In which area of your amalysis is there
the greatest potential for error? Why?
Is there anything that could be done
to improve estimates in this area?

In which area of your amalysis is there
the greatest potential for error? Why?
Is there anything that could be done
to improve estimates in this area?
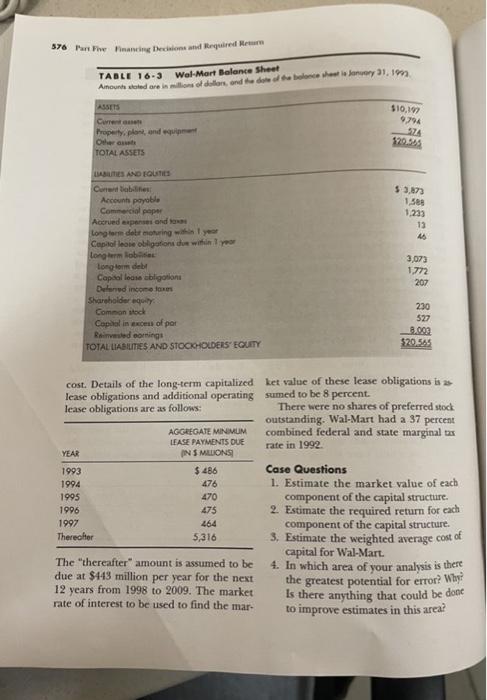
TABLE 16-3 Wal-Mart Balance Sheet donde te br.),1903 Oh YO AMES . 574 Apple 3 18 10 13 202 230 597 02 BONES AND SOCIOSO Dump of these wohl regime There were more ning Wal Marta Minedidelia AR Case Questions 48 1. E the market value of each 200 19 05 2 1992 wa wa The themelore there 54 leche It was the thread matters to be the main Wel Mert Cost of Capital Wat with bilioni nomine di the wife largest a little pe care dhe ar ht.com W. Martin de 5.12. tica hard Snow 200 de pershare din perhe Cales - paydonid Maaleht recens. The sales were able 16. Met of the com open the wall Best club we were the true, then Wing 11 the haloge sale. The main of Wales with a star Mersul te Market value of $5.587. Aming Westwinderwagen de The Water Martheid sed the trend dining in the meet will menting irit in ma Corsi didele pay. phone. New capelade W. Martel sinh with daily balance wel mee working contanding form of 5.164 illon som Wat was to make the weighed eller al cal esment des de waar wel Martha capital copil det news on the when Walan 23 the other shares of The di badala 1.3 and in wing ang ibig Gender 350 a Theme Geci dan the lowered UST.pt. this the and Tablemowe will 1 02 02 01 DO ol 12 576 Part The Financing Decisions and required Hearn TABLE 16-3 Wal-Mart Balance Sheet Anoonheidsre indator, and the done to bolonce the every 1.1m ASSETS Curred Property, plant, and Odhon TOTAL ASSETS $10,19 9,794 574 120,543 $ 3.73 1.568 1.233 13 LIBES AND EQUITIES Cobabies Account payable Commercial paper Accrued expenses and Long term delt moring Capitol leave obligations due within your Long term lob long term del Capdol loose obligatione Deland income taxes Shareholdere Common och Copal in excess of por Rised omning TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY 3,073 1772 207 230 527 8.00 $20.595 LEASE PAYMENTS DUE YEAR $ 486 476 cost. Details of the long-term capitalized ket value of these lease obligations is as lease obligations and additional operating sumed to be 8 percent. lease obligations are as follows: There were no shares of preferred stock outstanding. Wal-Mart had a 37 percent AGGREGATE MINIMUM combined federal and state marginal tax rate in 1992 INS MILLONS 1993 Case Questions 1994 1. Estimate the market value of each 1995 470 component of the capital structure 1996 475 2. Estimate the required return for each 1997 464 component of the capital structure. Thereafter 5,316 3. Estimate the weighted average cost of capital for Wal-Mart. The "thereafter" amount is assumed to be 4. In which area of your analysis is there due at $143 million per year for the next the greatest potential for error? Why? 12 years from 1998 to 2009. The market rate of interest to be used to find the mar. Is there anything that could be done to improve estimates in this areat CASE PROBLEM Chapter 16 Cost of Capital 575 Wal-Mart Cost of Capital Wal- Mart, with $55 billion in sales in 1992, 3 percent in 1993. Based on dividends to nearly 2,000 Wal-Mart discount stores in 1993 were expected to be $.12. Historical is the world's largest retailer. It operates date, dividends per share during the year the United States, approximately 200 Sam's dividends per share and caring per share Clubs membership-warehouse stores, and a specialty distribution seginent that serves were as shown at the bottom of this page 30,000 convenience stores and independ- 1993, summarizes the company's financial Wal-Mart's balance sheet, of January 31. ent grocers. Discount stores sales ac. structure (Table 16-3). Most of the com- counted for 78 percent of 1992 sales. Mempany's debt was not actively traded. How bership club sales were the second-largest ever, the company disclosed in a note to area, accounting for 22 percent of 1992 the financial statements that long term sales. The remaining 5 percent of Wal debt with a book value of $5.073 had a fait Mart's sales were accounted for by McLane market value of $9.857 billion. Assuming Western convenience store and inde the average stated rate on outstanding se pendent grocer supply division. Thus, Wal curities was 75 percent , the yield to matu Mart was one of the companies that had re- rity would be 6.87 percent. It was assumed sisted the trend toward diversifying into that other long-term debt would sell at a everything from aardvarks to zymometers. similar yield to maturity if the debt were Concentration did not mean lack of publicly sold. growth, however. New capital expendi- Wal-Mart was a heavy user of commer nures in 1992 alone were $3.5 billion, plus cial paper with an average daily balance an associated investment in working capi- outstanding for 1992 of $1.184 billion al of $1.8 billion. If Wal-Mart was to make The weighted average before tax interest rate on this paper was 8.5 percent. optimal capital investment decisions, it Wal-Mart has $1.818 billion in capital was clear that an accurate estimate of the lease obligations on the balance sheet. In Wal-Mart presently had 2.3 billion the footnote there is a historical 8 10 shares of common stock outstanding. The and was selling at calculating this obligation. Given the over- cost of capital was needed. 14 percent imputed discount rate used in stock had a beta of $30 a share in 1992. The yield to maturity all decline in interest rates, the lower end on U.S. Treasury bonds was 6.5 percent of the range, or 8 percent, is probably the and Treasury bills were selling to yield better estimate of what future leases will 1988 1989 1990 1991 1087 1992 1986 YEAR 1982 1984 1985 1983 .03 28 02 15 06 48 07 57 204 37 02 20 09 .70 Dividends Earnings .01 12 .01 .09 .01 .06 .87 The analysis, along with necessary estimates, was prepared by the authoe and does not represent the view of manager at Wal-Mart TABLE 16-3 Wal-Mart Balance Sheet donde te br.),1903 Oh YO AMES . 574 Apple 3 18 10 13 202 230 597 02 BONES AND SOCIOSO Dump of these wohl regime There were more ning Wal Marta Minedidelia AR Case Questions 48 1. E the market value of each 200 19 05 2 1992 wa wa The themelore there 54 leche It was the thread matters to be the main Wel Mert Cost of Capital Wat with bilioni nomine di the wife largest a little pe care dhe ar ht.com W. Martin de 5.12. tica hard Snow 200 de pershare din perhe Cales - paydonid Maaleht recens. The sales were able 16. Met of the com open the wall Best club we were the true, then Wing 11 the haloge sale. The main of Wales with a star Mersul te Market value of $5.587. Aming Westwinderwagen de The Water Martheid sed the trend dining in the meet will menting irit in ma Corsi didele pay. phone. New capelade W. Martel sinh with daily balance wel mee working contanding form of 5.164 illon som Wat was to make the weighed eller al cal esment des de waar wel Martha capital copil det news on the when Walan 23 the other shares of The di badala 1.3 and in wing ang ibig Gender 350 a Theme Geci dan the lowered UST.pt. this the and Tablemowe will 1 02 02 01 DO ol 12 576 Part The Financing Decisions and required Hearn TABLE 16-3 Wal-Mart Balance Sheet Anoonheidsre indator, and the done to bolonce the every 1.1m ASSETS Curred Property, plant, and Odhon TOTAL ASSETS $10,19 9,794 574 120,543 $ 3.73 1.568 1.233 13 LIBES AND EQUITIES Cobabies Account payable Commercial paper Accrued expenses and Long term delt moring Capitol leave obligations due within your Long term lob long term del Capdol loose obligatione Deland income taxes Shareholdere Common och Copal in excess of por Rised omning TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY 3,073 1772 207 230 527 8.00 $20.595 LEASE PAYMENTS DUE YEAR $ 486 476 cost. Details of the long-term capitalized ket value of these lease obligations is as lease obligations and additional operating sumed to be 8 percent. lease obligations are as follows: There were no shares of preferred stock outstanding. Wal-Mart had a 37 percent AGGREGATE MINIMUM combined federal and state marginal tax rate in 1992 INS MILLONS 1993 Case Questions 1994 1. Estimate the market value of each 1995 470 component of the capital structure 1996 475 2. Estimate the required return for each 1997 464 component of the capital structure. Thereafter 5,316 3. Estimate the weighted average cost of capital for Wal-Mart. The "thereafter" amount is assumed to be 4. In which area of your analysis is there due at $143 million per year for the next the greatest potential for error? Why? 12 years from 1998 to 2009. The market rate of interest to be used to find the mar. Is there anything that could be done to improve estimates in this areat CASE PROBLEM Chapter 16 Cost of Capital 575 Wal-Mart Cost of Capital Wal- Mart, with $55 billion in sales in 1992, 3 percent in 1993. Based on dividends to nearly 2,000 Wal-Mart discount stores in 1993 were expected to be $.12. Historical is the world's largest retailer. It operates date, dividends per share during the year the United States, approximately 200 Sam's dividends per share and caring per share Clubs membership-warehouse stores, and a specialty distribution seginent that serves were as shown at the bottom of this page 30,000 convenience stores and independ- 1993, summarizes the company's financial Wal-Mart's balance sheet, of January 31. ent grocers. Discount stores sales ac. structure (Table 16-3). Most of the com- counted for 78 percent of 1992 sales. Mempany's debt was not actively traded. How bership club sales were the second-largest ever, the company disclosed in a note to area, accounting for 22 percent of 1992 the financial statements that long term sales. The remaining 5 percent of Wal debt with a book value of $5.073 had a fait Mart's sales were accounted for by McLane market value of $9.857 billion. Assuming Western convenience store and inde the average stated rate on outstanding se pendent grocer supply division. Thus, Wal curities was 75 percent , the yield to matu Mart was one of the companies that had re- rity would be 6.87 percent. It was assumed sisted the trend toward diversifying into that other long-term debt would sell at a everything from aardvarks to zymometers. similar yield to maturity if the debt were Concentration did not mean lack of publicly sold. growth, however. New capital expendi- Wal-Mart was a heavy user of commer nures in 1992 alone were $3.5 billion, plus cial paper with an average daily balance an associated investment in working capi- outstanding for 1992 of $1.184 billion al of $1.8 billion. If Wal-Mart was to make The weighted average before tax interest rate on this paper was 8.5 percent. optimal capital investment decisions, it Wal-Mart has $1.818 billion in capital was clear that an accurate estimate of the lease obligations on the balance sheet. In Wal-Mart presently had 2.3 billion the footnote there is a historical 8 10 shares of common stock outstanding. The and was selling at calculating this obligation. Given the over- cost of capital was needed. 14 percent imputed discount rate used in stock had a beta of $30 a share in 1992. The yield to maturity all decline in interest rates, the lower end on U.S. Treasury bonds was 6.5 percent of the range, or 8 percent, is probably the and Treasury bills were selling to yield better estimate of what future leases will 1988 1989 1990 1991 1087 1992 1986 YEAR 1982 1984 1985 1983 .03 28 02 15 06 48 07 57 204 37 02 20 09 .70 Dividends Earnings .01 12 .01 .09 .01 .06 .87 The analysis, along with necessary estimates, was prepared by the authoe and does not represent the view of manager at Wal-Mart