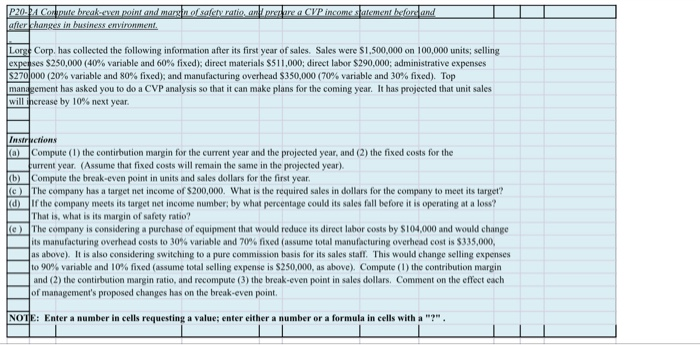
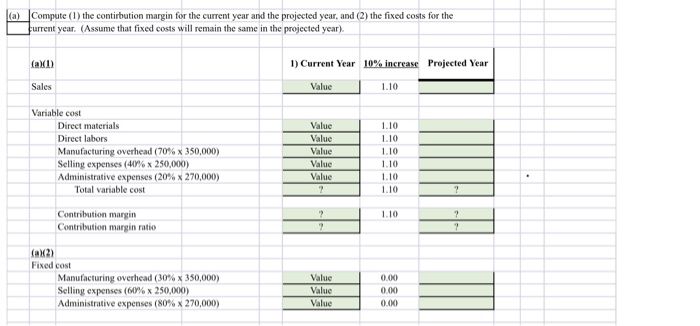
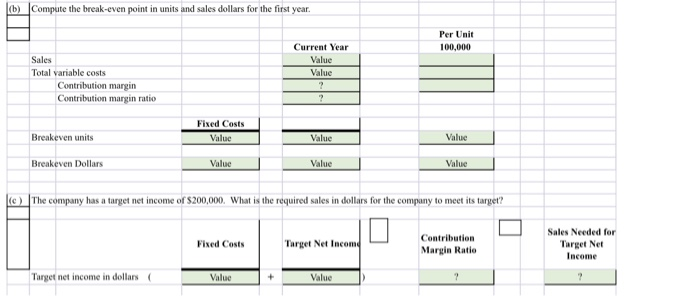
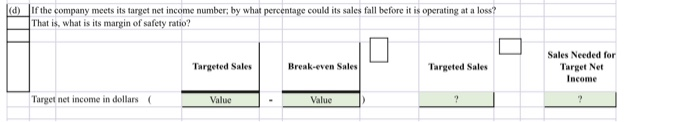
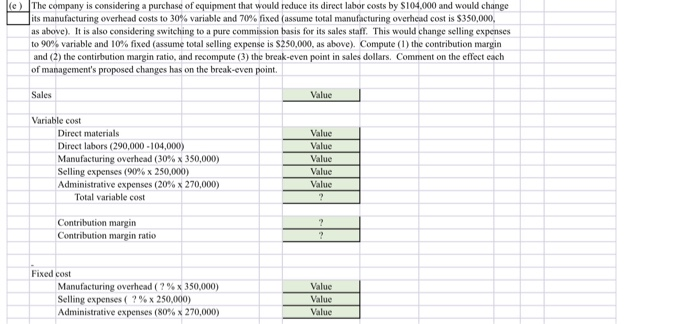
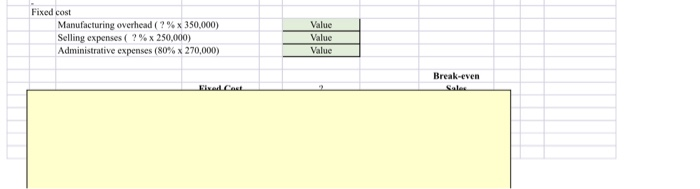
IP20. Corte hakuwen mint and margin of safety ratio, and prepare a CVP income statement before and after hanges in business environment. Long Corp. has collected the following information after its first year of sales. Sales were $1,500,000 on 100,000 units, selling expe ses $250,000 (40% variable and 60% fixed); direct materials S511,000; direct labor $290,000, administrative expenses $270000 (20% variable and 80% fixed), and manufacturing overhead $350,000 (70% variable and 30% fixed). Top management has asked you to do a CVP analysis so that it can make plans for the coming year. It has projected that unit sales will increase by 10% next year. Instructions a) Compute (1) the contirbution margin for the current year and the projected year, and (2) the fixed costs for the urrent year. (Assume that fixed costs will remain the same in the projected year) (b) Compute the break-even point in units and sales dollars for the first year. (c) The company has a target net income of $200,000. What is the required sales in dollars for the company to meet its target? (d) ir the company meets its target net income number, by what percentage could its sales fall before it is operating at a loss? That is what is its margin of safety ratio? @ The company is considering a purchase of equipment that would reduce its direct labor costs by $104,000 and would change its manufacturing overhead costs to 30% variable and 70% fixed (assume total manufacturing overhead cost is $335,000, Jas above). It is also considering switching to a pure commission basis for its sales stall. This would change selling expenses | to 90% variable and 10% fixed (assume total selling expense is $250,000, as above). Compute (1) the contribution margin and (2) the contirbution margin ratio, and recompute (3) the break-even point in sales dollars. Comment on the effect each of management's proposed changes has on the break-even point. NOTE: Enter a number in cells requesting a value; enter either a number or a formula in cells with a "?". La) Compute (1) the contirbution margin for the current year and the projected year, and (2) the fixed costs for the furrent year. (Assume that fixed costs will remain the same in the projected year) (x1) 1) Current Year 10% increase Projected Year Sales Value 1.10 Variable cost Direct materials Direct labors Manufacturing overhead (70% x 350,000) Selling expenses (40% x 250,000) Administrative expenses (20% x 270,000) Total variable cost Value Value Value Value Value 1.10 1.10 1.10 1.10 1.10 1.10 1.10 Contribution margin Contribution margin ratio (X2) Fixed cost Manufacturing overhead (30% x 350,000) Selling expenses (60% x 250,000) Administrative expenses (80% x 270,000) Value Value Value 0.00 0.00 0.0 (b) Compute the break-even point in units and sales dollars for the first year. Per Unit 100.000 Current Year Value Value Sales Total variable costs Contribution margin Contribution margin ratio Fixed Costs Breakeven units Value Value Value Breakeven Dollars Value Value Value c) The company has a target net income of $200,000. What is the required sales in dollars for the company to meet its target? Fixed Costs Target Net Income Contribution Margin Ratio Sales Needed for Target Net Income Target net income in dollars ( Value + Value (d) If the company meets its target net income number, by what percentage could its sales fall before it is operating at a loss? That is, what is its margin of safety ratio? Targeted Sales Break-even Sales Targeted Sales Sales Needed for Target Net Income Target net income in dollars Value - Value le) The company is considering a purchase of equipment that would reduce its direct labor costs by $104,000 and would change its manufacturing overhead costs to 30% variable and 70% fixed assume total manufacturing overhead cost is $350,000, as above). It is also considering switching to a pure commission basis for its sales staff. This would change selling expenses to 90% variable and 10% fixed (assume total selling expense is $250,000, as above). Compute (1) the contribution margin and (2) the contibution margin ratio, and recompute (3) the break-even point in sales dollars. Comment on the effect each of management's proposed changes has on the break-even point. Sales Value Variable cost Direct materials Direct labors (290,000 -104,000) Manufacturing overhead (30% x 350,000) Selling expenses (90% x 250,000) Administrative expenses (20% x 270,000) Total variable cost Value Value Value Value Value Contribution margin Contribution margin ratio Fixed cost Manufacturing overhead (?%x 350,000) Selling expenses (?%x 250,000) Administrative expenses (80% x 270,000) Value Value Value Fixed cost Manufacturing overhead (?%x 350,000) Selling expenses ( ?%x 250,000) Administrative expenses (80% x 270,000) Value Value Value Break-even FilCast