
COMPUTER PLAYER'S TURN, [1]... Press
4 and 6 for a 10
go to space 11, go to space 21
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] *[6] + [7] [8] [9] [$]+[11] [12]
- [13] [14] +[15] [16] [17] [18] [19] - [20] [3] [22] ! [23]
HUMAN PLAYER'S TURN, [10]... Press
3 and 2 for 5
go to space 15, go to space 20, come back to space 10
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] *[6] + [7] [8] [9] [$]+[11] [12]
-[13] [14] +[15] [16] [17] [18] [19] - [20] [8] [22] ![23]
COMPUTER PLAYER'S TURN, [21]... Press
1 and 2 for a 3
go to space 24
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] *[6] +[7] [8] [9] [$] +[11] [12]
-[13] [14] +[15] [16] [17] [18] [19] - [20] [21] [22] ! [23]
Game over! Computer Won!
Press to return to the main menu
Please implement the project with C language
Symbol Spaces Action goose 7, 11, 15 | move your piece again by the same distance bridge 16 go to space 12 maze 13, 20 go back to your previous space skull 23 return to the beginning Symbol Spaces Action goose 7, 11, 15 | move your piece again by the same distance bridge 16 go to space 12 maze 13, 20 go back to your previous space skull 23 return to the beginningStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


