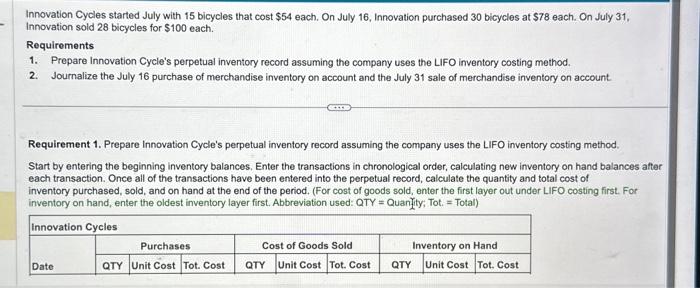
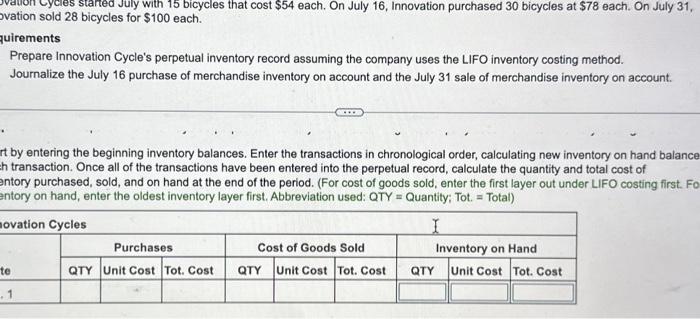
Innovation Cycles started July with 15 bicycles that cost $54 each. On July 16 , Innovation purchased 30 bicycles at $78 each. On July 31 . Innovation sold 28 bicycles for $100 each. Requirements 1. Prepare Innovation Cycle's perpetual inventory record assuming the company uses the LIFO inventory costing method. 2. Journalize the July 16 purchase of merchandise inventory on account and the July 31 sale of merchandise inventory on account Requirement 1. Prepare Innovation Cycle's perpetual inventory record assuming the company uses the LIFO inventory costing method. Start by entering the beginning inventory balances. Enter the transactions in chronological order, calculating new inventory on hand balances atter each transaction. Once all of the transactions have been entered into the perpetual record, calculate the quantity and total cost of inventory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (For cost of goods sold, enter the first layer out under LIFO costing first. For inventory on hand, enter the oldest inventory layer first. Abbreviation used: QTY = Quanity; Tot: = Total) vation sold 28 bicycles for $100 each. uirements Prepare Innovation Cycle's perpetual inventory record assuming the company uses the LIFO inventory costing method. Journalize the July 16 purchase of merchandise inventory on account and the July 31 sale of merchandise inventory on account. t by entering the beginning inventory balances. Enter the transactions in chronological order, calculating new inventory on hand balance in transaction. Once all of the transactions have been entered into the perpetual record, calculate the quantity and total cost of intory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (For cost of goods sold, enter the first layer out under LIFO costing first. Fo intory on hand, enter the oldest inventory layer first. Abbreviation used: QTY = Quantity; Tot. = Total) vation sold 28 bicycles for $100 each. uirements Prepare Innovation Cycle's perpetual inventory record assuming the company uses the LIFO inventory costing method. Journalize the July 16 purchase of merchandise inventory on account and the July 31 sale of merchandise inventory on account. t by entering the beginning inventory balances. Enter the transactions in chronological order, calculating new inventory on hand balance in transaction. Once all of the transactions have been entered into the perpetual record, calculate the quantity and total cost of intory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (For cost of goods sold, enter the first layer out under LIFO costing first. Fo intory on hand, enter the oldest inventory layer first. Abbreviation used: QTY = Quantity; Tot. = Total) Innovation Cycles started July with 15 bicycles that cost $54 each. On July 16 , Innovation purchased 30 bicycles at $78 each. On July 31 . Innovation sold 28 bicycles for $100 each. Requirements 1. Prepare Innovation Cycle's perpetual inventory record assuming the company uses the LIFO inventory costing method. 2. Journalize the July 16 purchase of merchandise inventory on account and the July 31 sale of merchandise inventory on account Requirement 1. Prepare Innovation Cycle's perpetual inventory record assuming the company uses the LIFO inventory costing method. Start by entering the beginning inventory balances. Enter the transactions in chronological order, calculating new inventory on hand balances atter each transaction. Once all of the transactions have been entered into the perpetual record, calculate the quantity and total cost of inventory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (For cost of goods sold, enter the first layer out under LIFO costing first. For inventory on hand, enter the oldest inventory layer first. Abbreviation used: QTY = Quanity; Tot: = Total) vation sold 28 bicycles for $100 each. uirements Prepare Innovation Cycle's perpetual inventory record assuming the company uses the LIFO inventory costing method. Journalize the July 16 purchase of merchandise inventory on account and the July 31 sale of merchandise inventory on account. t by entering the beginning inventory balances. Enter the transactions in chronological order, calculating new inventory on hand balance in transaction. Once all of the transactions have been entered into the perpetual record, calculate the quantity and total cost of intory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (For cost of goods sold, enter the first layer out under LIFO costing first. Fo intory on hand, enter the oldest inventory layer first. Abbreviation used: QTY = Quantity; Tot. = Total) vation sold 28 bicycles for $100 each. uirements Prepare Innovation Cycle's perpetual inventory record assuming the company uses the LIFO inventory costing method. Journalize the July 16 purchase of merchandise inventory on account and the July 31 sale of merchandise inventory on account. t by entering the beginning inventory balances. Enter the transactions in chronological order, calculating new inventory on hand balance in transaction. Once all of the transactions have been entered into the perpetual record, calculate the quantity and total cost of intory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (For cost of goods sold, enter the first layer out under LIFO costing first. Fo intory on hand, enter the oldest inventory layer first. Abbreviation used: QTY = Quantity; Tot. = Total)