Question: IT - Communications System Technology subject Please help me to solve answers steps of the following red circles questions as below : Section A: Background
IT - Communications System Technology subject
Please help me to solve answers steps of the following red circles questions as below :

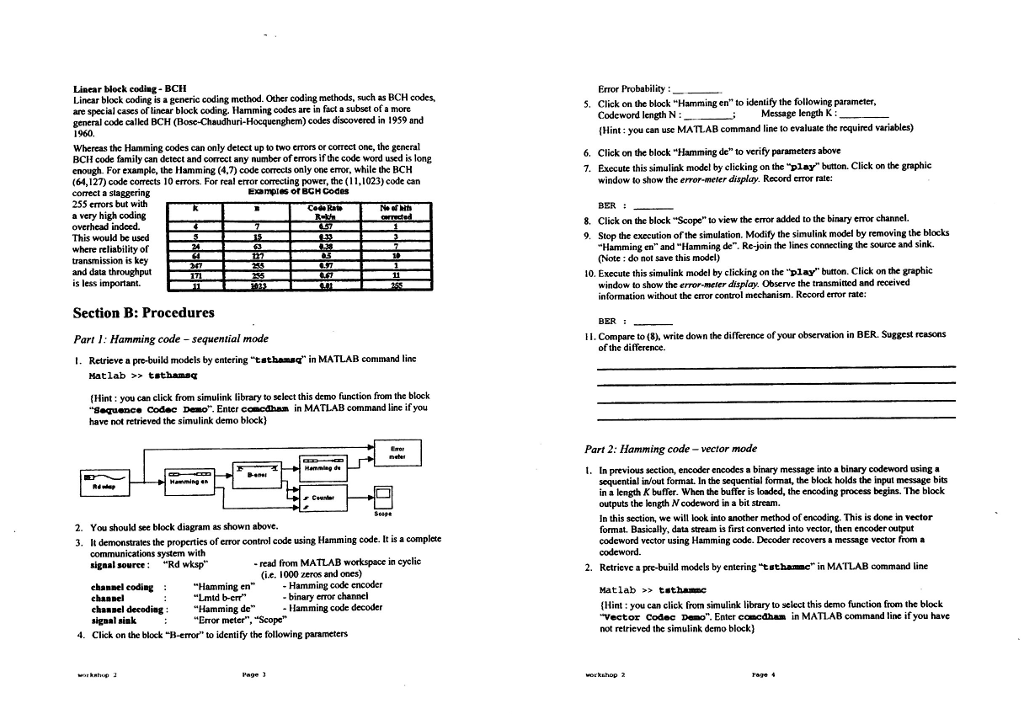

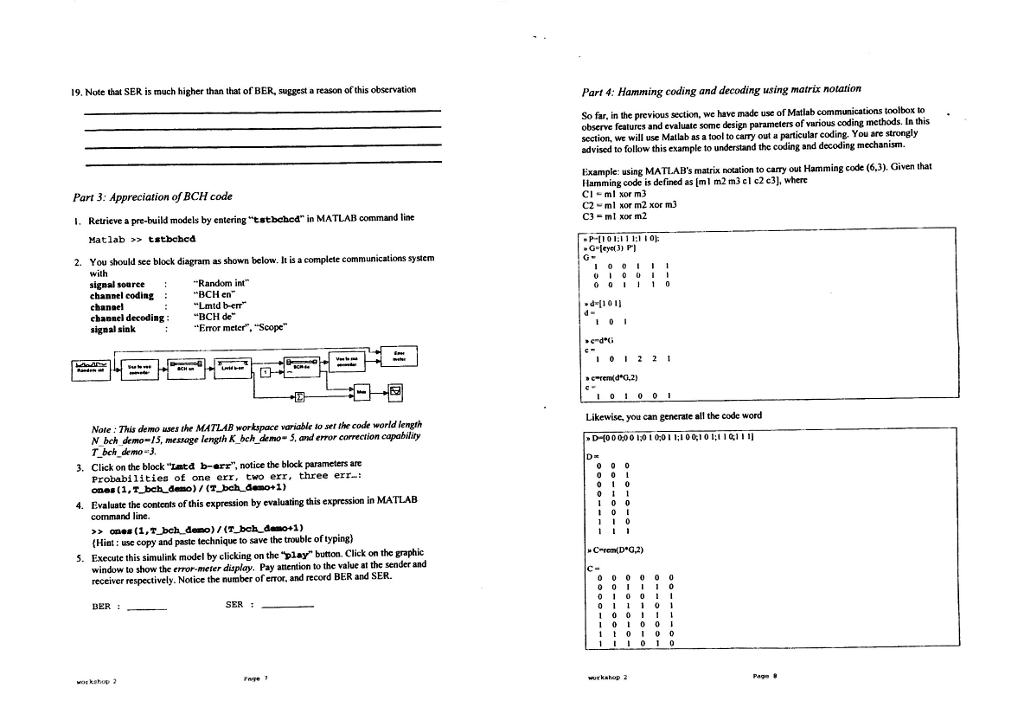


Section A: Background ERROR CODE Error-control coding techniques are used to detect and/or correct errors that occur in the message transmission in a digital communication system. The transmitting side of the error- control coding adds redundant bits or symbols to the original information signal sequence The receiving side of the error-control coding uses these redundant bits or symbols to detect and/or correet the errors that occurred during transmission. The transmission coding process is known as encoding, and the receiving coding process is known as decoding. There are two forms of error control coding: ARQ and FEC. 1. Coding in ARQ When a receiver detects errors in a block of data,it requests that the data block be retransmitted Usually used in computer communication systems since it is relatively inexpensive to implement and there is generally a duplex channel so that the receiving end can transmit back an acknowledgement (ACK) for correctly received data or a request for retransmission (NAC) when the data are received in error Require duplex (half or full duplex) operation There are basically two coding commonly used for ARQ detection . Parity check codes, e Cyclic Redundancy Checks (CRC) 2. Forward error correction (FEC) There are two major classes in FEC: block and convolutional. Here are some of their features:- Transmitted data are encoded so that the receiver can correct as well as detect errors. Used to correct errors on simplex channels where returning of an ACK/NAC indicator is not feasible Preferred on systems with large transmission delays because if ARQ is used, the effective data rate would be small owing to much time spent on waiting the ACK/NAC. In block coding, successive blocks of K information (message) symbols are formed. The coding algorithm then transforms each block into a codeword consisting of N symbols where N>K. This structure is called an (N, K) code. The ratio KM is called the code rate. A key point is that each codeword is formed independently from other codewords. Convolutional codes differ from block codes in that there are no independent codewords. The encoding process can be envisioned as a sliding window, M symbols wide, which moves over the sequence of information symbols in steps of K symbols. M is called the constraint length of the code and K is usually equal to 1. With each step of the sliding window, the encoding process generates N symbols based on the M symbols visible in the window. The code rate is K/N. Hamming Codes A Hamming code is a special case of linear block code. The codeword length N of Hamming code is a fixed number equal to 2"-1, where Mis an integer larger than or equal to 3. M is also the parity check length. The message length of Hamming code is 2"M1.Hamming code is a single error- correction code, which means that only one-bit corrections are possible per codeword. A list of some valid Hamming code parameters (codeword length N, message length K, and parity check length M) is provided in the table below: 12 workshop 2 Page 2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


