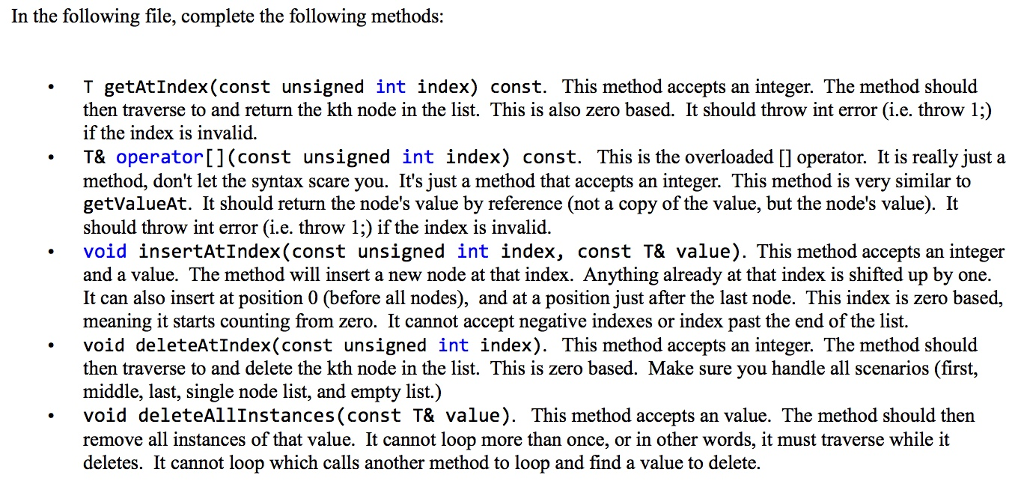
Question
#include #include #include #include using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::string; using std::stringstream; //************************************************************************ //A class I designed to help keep track of how
#include
using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::string; using std::stringstream;
//************************************************************************ //A class I designed to help keep track of how much memory you allocate //Do not modify, this is not part of your assignment, it just helps test it. //For this to work, a class needs to inherit off of this one. //Then this does the rest of the work, since it //overloads new, new[], delete, and delete[]. //************************************************************************ class ManageMemory { public:
static std::size_t getTotalSize() { std::size_t total = 0; std::map
//I overloaded the new and delete keywords so I could manually track allocated memory. void* operator new(std::size_t x){ void *ptr = ::operator new(x); mapOfAllocations[ptr] = x; return ptr; } void* operator new[](std::size_t x) { void *ptr = ::operator new[](x); mapOfAllocations[ptr] = x; return ptr; } void operator delete(void* x) { mapOfAllocations.erase(x); ::operator delete(x); } void operator delete[](void* x) { mapOfAllocations.erase(x); ::operator delete[](x); } private: static std::map
//****************** //The node class //****************** template
//****************** //The linked list base class //This contains within it a class declaration for an iterator //****************** template
//public members of the SinglyLinkedList class ~SinglyLinkedList(); string getStringFromList();
void insertFront(const T&); void insertBack(const T&); T getAtIndex(const unsigned int index) const; //For your assignment T& operator[](const unsigned int index); //For your assignment void insertAtIndex(const unsigned int index, const T& value); //For your assignment void deleteAtIndex(const unsigned int index); //For your assignment void deleteAllInstances(const T& value); //For your assignment
protected:
Node
};
template
template
//empty list scenario if (front == nullptr) { back = temp; } else { temp->link = front; }
front = temp; count++; }
template
if (front == nullptr) { front = temp; } else { //put it on back->link = temp; } back = temp; count++; }
//TODO: Complete this method template
//TODO: Complete this method template
//TODO: Complete this method template
}
//TODO: Complete this method template
}
//TODO: Complete this method template
}
//This method helps return a string representation of all nodes in the linked list, do not modify. template Node while (currentNode != nullptr) { ss data; currentNode = currentNode->link; }; } return ss.str(); } //This helps with testing, do not modify. bool checkTest(string testName, string whatItShouldBe, string whatItIs) { if (whatItShouldBe == whatItIs) { cout //This helps with testing, do not modify. bool checkTest(string testName, int whatItShouldBe, int whatItIs) { if (whatItShouldBe == whatItIs) { cout //This helps with testing, do not modify. bool checkTestMemory(string testName, int whatItShouldBe, int whatItIs) { if (whatItShouldBe == whatItIs) { cout //This helps with testing, do not modify. void testGetAtIndex() { SinglyLinkedList //Test just to make sure the data went in the list. checkTest("testGetAtIndex #1", "10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19", d->getStringFromList()); //Test retrieving items. int item = d->getAtIndex(0); checkTest("testGetAtIndex #2", 10, item); item = d->getAtIndex(5); checkTest("testGetAtIndex #3", 15, item); item = d->getAtIndex(9); checkTest("testGetAtIndex #4", 19, item); //Make sure the list was undisturbed during this time checkTest("testGetAtIndex #5", "10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19", d->getStringFromList()); //Try to access out of bounds. string caughtError = ""; try { int item = d->getAtIndex(-1); } catch (int error) { caughtError = "caught"; } checkTest("testGetAtIndex #6", "caught", caughtError); try { int item = d->getAtIndex(100); } catch (int error) { caughtError = "caught"; } checkTest("testGetAtIndex #7", "caught", caughtError); delete d; d = new SinglyLinkedList //This helps with testing, do not modify. void testSquareBrackets() { SinglyLinkedList //Test just to make sure the data went in the list. checkTest("testSquareBrackets #1", "10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19", d.getStringFromList()); //Test retrieving items. int item = d[0]; checkTest("testSquareBrackets #2", 10, item); item = d[5]; checkTest("testSquareBrackets #3", 15, item); item = d[9]; checkTest("testSquareBrackets #4", 19, item); //Make sure the list was undisturbed during this time checkTest("testSquareBrackets #5", "10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19", d.getStringFromList()); /ow test the return by reference d[1] = 1000; checkTest("testSquareBrackets #6", "10 1000 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19", d.getStringFromList()); //Try to access out of bounds. string caughtError = ""; try { int item = d[-1]; } catch (int error) { caughtError = "caught"; } checkTest("testSquareBrackets #7", "caught", caughtError); try { int item = d[100]; } catch (int error) { caughtError = "caught"; } checkTest("testSquareBrackets #8", "caught", caughtError); } //This helps with testing, do not modify. void testInsertAtIndex() { SinglyLinkedList //Test just to make sure the data went in the list. checkTest("testInsertAtIndex #1", "10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19", s->getStringFromList()); s->insertAtIndex(3, 33); checkTest("testInsertAtIndex #2", "10 11 12 33 13 14 15 16 17 18 19", s->getStringFromList()); s->insertAtIndex(0, 9); checkTest("testInsertAtIndex #3", "9 10 11 12 33 13 14 15 16 17 18 19", s->getStringFromList()); s->insertAtIndex(12, 20); checkTest("testInsertAtIndex #4", "9 10 11 12 33 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20", s->getStringFromList()); delete s; s = new SinglyLinkedList s->insertAtIndex(0, 42); checkTest("testInsertAtIndex #5", "42", s->getStringFromList()); s->insertAtIndex(1, 82); checkTest("testInsertAtIndex #6", "42 82", s->getStringFromList()); delete s; } //This helps with testing, do not modify. void testDeleteAtIndex() { SinglyLinkedList //Test just to make sure the data went in the list. checkTest("testDeleteAtIndex #1", "10 11 12 13 14 15 16", d->getStringFromList()); //Test deleting front items. d->deleteAtIndex(0); checkTest("testDeleteAtIndex #2", "11 12 13 14 15 16", d->getStringFromList()); d->deleteAtIndex(0); checkTest("testDeleteAtIndex #3", "12 13 14 15 16", d->getStringFromList()); //Test deleting a middle item d->deleteAtIndex(2); checkTest("testDeleteAtIndex #4", "12 13 15 16", d->getStringFromList()); //Test deleting back itmes d->deleteAtIndex(3); checkTest("testDeleteAtIndex #5", "12 13 15", d->getStringFromList()); d->deleteAtIndex(2); checkTest("testDeleteAtIndex #6", "12 13", d->getStringFromList()); //Test deleting a Kth element that doesn't exist. d->deleteAtIndex(500); checkTest("testDeleteAtIndex #7", "12 13", d->getStringFromList()); //Test deleting a back item d->deleteAtIndex(1); checkTest("testDeleteAtIndex #8", "12", d->getStringFromList()); //Test deleting item that doesn't exist d->deleteAtIndex(1); checkTest("testDeleteAtIndex #9", "12", d->getStringFromList()); //Test deleting item on the front d->deleteAtIndex(0); checkTest("testDeleteAtIndex #10", "The list is empty.", d->getStringFromList()); //Test attempting to delete from an empty list d->deleteAtIndex(0); checkTest("testDeleteAtIndex #11", "The list is empty.", d->getStringFromList()); delete d; } //This helps with testing, do not modify. void testdeleteAllInstances() { SinglyLinkedList d->insertBack(4); d->insertBack(2); d->insertBack(6); d->insertBack(5); d->insertBack(6); d->insertBack(9); //Do a delete, test it. d->deleteAllInstances(6); checkTest("testdeleteAllInstances #1", "4 2 5 9", d->getStringFromList()); delete d; d = new SinglyLinkedList delete d; d = new SinglyLinkedList delete d; d = new SinglyLinkedList //Do a delete, test it. d->deleteAllInstances(9); checkTest("testdeleteAllInstances #4", "4 2 5 1 2", d->getStringFromList()); //Test deleting something that doesn't exist d->deleteAllInstances(7); checkTest("testdeleteAllInstances #5", "4 2 5 1 2", d->getStringFromList()); //A few more tests d->deleteAllInstances(2); checkTest("testdeleteAllInstances #6", "4 5 1", d->getStringFromList()); d->deleteAllInstances(4); checkTest("testdeleteAllInstances #7", "5 1", d->getStringFromList()); d->deleteAllInstances(5); checkTest("testdeleteAllInstances #8", "1", d->getStringFromList()); d->deleteAllInstances(1); checkTest("testdeleteAllInstances #9", "The list is empty.", d->getStringFromList()); //retest deleting something that doesn't exist. d->deleteAllInstances(7); checkTest("testdeleteAllInstances #10", "The list is empty.", d->getStringFromList()); delete d; //Now ramp it up and do some huge tests. Start by timing how long a smaller approach takes. d = new SinglyLinkedList cout ; //Fill the list with a pattern of //1 2 2 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 1 2 2 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 ... for (int i = 0; i insertBack(i % 4 + 1); } } cout deleteAllInstances(3); end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); diff = end - start; double actualTime = diff.count() / 1000.0; if (actualTime } else { cout } void pressAnyKeyToContinue() { cout //Linux and Mac users with g++ don't need this //But everyone else will see this message. cin.get(); } int main() { //Each of these checks how many bytes you have used. checkTestMemory("Memory Leak/Allocation Test #1", 0, ManageMemory::getTotalSize()); //For your assignment, write the code to make these three methods work //You should not modify the code here in main. testGetAtIndex(); checkTestMemory("Memory Leak/Allocation Test #2", 0, ManageMemory::getTotalSize()); testSquareBrackets(); checkTestMemory("Memory Leak/Allocation Test #3", 0, ManageMemory::getTotalSize()); testInsertAtIndex(); checkTestMemory("Memory Leak/Allocation Test #4", 0, ManageMemory::getTotalSize()); testDeleteAtIndex(); checkTestMemory("Memory Leak/Allocation Test #5", 0, ManageMemory::getTotalSize()); testdeleteAllInstances(); checkTestMemory("Memory Leak/Allocation Test #6", 0, ManageMemory::getTotalSize()); pressAnyKeyToContinue(); return 0; }
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


