
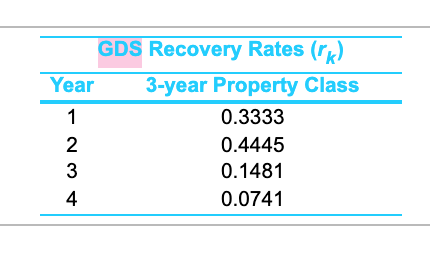

Individual industries will use energy as efficiently as it is economical to do so, and there are several incentives to improve the efficiency of energy consumption. To illustrate, consider the selection of a new water pump. The pump is to operate 800 hours per year. Pump A costs $2,200, has an overall efficiency of 81.89%, and it delivers 11.2 hp. The other available alternative, pump B, costs $1,100, has an overall efficiency of 44.6%, and delivers 12.7 hp. Both pumps have a useful life of five years and will be sold at that time. (Remember 1 hp = 0.746 kW.) Pump A will use SL depreciation over five years with an estimated SV of zero. Pump B will use the MACRS depreciation method with a class life of three years. After five years, pump A has an actual market value of $400, and pump B has an actual market value of $180. Using the IRR method on the after-tax cash flows and a before-tax MARR of 15%, is the incremental investment in pump A economically justifiable? The effective income tax rate is 24%. The cost of electricity is $0.06/kWh, and the pumps are subject to a study period of five years. Click the icon to view the GDS Recovery Rates (rk) for the 3-year property class. The IRR of the incremental investment is 22 %. (Round to one decimal place.) GDS Recovery Rates (mk) Year 3-year Property Class 1 0.3333 2 0.4445 3 0.1481 4 0.0741 WN - Try again. =- Develop the after-tax analysis. Let Rk be the revenues (and savings) from the project during period k, Ek be the cash outflows, dk be the depreciation, t be the effective income tax rate on ordinary income. Then the income tax is Tk= -t(Rk-Ek-dk). BTCF and ATCF values are calculated with BTCFK = Rk - Eki ATCFk = BTCFk+Tk = Recall that the depreciation deduction (dk) for an asset under MACRS (GDS) is computed with dk=rk.B, 1 sksN+1, where rk is the recovery rate for year k, B is the cost basis. SL depreciation assumes that a constant amount is depreciated each year over the depreciable (useful) life of the asset: dx = (B-SVN) /N, where N is the depreciable life of the asset and SVN is the estimated salvage value at end of year N. Calculate the incremental ATCFs (A-B) and find IRR for this incremental investment. The Excel function IRR(range, guess) requires the net cash flows for the study period and an initial guess for the IRR value. OK Individual industries will use energy as efficiently as it is economical to do so, and there are several incentives to improve the efficiency of energy consumption. To illustrate, consider the selection of a new water pump. The pump is to operate 800 hours per year. Pump A costs $2,200, has an overall efficiency of 81.89%, and it delivers 11.2 hp. The other available alternative, pump B, costs $1,100, has an overall efficiency of 44.6%, and delivers 12.7 hp. Both pumps have a useful life of five years and will be sold at that time. (Remember 1 hp = 0.746 kW.) Pump A will use SL depreciation over five years with an estimated SV of zero. Pump B will use the MACRS depreciation method with a class life of three years. After five years, pump A has an actual market value of $400, and pump B has an actual market value of $180. Using the IRR method on the after-tax cash flows and a before-tax MARR of 15%, is the incremental investment in pump A economically justifiable? The effective income tax rate is 24%. The cost of electricity is $0.06/kWh, and the pumps are subject to a study period of five years. Click the icon to view the GDS Recovery Rates (rk) for the 3-year property class. The IRR of the incremental investment is 22 %. (Round to one decimal place.) GDS Recovery Rates (mk) Year 3-year Property Class 1 0.3333 2 0.4445 3 0.1481 4 0.0741 WN - Try again. =- Develop the after-tax analysis. Let Rk be the revenues (and savings) from the project during period k, Ek be the cash outflows, dk be the depreciation, t be the effective income tax rate on ordinary income. Then the income tax is Tk= -t(Rk-Ek-dk). BTCF and ATCF values are calculated with BTCFK = Rk - Eki ATCFk = BTCFk+Tk = Recall that the depreciation deduction (dk) for an asset under MACRS (GDS) is computed with dk=rk.B, 1 sksN+1, where rk is the recovery rate for year k, B is the cost basis. SL depreciation assumes that a constant amount is depreciated each year over the depreciable (useful) life of the asset: dx = (B-SVN) /N, where N is the depreciable life of the asset and SVN is the estimated salvage value at end of year N. Calculate the incremental ATCFs (A-B) and find IRR for this incremental investment. The Excel function IRR(range, guess) requires the net cash flows for the study period and an initial guess for the IRR value. OK









