Question
Instructions - Do the two problems here: A and B. Problem A is a variation of the Sanotronics problem solved in class. Please read the
Instructions
- Do the two problems here: A and B. Problem A is a variation of the Sanotronics problem solved in class. Please read the problem description provided in the textbox thoroughly before you start working on the Excel sheet.
- Use the random numbers on the templates provided. As you will notice, most of the rows in the simulation tables are hidden for easy navigation. Please keep them hidden. On the other hand, if you are getting error messages in visible cells, you may want to unhide the hidden rows to check them (select the row just before and the row just after hidden rows, right-click, unhide). After you correct the errors, you can hide them again.
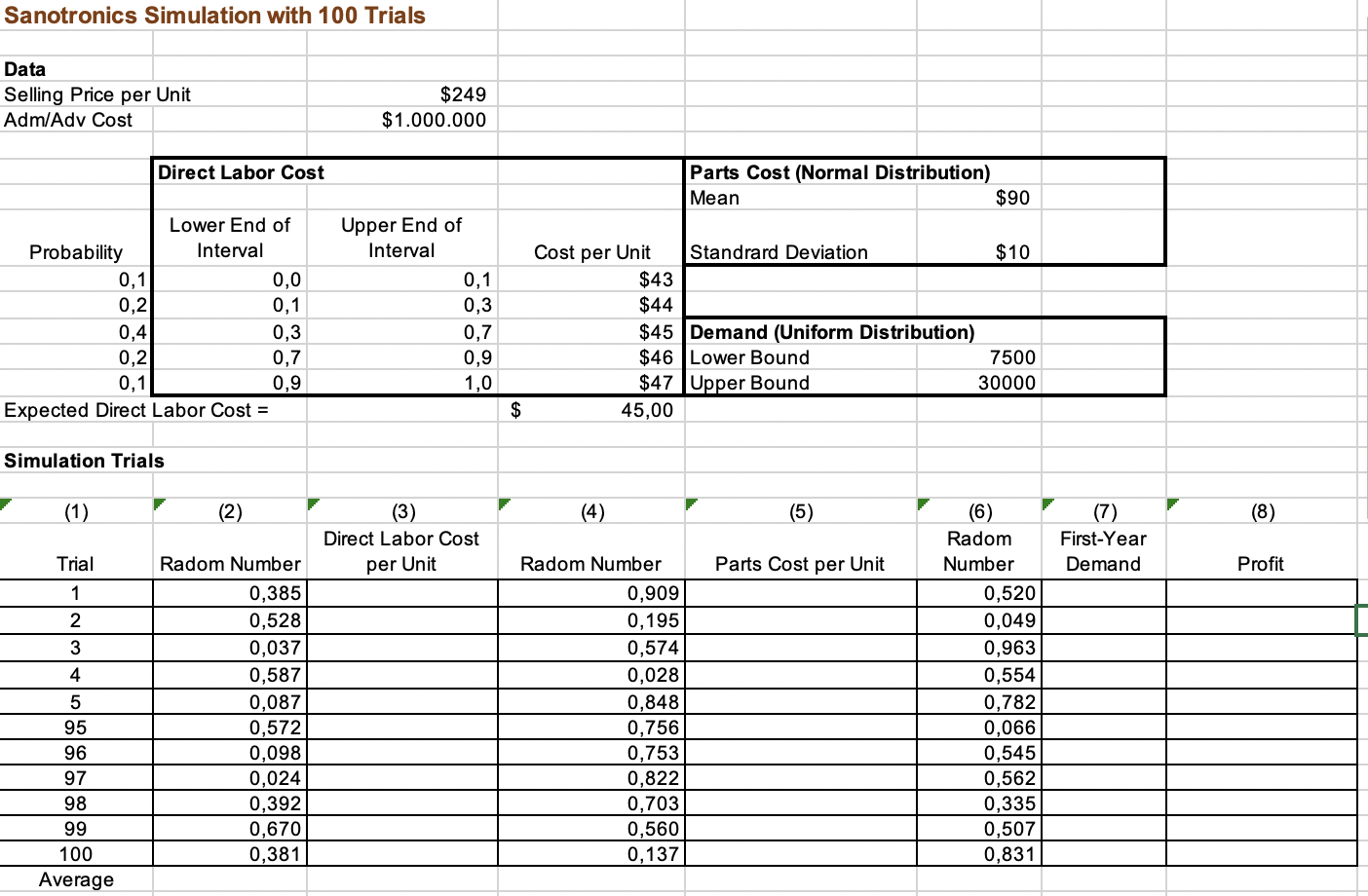
This is the Sanotronics simulation with 100 trials that was covered in the lecture. Here, we want to illustrate how the results can change when different distributions are used for some of the random variables.
Suppose the following changes occur in the assumptions.
- Parts cost follows a normal distribution with mean of $90 and standard deviation of $10.
- Demand now follows a uniform distribution between 7,500 and 30,000 units.
The appropriate changes have been made in the Excel sheet. Do not change the given random numbers.
Round all answers up to 2 decimal places.
1) What is the direct labor cost per unit for trial 1?
2) What is the parts cost per unit for trial 1?
3) What is the demand for trial 1?
4) What is the mean profit?
5) What is the maximum profit?
5) What is the probability of loss (in %) ?
6) What is the value at risk (rounded to whole $)? Remember to give the absolute value.
7) Is this more or less risky than the original example solved in class?
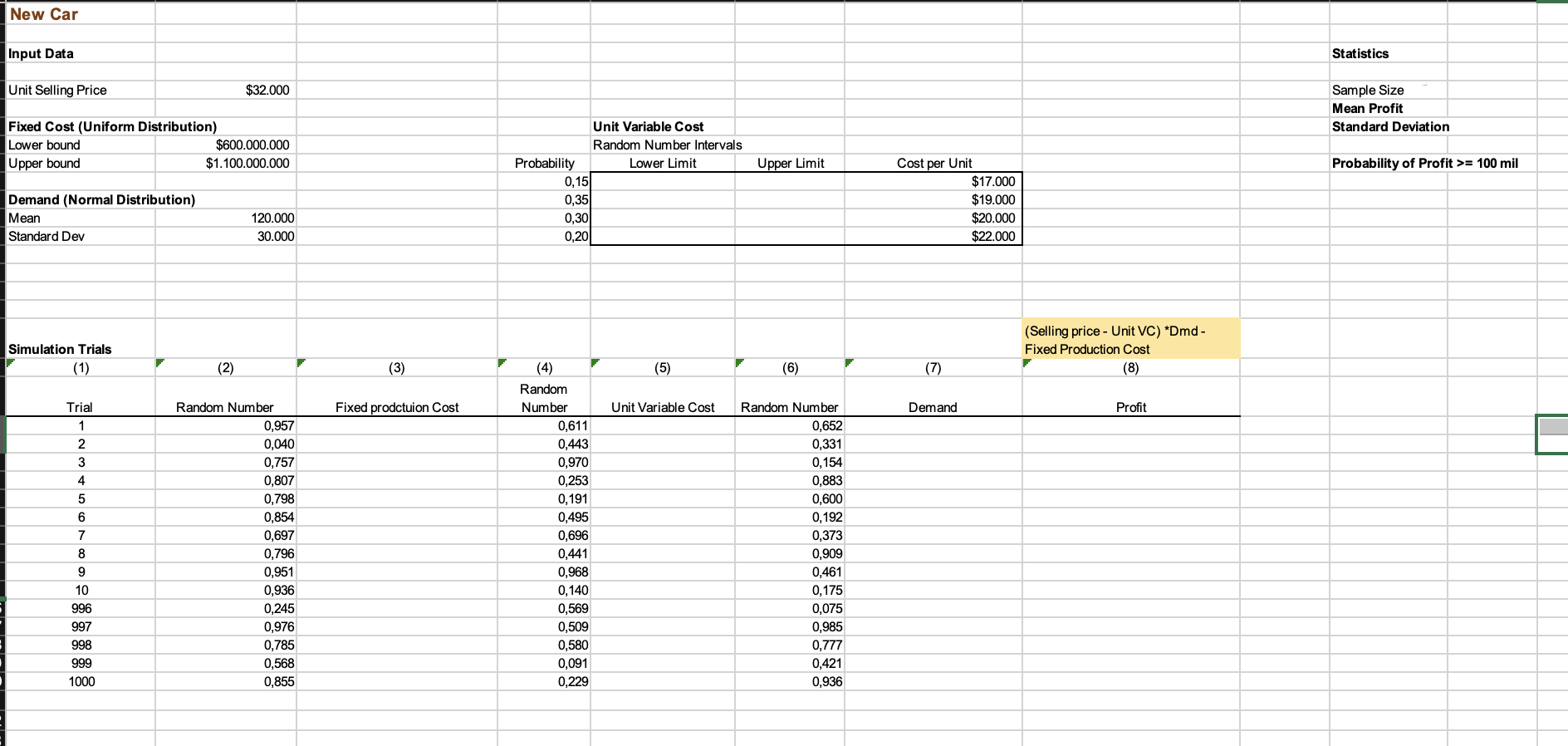
GM is trying to decide whether to introduce a new car model. The selling price for the car will be $32,000.
The fixed production cost of developing the car is assumed to be uniformly distributed between $600 million and $1.1 billion.
The demand for the car is described by a normal distribution with a mean of 120,000 units and a standard deviation of 30,000.
The unit variable cost for the car is distributed as shown below.
Cost per Unit Probability
$17,000 0.15
$19,000 0.35
$20,000 0.30
$22,000 0.20
Complete the random number interval table for unit variable cost.
Simulate the profit with 1000 trials.
8) What is the fixed production cost for trial 1?
9) What is the mean profit from the simulation?
10) What is the standard deviation of profit?
11) What is the probability of making at least 100 million dollars in profit?
12) GM is willing to introduce the car if there is at least 95% probability of making a profit AND at least 85% probability of making profit of at least $100 million. Compute these two probabilities. What will be your recommendation?
Sanotronics Simulation with 100 Trials Data Selling Price per Unit Adm/Adv Cost Probability (1) 0,1 0,2 0,4 0,2 0,1 Expected Direct Labor Cost = Simulation Trials Trial 1 2 3 4 5 95 96 97 98 Direct Labor Cost 99 100 Average Lower End of Interval (2) 0,0 0,1 0,3 0,7 0,9 Radom Number 0,385 0,528 0,037 0,587 0,087 0,572 0,098 0,024 0,392 0,670 0,381 $249 $1.000.000 Upper End of Interval 0,1 379 0,3 0,7 0,9 1,0 (3) Direct Labor Cost per Unit $ Cost per Unit (4) 45,00 $43 $44 $45 Demand (Uniform Distribution) $46 Lower Bound $47 Upper Bound Radom Number Parts Cost (Normal Distribution) Mean 0,909 0,195 0,574 0,028 0,848 0,756 0,753 0,822 0,703 0,560 0,137 Standrard Deviation (5) Parts Cost per Unit $90 $10 7500 30000 (6) Radom Number 0,520 0,049 0,963 0,554 0,782 0,066 0,545 0,562 0,335 0,507 0,831 (7) First-Year Demand (8) Profit
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 Direct labor cost per unit for trial 1 The direct labor cost per unit is given as 45 for all trials according to the information provided Therefore ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


