Question: Introduction Virtual reality (VR) has become a disruptive technology that has the ability to completely impact many facets of our life. Virtual reality has created
Introduction
Virtual reality (VR) has become a disruptive technology that has the ability to completely impact many facets of our life. Virtual reality has created new opportunities for immersive and engaging experiences across a variety of industries, from gaming and entertainment to education and healthcare. Over time, the VR industry has developed quickly because to technological breakthroughs and the findings of scholarly studies. We will examine the history of VR, review significant studies, and talk about emerging themes that are influencing the growth of this fascinating subject in this essay. We will study the essential aspects of VR, including its technological breakthroughs, applications, and societal impact.By delving into the history, development, and future trends of VR technology, including its precursor technologies, major landmarks in the history of science that have influenced its development, and potential future developments. we will gain a deeper understanding of the past, present, and future of virtual reality.
History of Virtual Reality
Development of Virtual Reality
The development of virtual reality (VR) has been a long and fascinating journey that has spanned several decades. Although the concept of VR has been around since the early 20th century, it wasn't until the 1980s that the technology began to take shape in a meaningful way.
One of the key players in the early development of VR was Jaron Lanier, who is widely regarded as the father of virtual reality. In 1984, he founded VPL Research, which was one of the first companies to develop and sell VR technology. VPL Research's VR systems were primarily used for scientific and industrial applications, such as flight simulators and medical training tools.
During the 1990s, VR technology began to evolve rapidly, with new and improved hardware and software being developed that made VR more immersive and interactive. The introduction of 3D graphics cards and high-speed internet connections made it possible to create more realistic and complex virtual environments.
In recent years, VR has made significant strides in becoming more accessible and mainstream. Major tech companies like Oculus and HTC have developed affordable and user-friendly VR headsets that have brought VR to a wider audience. VR has also found new applications in fields like education, entertainment, and healthcare, where it is being used to train medical professionals and provide therapy for patients.
Despite the progress that has been made in the development of VR, there are still significant challenges that need to be addressed. One of the biggest challenges is creating VR experiences that are truly immersive and feel natural. Another challenge is developing more sophisticated input devices that can accurately track the user's movements and gestures in real-time.
Overall, the development of virtual reality has been an exciting and ongoing process that continues to push the boundaries of what is possible with technology. With continued advancements in hardware and software, it is likely that VR will become even more immersive, interactive, and widely adopted in the years to come.
Pioneering Companies and Individuals
Virtual Reality technology has been around since the 1960s, but it was not until the 1980s and 1990s that companies began to develop commercial VR products. One of the earliest companies to produce VR headsets was VPL Research, founded by computer scientist Jaron Lanier in 1985. VPL's headsets were bulky and expensive, but they were the first to provide true immersion and interactive experiences.
Other early pioneers in the field included companies like Virtuality Group, which developed VR systems for arcades and entertainment centers, and Autodesk, which created software tools for VR content creation. In recent years, companies like Oculus (owned by Facebook), HTC, and Sony have dominated the consumer VR market with more affordable and high-quality headsets.
Impact of VR on Various Industries
Virtual Reality has the potential to transform a wide range of industries by creating new ways to visualize, simulate, and interact with the world. Some of the industries that have already been impacted by VR technology include:
Entertainment and Gaming
Virtual Reality has revolutionized the gaming industry, providing players with fully immersive experiences that go beyond traditional gameplay. VR technology is also being used in movies and other forms of entertainment to create new, interactive experiences for viewers.
Education and Training
Virtual Reality is being used to enhance traditional education and training methods by providing immersive and interactive simulations. This technology is particularly useful for fields like medicine, where students can practice surgical procedures in a safe and controlled environment.
Healthcare
Virtual Reality is being used in a variety of ways to improve patient care, from pain management to treating phobias and anxiety disorders. VR can also help doctors and medical researchers visualize complex data and improve their understanding of human anatomy.
Real Estate and Architecture
Virtual Reality is being used to create realistic 3D models of buildings and environments, allowing architects and real estate developers to showcase their designs to clients and investors. This technology can also be used to give prospective buyers a virtual tour of a property before it is even built.
Overall, Virtual Reality has the potential to transform how we learn, work, and interact with the world around us. As the technology continues to improve and become more accessible, we can expect to see even more industries embrace its potential.
Precursor Technologies
Their Influences
The concept of virtual reality has been influenced by several precursor technologies that paved the way for its development. One of the earliest precursor technologies of VR was the stereoscope, invented by Charles Wheatstone in the 1830s, which allowed users to view two-dimensional images in a way that created an illusion of depth perception (Rheingold, 1991). This early form of stereoscopic viewing laid the foundation for the idea of creating immersive visual experiences in a virtual environment.
Another significant precursor technology was the head-mounted display (HMD), which was first introduced in the 1960s by Ivan Sutherland (Rheingold, 1991). The HMD was a wearable device that allowed users to view computer-generated images in a virtual environment by wearing a headset that was attached to a computer system. Although the early HMDs were bulky and expensive, they represented a crucial step towards the development of modern VR headsets (Lanier, 1992)
Early Forms of Immersive Technology
The concept of creating immersive experiences through technology is not a new one. The earliest examples of immersive technology can be traced back to panoramic paintings, which were popular in the 19th century. These large-scale paintings were displayed in circular rooms, providing viewers with a sense of immersion in the depicted scene.
In the early 20th century, the development of the stereoscope allowed people to view images in 3D, providing a more immersive experience. Later, in the 1960s, the first flight simulators were developed, allowing pilots to train in a safe and controlled environment. These simulators provided a sense of immersion through the use of realistic controls and visual displays.
Development of 3D Graphics and Displays
The development of 3D graphics and displays has played a crucial role in the evolution of immersive technology. In the 1970s and 1980s, computer graphics began to emerge as a field of study, and researchers began to develop techniques for rendering 3D images on a computer screen. The first 3D wireframe models were simple, but they paved the way for more advanced techniques like ray tracing and texture mapping.
In the 1990s, the first consumer-grade 3D graphics cards were released, allowing home computer users to experience 3D graphics in games and other applications. This technology paved the way for the development of more advanced graphics engines and realistic visual effects.
Evolution of Video Game Technology
Video games have been a driving force behind the development of immersive technology. In the 1970s and 1980s, arcade games like Space Invaders and Pac-Man provided a simple form of immersion through their gameplay and graphics. In the 1990s, 3D graphics technology allowed game developers to create more immersive environments, and games like Doom and Quake provided a sense of immersion through their first-person perspective.
In the 2000s, console gaming and online gaming became more popular, and games like Halo and World of Warcraft provided players with even more immersive experiences. Today, with the advent of Virtual Reality headsets, gamers can experience fully immersive environments that provide a sense of presence and interactivity like never before.
Science and Technology Influences
Emerging Technologies and the Future of VR
Virtual reality has the potential to integrate with emerging technologies that could shape its future and further enhance its capabilities. One of these emerging technologies is artificial intelligence (AI), which has the potential to transform the way users interact with virtual environments. By incorporating AI algorithms and machine learning techniques, VR experiences can become more adaptive, personalized, and responsive to users' actions and preferences. AI can also enhance the realism of virtual environments by creating more realistic and intelligent virtual characters and objects that can interact with users in a more natural and realistic way.
Another emerging technology that could shape the future of VR is neuroscience. Research in neuroscience can help understand how the brain processes and responds to virtual experiences, and how VR can be used to create more immersive and impactful experiences. For example, research on spatial cognition and perception can inform the design of virtual environments that are more intuitive and easier to navigate, while research on emotional and physiological responses to virtual stimuli can help create more emotionally engaging VR experiences. The integration of neuroscience with VR can also lead to the development of new therapeutic applications of VR, such as virtual reality exposure therapy for treating phobias and anxiety disorders.
In addition to AI and neuroscience, other emerging technologies such as 5G networks, cloud computing, and augmented reality (AR) can also have a significant impact on the future of VR. 5G networks can provide high-speed and low-latency connectivity, enabling seamless and immersive VR experiences that can be accessed from anywhere. Cloud computing can provide the computational power and storage necessary for creating and rendering complex virtual environments, while AR can enhance the realism and interactivity of VR experiences by integrating virtual and real-world elements. Overall, the integration of emerging technologies with VR can open up new possibilities for applications and experiences that were previously impossible or difficult to achieve. As these technologies continue to develop and mature, the future of VR is likely to become even more exciting and transformative.
Key Works in the Field of VR
Future Trends
Virtual reality (VR) has come a long way since its inception, with advancements in technology continuously pushing the boundaries of what's possible. As the field of VR continues to evolve rapidly, it's essential to keep an eye on future trends that will shape its development further. In this discussion, we will explore some of the key future trends in VR, including increased mobility, enhanced realism, expanded applications, social interaction, and cross-platform compatibility. These trends will undoubtedly impact the future of VR and shape the way we interact with virtual environments.
Increased Mobility
The increased mobility of VR headsets and wireless technologies is enabling users to experience VR without being physically tethered to a specific location. Portable VR headsets, such as the Oculus Quest and HTC Vive Focus, are already available in the market, allowing users to experience VR on the go. These headsets are equipped with powerful processors, high-resolution displays, and motion-tracking sensors that enable users to interact with virtual environments without being constrained by cables or external sensors. With the ongoing advancements in portable VR headsets and wireless technologies, VR experiences are becoming more mobile and untethered, allowing users to move freely and interact with virtual environments without being confined to a specific physical location.
Moreover, wireless VR technologies are also emerging, which will further enhance the mobility of VR experiences. Technologies such as Wi-Fi 6, 5G, and Li-Fi are being developed to enable high-speed wireless connectivity and low-latency communication between VR headsets and computers or servers. This will allow users to experience VR in real-time without being physically tethered to a specific location, such as a computer or a gaming console.
The increased mobility of VR experiences will enable users to explore and interact with virtual environments in new ways, such as in outdoor or public spaces, or during travel. It will also open up new possibilities for VR applications in fields such as tourism, education, and training, where users can experience and learn about different environments and scenarios without being physically present.
Enhanced Realism
Enhanced realism in VR is all about creating a more believable and immersive experience for the user. Advancements in graphics, display technologies, and hardware capabilities are expected to continue improving the visual quality and realism of VR experiences, making them even more immersive and engaging.
As technology continues to improve, VR developers are able to create more detailed and realistic virtual environments. This includes advancements in graphics, such as high-resolution textures and improved lighting effects, which make virtual objects look more lifelike. In addition, display technologies like OLED and 4K screens can create higher-quality images with more accurate colors and better contrast.
Hardware capabilities are also improving, allowing for more complex and realistic interactions with the virtual world. For example, haptic feedback systems can provide tactile sensations that make virtual objects feel more real, while motion tracking technology can track the user's movements more accurately, allowing for more natural and intuitive interactions.
All these advancements combine to develop a more immersive and engaging VR experience, where users can feel like they are truly in a different world. As technology continues to improve, we can expect to see even more realistic and detailed virtual environments that blur the line between reality and simulation.
Expanded Applications
VR is being increasingly used in diverse fields such as healthcare, education, training, and therapy, and this trend is expected to continue growing in the future. Applications of VR in areas such as virtual tourism, virtual social experiences, and virtual shopping are also expected to gain traction.
As the technology and accessibility of VR continues to improve, its applications are expanding beyond traditional areas such as gaming and entertainment. In the field of healthcare, VR is being used for a range of applications, from pain management to surgical training. For example, virtual reality can be used to create immersive environments that distract patients from pain during procedures, reducing the need for medication. In the education and training sectors, VR is being used to simulate real-world scenarios, allowing students to gain practical experience in a safe and controlled environment. In addition, VR is being used for therapy, particularly for disorders such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), by creating a safe and controlled environment for patients to confront their fears.
Apart from these traditional areas, VR is also being used in emerging fields such as virtual tourism, virtual social experiences, and virtual shopping. With VR, users can explore different parts of the world without leaving their homes, providing a new form of tourism. Virtual social experiences allow users to interact with others in a virtual environment, providing a new platform for socialization and entertainment. Virtual shopping allows users to browse and purchase products in a virtual store, providing a unique and immersive shopping experience.
Social Interactions in VR
Social VR, where users can interact and communicate with others in virtual environments, is expected to become more prominent. Virtual social experiences, virtual events, and virtual communities are expected to flourish, providing users with new ways to connect and engage with others. Social VR has the potential to transform the way people connect with each other by providing a more immersive and interactive platform for socializing and networking.
One of the key advantages of social VR is that it can allow people to interact with each other in a more natural and intuitive way. For example, users can make avatars that represent them in the virtual environment, and these avatars can move and interact with others in a way that mirrors real-life interactions. Social VR also enables users to engage in activities together, such as playing games or attending virtual events, which can develop a shared sense of experience and connection.
In addition, social VR can provide new opportunities for socializing and networking, particularly for people who may have limited opportunities for in-person interactions. Virtual communities can be created around shared interests or goals, and users can connect and collaborate with others who share their passions or pursuits. This can be particularly valuable in fields such as education and business, where virtual environments can provide new opportunities for learning and collaboration.
Overall, the growth of social VR is expected to provide new ways for people to connect and engage with each other, creating new opportunities for socializing, networking, and collaboration.
Cross-platform Compatibility
Cross-platform compatibility refers to the ability of VR devices and platforms to work seamlessly with each other, regardless of their manufacturer or operating system. Currently, different VR systems have different hardware and software requirements, making it challenging for developers to construct applications that can be used across multiple platforms. As a result, users often have to choose a specific VR platform to use, limiting their access to certain applications and experiences.
However, the development of standards and technologies that allow for cross-platform compatibility is expected to change this. For example, the OpenXR standard, developed by a consortium of major tech companies, aims to develop a universal standard for VR and AR applications that can work across different platforms. Other initiatives, such as WebXR, aim to develop a standard for VR experiences that can be accessed through web browsers, eliminating the need for users to download and install specific software.
The benefits of cross-platform compatibility are clear: it allows for greater accessibility and choice for users, while also providing developers with a larger potential audience for their applications. As the field of VR continues to grow, it is likely that cross-platform compatibility will become increasingly important, making VR experiences more seamless and accessible to a wider range of users.
Technological Advancements in VR
Major Landmarks in the History of Science
The development of VR has been closely tied to major landmarks in the history of science that have influenced its progress. One significant landmark was the advancement of computer graphics and computer processing power. The development of more powerful computers with increased processing capabilities has enabled the creation of more realistic and immersive virtual environments. The advancement of computer graphics has also played a critical role in enhancing the visual quality of VR experiences, making them more realistic and engaging.
Another major landmark was the progress in sensor technologies, such as motion tracking and haptic feedback. Motion tracking technologies, such as gyroscopes and accelerometers, have allowed for more precise tracking of users' movements in VR, allowing for more natural and intuitive interactions with virtual objects and environments. Haptic feedback technologies, such as vibration or touch feedback, have added a new dimension to the VR experience by providing users with a sense of touch and feel in virtual environments, further enhancing immersion and presence.
Additionally, advancements in networking and communication technologies have facilitated the development of collaborative VR experiences, where multiple users can interact and communicate with each other in a shared virtual environment. This has opened new possibilities for applications such as virtual meetings, remote collaboration, and social VR, where users can interact and engage with others in a virtual space.
Instructions

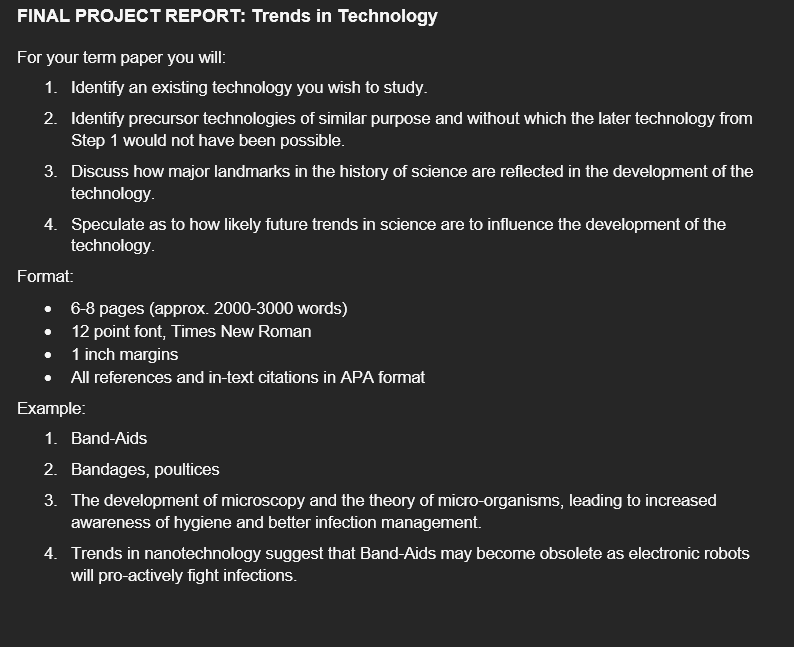
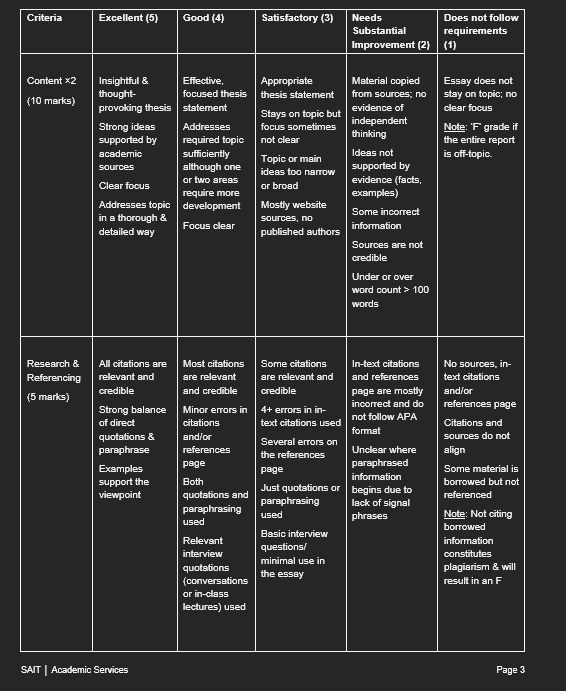
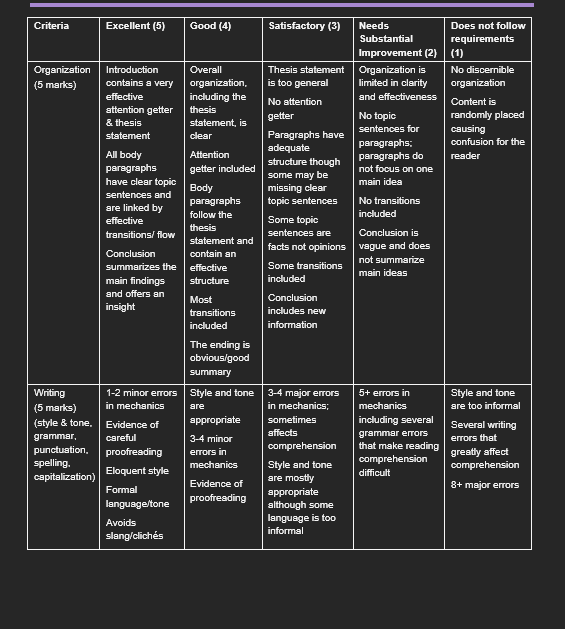

Purpose: This paper will give you an opportunity to explore a current technology in terms of its history, place in the general progression of science and likely future development. Instructions: 1. This assessment will be completed individually outside of class. 2. You will address the requirements completely, using grammatically correct language. 3. See the course schedule for specific dates for deadline. Marking Criteria: The essay will be graded based on completeness of the answer, formatting, clarity, and organization. Refer to the attached Final Report Rubric for more details.FINAL PROJECT REPORT: Trends in Technology For your term paper you will: - Identify an existing technology you wish to study. - Identify precursor technologies of similar purpose and without which the later technology from Step 1 would not have been possible. - Discuss how major landmarks in the history of science are reected in the development of the technology. 4- Speculate as to how likely future trends in science are to inuence the development of the technology. Format: - 68 pages (approx. EUUDSDDD words) - 12 point font, Times New Roman - 1 inch margins - All references and intext citations in APA fomiat Example: 1- BandAids 2- Bandages, poultices 3- The development of microscopy and the theory of microorganisms, leading to increased awareness of hygiene and better infection management. 4- Trends in nanotechnology suggest that BandAids may become obsolete as electronic robots will proactively ght infections. Criteria Excellent (5) Good (4) Satisfactory (3) Needs Does not follow Substantial requirements Improvement (2) (1) Content x2 Insightful & Effective, Appropriate Material copied Essay does not thought- focused thesis thesis statement from sources; no stay on topic; no (10 marks) provoking thesis statement evidence of clear focus Stays on topic but independent Strong ideas Addresses focus sometimes Note: 'F grade if thinking supported by required topic not clear the entire report academic sufficiently Ideas not Topic or main is off-topic. sources although one ideas too narrow supported by or two areas evidence (facts, Clear focus or broad require more examples) Addresses topic development Mostly website Some incorrect in a thorough & sources, no Focus clear detailed way published authors information Sources are not credible Under or over word count > 100 words Research & All citations are Most citations Some citations In-text citations No sources, in- Referencing relevant and are relevant are relevant and and references text citations credible and credible credible page are mostly and/or (5 marks) incorrect and do references page Strong balance Minor errors in 4+ errors in in- not follow APA of direct citations text citations used Citations and format quotations & and/or sources do not Several errors on paraphrase references the references Unclear where align page paraphrased Examples page Some material is support the Both information borrowed but not Just quotations or viewpoint quotations and begins due to referenced paraphrasing lack of signal paraphrasing used phrases Note: Not citing used borrowed Basic interview Relevant information questions/ interview constitutes minimal use in quotations plagiarism & will the essay (conversations result in an F or in-class lectures) used SAIT | Academic Services Page 3Criteria Excellent (5) Good (4) Satisfactory (3) Needs Does not follow Substantial requirements Improvement (2) (1) Organization Introduction Overall Thesis statement Organization is No discernible (5 marks) contains a very organization, is too general limited in clarity organization effective including the No attention and effectiveness Content is attention getter thesis getter No topic randomly placed & thesis statement, is sentences for causing statement clear Paragraphs have confusion for the adequate paragraphs; All body Attention structure though paragraphs do reader paragraphs getter included not focus on one some may be have clear topic main idea Body missing clear sentences and paragraphs topic sentences No transitions are linked by follow the included effective Some topic thesis transitions/ flow sentences are Conclusion is statement and facts not opinions vague and does Conclusion contain an not summarize summarizes the effective Some transitions main ideas main findings structure included and offers an Most Conclusion insight transitions includes new included information The ending is obvious/good summary Writing 1-2 minor errors Style and tone 3-4 major errors 5+ errors in Style and tone (5 marks) in mechanics are in mechanics; mechanics are too informal (style & tone. Evidence of appropriate sometimes including several Several writing grammar, careful 3-4 minor affects grammar errors errors that comprehension that make reading punctuation. proofreading errors in greatly affect spelling. mechanics Style and tone comprehension comprehension capitalization) Eloquent style are mostly difficult Evidence of 8+ major errors Formal appropriate language/tone proofreading although some Avoids language is too slang/cliches informalContents Introduction. History of Virtual Reality Development of Virtual Reality . Pioneering Companies and Individuals Impact of VR on Various Industries . Entertainment and Gaming Education and Training 6 Healthcare . Real Estate and Architecture. Precursor Technologies. Their Influences . Early Forms of Immersive Technology Development of 3D Graphics and Displays. Evolution of Video Game Technology . Science and Technology Influences. Emerging Technologies and the Future of VR 9 Key Works in the Field of VR.. 11 Future Trends. 11 Increased Mobility 11 Enhanced Realism 12 Expanded Applications 13 Social Interactions in VR. 14 Cross-platform Compatibility . 15 Technological Advancements in VR. 16 Major Landmarks in the History of Science 16 Conclusion 17
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


