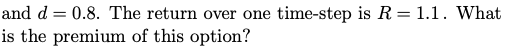Introduction:

Question:

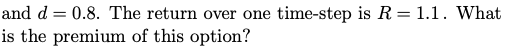
Barrier options are just one of the many types of exotic options 1. Another type of exotic option is a chooser option. Like all options, a chooser option gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the underlying asset. A chooser option allows the holder to decide whether the option is a put or a call as some fixed point in time after the holder has purchased the option-often this point in time is about halfway through the life of the option. Chooser options are typically European style, and there is only one strike price. Traders might seek to purchase chooser options when a market is quite volatile and when unsure if prices will rise or fall. A chooser option is available with strike K=$20 and expiry in two time-steps. The holder must choose whether is is a put or call at the first time-step. The underlying asset's value follows Cox-Ross-Rubenstein notation with S=$20,u=1.3 and d=0.8. The return over one time-step is R=1.1. What is the premium of this option? Barrier options are just one of the many types of exotic options 1. Another type of exotic option is a chooser option. Like all options, a chooser option gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the underlying asset. A chooser option allows the holder to decide whether the option is a put or a call as some fixed point in time after the holder has purchased the option-often this point in time is about halfway through the life of the option. Chooser options are typically European style, and there is only one strike price. Traders might seek to purchase chooser options when a market is quite volatile and when unsure if prices will rise or fall. A chooser option is available with strike K=$20 and expiry in two time-steps. The holder must choose whether is is a put or call at the first time-step. The underlying asset's value follows Cox-Ross-Rubenstein notation with S=$20,u=1.3 and d=0.8. The return over one time-step is R=1.1. What is the premium of this option