Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
In your own words, identify and describe the sixprinciples of internal control listed in the screenshot PRINCIPLES OF INTERNAL CONTROL The purpose of internal control
In your own words, identify and describe the sixprinciples of internal control listed in the screenshot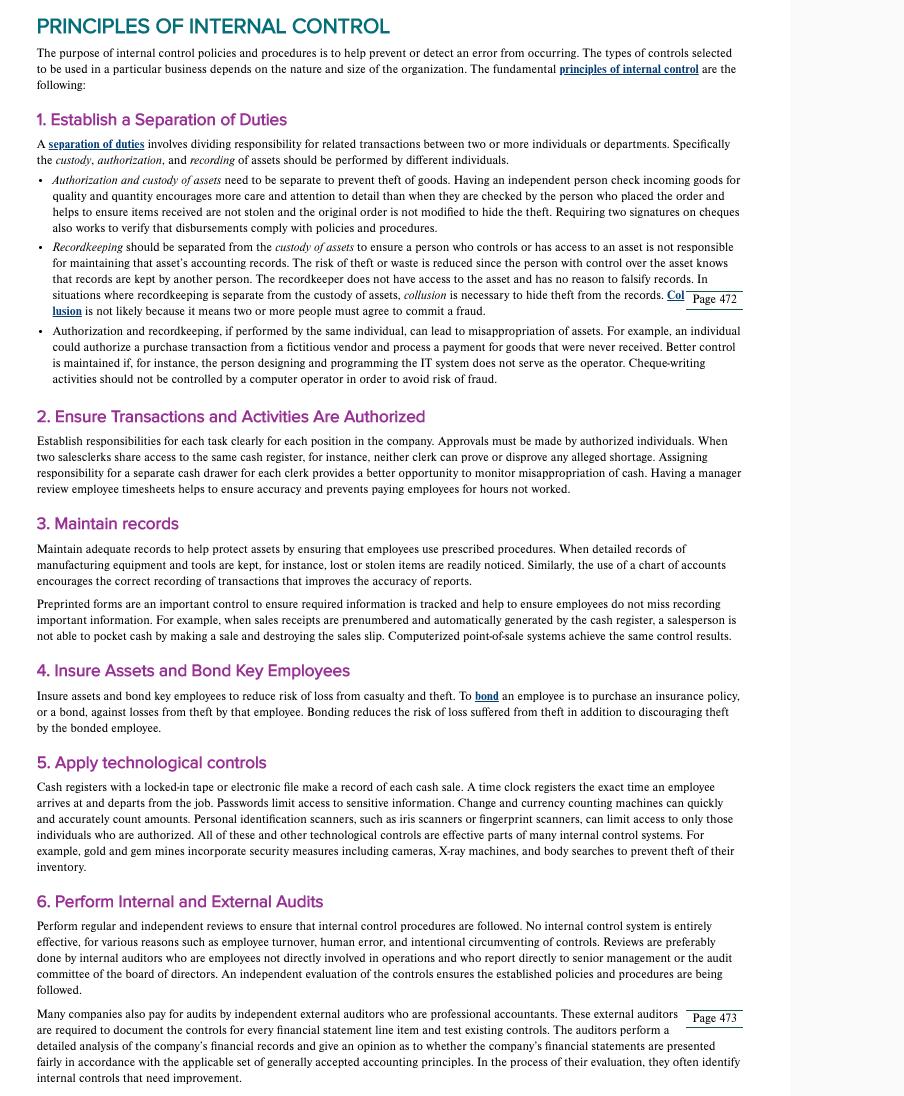
PRINCIPLES OF INTERNAL CONTROL The purpose of internal control policies and procedures is to help prevent or detect error from occurring. The types of controls selected to be used in a particular business depends on the nature and size of the organization. The fundamental principles of internal control are the following: 1. Establish a Separation of Duties A separation of duties involves dividing responsibility for related transactions between two or more individuals or departments. Specifically the custody, authorization, and recording of assets should be performed by different individuals. Authorization and custody of assets need to be separate to prevent theft of goods. Having an independent person check incoming goods for quality and quantity encourages more care and attention to detail than when they are checked by the person who placed the order and helps to ensure items received are not stolen and the original order is not modified to hide the theft. Requiring two signatures on cheques also works to verify that disbursements comply with policies and procedures. Recordkeeping should be separated from the custody of assets to ensure a person who controls or has access to an asset is not responsible for maintaining that asset's accounting records. The risk of theft or waste is reduced since the person with control over the asset knows that records are kept by another person. The recordkeeper does not have access to the asset and has no reason to falsify records. In situations where recordkeeping is separate from the custody of assets, collusion is necessary to hide theft from the records. Col Page 472 lusion is not likely because it means two or more people must agree to commit a fraud. Authorization and recordkeeping, if performed by the same individual, can lead to misappropriation of assets. For example, an individual could authorize a purchase transaction from a fictitious vendor and process a payment for goods that were never received. Better control is maintained if, for instance, the person designing and programming the IT system does not serve as the operator. Cheque-writing activities should not be controlled by a computer operator in order to avoid risk of fraud. 2. Ensure Transactions and Activities Are Authorized Establish responsibilities for each task clearly for each position in the company. Approvals must be made by authorized individuals. When two salesclerks share access to the same cash register, for instance, neither clerk can prove or disprove any alleged shortage. Assigning responsibility for a separate cash drawer for each clerk provides a better opportunity to monitor misappropriation of cash. Having a manager review employee timesheets helps to ensure accuracy and prevents paying employees for hours not worked. 3. Maintain records Maintain adequate records to help protect assets by ensuring that employees use prescribed procedures. When detailed records of manufacturing equipment and tools are kept, for instance, lost or stolen items are readily noticed. Similarly, the use of a chart of accounts encourages the correct recording of transactions that improves the accuracy of reports. Preprinted forms are an important control to ensure required information is tracked and help to ensure employees do not miss recording important information. For example, when sales receipts are prenumbered and automatically generated by the cash register, a salesperson is not able to pocket cash by making a sale and destroying the sales slip. Computerized point-of-sale systems achieve the same control results. 4. Insure Assets and Bond Key Employees Insure assets and bond key employees to reduce risk of loss from casualty and theft. To bond an employee is to purchase an insurance policy, or a bond, against losses from theft by that employee. Bonding reduces the risk of loss suffered from theft in addition to discouraging theft by the bonded employee. 5. Apply technological controls Cash registers with a locked-in tape or electronic file make a record of each cash sale. A time clock registers the exact time an employee arrives at and departs from the job. Passwords limit access to sensitive information. Change and currency counting machines can quickly and accurately count amounts. Personal identification scanners, such as iris scanners or fingerprint scanners, can limit access to only those individuals who are authorized. All of these and other technological controls are effective parts of many internal control systems. For example, gold and gem mines incorporate security measures including cameras, X-ray machines, and body searches to prevent theft of their inventory. 6. Perform Internal and External Audits Perform regular and independent reviews to ensure that internal control procedures are followed. No internal control system is entirely effective, for various reasons such as employee turnover, human error, and intentional circumventing of controls. Reviews are preferably done by internal auditors who are employees not directly involved in operations and who report directly to senior management or the audit committee of the board of directors. An independent evaluation of the controls ensures the established policies and procedures are being followed. Many companies also pay for audits by independent external auditors who are professional accountants. These external auditors Page 473 are required to document the controls for every financial statement line item and test existing controls. The auditors perform a detailed analysis of the company's financial records and give an opinion as to whether the company's financial statements are presented fairly in accordance with the applicable set of generally accepted accounting principles. In the process of their evaluation, they often identify internal controls that need improvement.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.50 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The primary objective of Internal Control is to ensure that the transactions processed are complete valid and accurate In order to achieve that control objective it is necessary to establish principle...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


