Question
Introduction: It is recommended that students shall finish learning chapter 5: Finite Automata before working on the following homework. In CS 4110, many discussed machines,
Introduction:
It is recommended that students shall finish learning chapter 5: Finite Automata before working on the following homework.
In CS 4110, many discussed machines, including Finite Automata and Pushdown Automata, are finite-state machines (FSM). A FSM is an abstract machine that can be in exactly one of a finite number of states at any given moment. The FSM can change from one state to another in response to some inputs; the change from one state to another is called a transition. An FSM is defined by a list of its states, its initial state, and the inputs that trigger each transition.
The behavior of state machines can be observed in many devices in modern society that perform a predetermined sequence of actions depending on a sequence of events with which they are presented. Simple examples are vending machines, which dispense products when the proper combination of coins is deposited; elevators, whose sequence of stops is determined by the floors requested by riders; traffic lights, which change sequence when cars are waiting; and combination locks, which require the input of a sequence of numbers in the proper order.
Example:
Consider the model of a simple vending machine. The machine is initially in the "ready" state, which maps to exactly two states in the following way:
- ready -> deposit -> waiting
- ready -> quit -> exit
The variables in bold-face represent transitions. Any input signal not corresponding to one of those transitions can either trigger an error or be ignored. Otherwise, the current state is updated and the process is repeated. If, for example, a deposit input signal is encountered, the FSM will move to the "waiting" state, which defines these transitions:
- waiting -> select -> dispense
- waiting -> refund -> refunding
The "dispense" state defines only one transition:
- dispense -> remove -> ready
Note, however, that in this example the "refunding" state doesn't actually require input in order to move to the "ready" state, so an implicit transition is defined as such:
- refunding -> ready
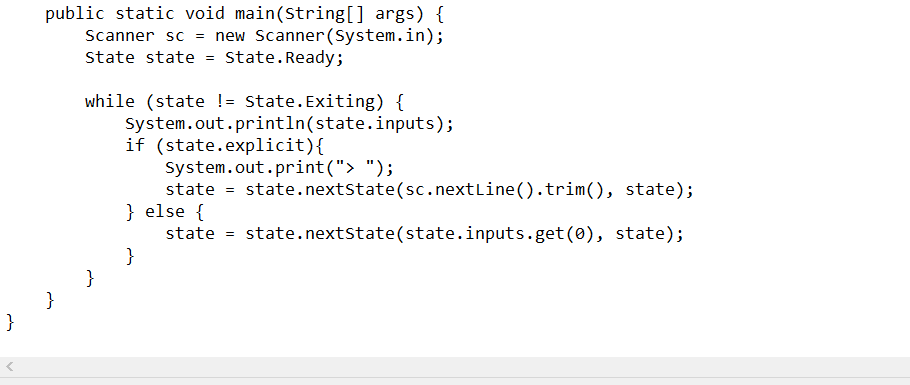
A sample Java program is provided to implement a finite state machine which handles both explicit and implicit transitions. Your are required to finish the following tasks for this
homework:
- Task 1 (25 points): implement a finite state machine which handles the turnstile transitions. Your program should have testing code to show how it works. You may choose to use unit testing or just use a main method for the testing purpose.

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


