Question
Inside the dijkstra class method, you are to output the following information to the console screen: To print out vertex selection sequence To show the
Inside the dijkstra class method, you are to output the following information to the console screen:
To print out vertex selection sequence
To show the MST nodes by the picked sequence pair with its distance to the starting vertex.
The output shall appears like the following:
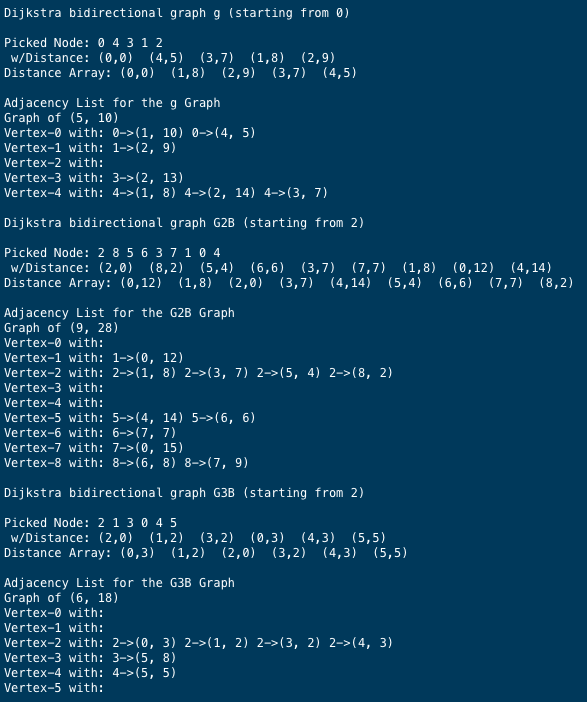
This assignment only expected to complete the edge picking and its proper weight as shown above. The adjacency was illustrated for reference only.
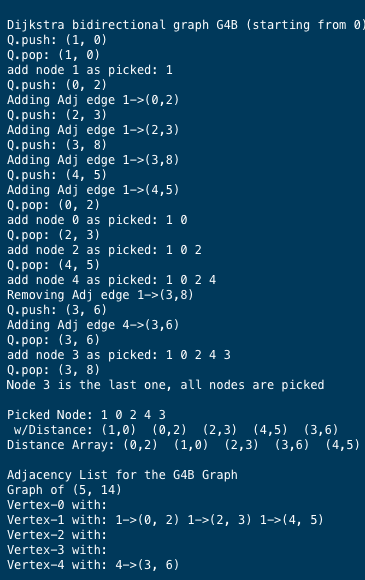
If you have implemented the proper removal of unused edges for the adjacency fix, here is a sample test run on the G4B with some debug trace turned on:
Here's the program that needs to be implemented.
dijkstra.cpp
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define ii pair
enum GRAPH_TYPE {DI, BI};
using namespace std;
// functor overloads the compare ii
class compareII {
public:
bool operator()(const ii &j, const ii &k) {
return j.second > k.second;}
};
class Graph
{
int V, E; // No. of vertices, edges
list
list
vector
vector
priority_queue
public:
Graph(int v_num) : V(v_num), E(0) {
edge = new list
distance = vector
}
void addEdge(int u, int v, int w, int type = DI) {
edge[u].push_back(ii(v, w)); E++;
if(type != DI) {
edge[v].push_back(ii(u, w)); E++; }
}
void dijkstra(int v);
void print();
void printGraph();
void printAdjacency();
};
void Graph::printGraph() {
cout
for (auto p : pv) { cout
cout
for (auto p : pv) { cout
cout
for (int n=0; n cout cout } void Graph::printAdjacency() { cout for (int n = 0; n cout for (auto a : adjList[n]) cout (" cout } } void Graph::dijkstra(int source) { distance = vector distance[source] = 0; Q.push(ii(source, 0)); adjList = new list while (!Q.empty()) { // pop the vertex with smallest distance d of vertex v from Q // smallest d of v from Q ii top = Q.top(); Q.pop(); int v = top.first, d = top.second; // push the selected vertex v into picked vertices array pv if (d for (auto e : edge[v]) { // go through all edges e // if the distance to new node is greater than distance from current node to this node // replace the distance // push the new node and distance into the queue } } } } // Driver program to test methods of graph class int main() { // Di-graph g(5,10) Graph g(5); g.addEdge(0,1,10,DI); g.addEdge(0,4,5,DI); g.addEdge(1,2,1,DI); g.addEdge(1,4,2,DI); g.addEdge(1,3,4,DI); g.addEdge(3,0,7,DI); g.addEdge(3,2,6,DI); g.addEdge(4,1,3,DI); g.addEdge(4,2,9,DI); g.addEdge(4,3,2,DI); cout g.dijkstra(0); g.printGraph(); cout g.printAdjacency(); // Bidirection G2B (9,28) Graph G2B(9); G2B.addEdge(0,1,4,BI); G2B.addEdge(0,7,8,BI); G2B.addEdge(1,2,8,BI); G2B.addEdge(1,7,11,BI); G2B.addEdge(2,3,7,BI); G2B.addEdge(2,5,4,BI); G2B.addEdge(2,8,2,BI); G2B.addEdge(3,4,9,BI); G2B.addEdge(3,5,14,BI); G2B.addEdge(4,5,10,BI); G2B.addEdge(5,6,2,BI); G2B.addEdge(6,7,1,BI); G2B.addEdge(6,8,6,BI); G2B.addEdge(7,8,7,BI); cout G2B.dijkstra(2); G2B.printGraph(); cout G2B.printAdjacency(); Graph G3B(6); G3B.addEdge(0,1,2,BI); G3B.addEdge(0,2,3,BI); G3B.addEdge(1,2,2,BI); G3B.addEdge(1,3,6,BI); G3B.addEdge(2,3,2,BI); G3B.addEdge(2,4,3,BI); G3B.addEdge(3,4,2,BI); G3B.addEdge(3,5,6,BI); G3B.addEdge(4,5,2,BI); cout G3B.dijkstra(2); G3B.printGraph(); cout G3B.printAdjacency(); // 2 3 // (0)--(1)--(2) // | / \ | // 6| 8/ \5 |4 // | / 1 \ | // (3)-------(4) Graph G4B(5); G4B.addEdge(0,1,2,BI); G4B.addEdge(0,3,6,BI); G4B.addEdge(1,2,3,BI); G4B.addEdge(1,3,8,BI); G4B.addEdge(1,4,5,BI); G4B.addEdge(2,4,4,BI); G4B.addEdge(3,4,1,BI); cout G4B.dijkstra(1); G4B.printGraph(); cout G4B.printAdjacency(); return 0;
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


