It would be helpful to see the methods
public HashMap> getWords()
public void addFromFile(String filename)
and how to store the occurrences in private fields PUNCTUATION, PUNCTUATION_MARKS,
Words, and prevWord.
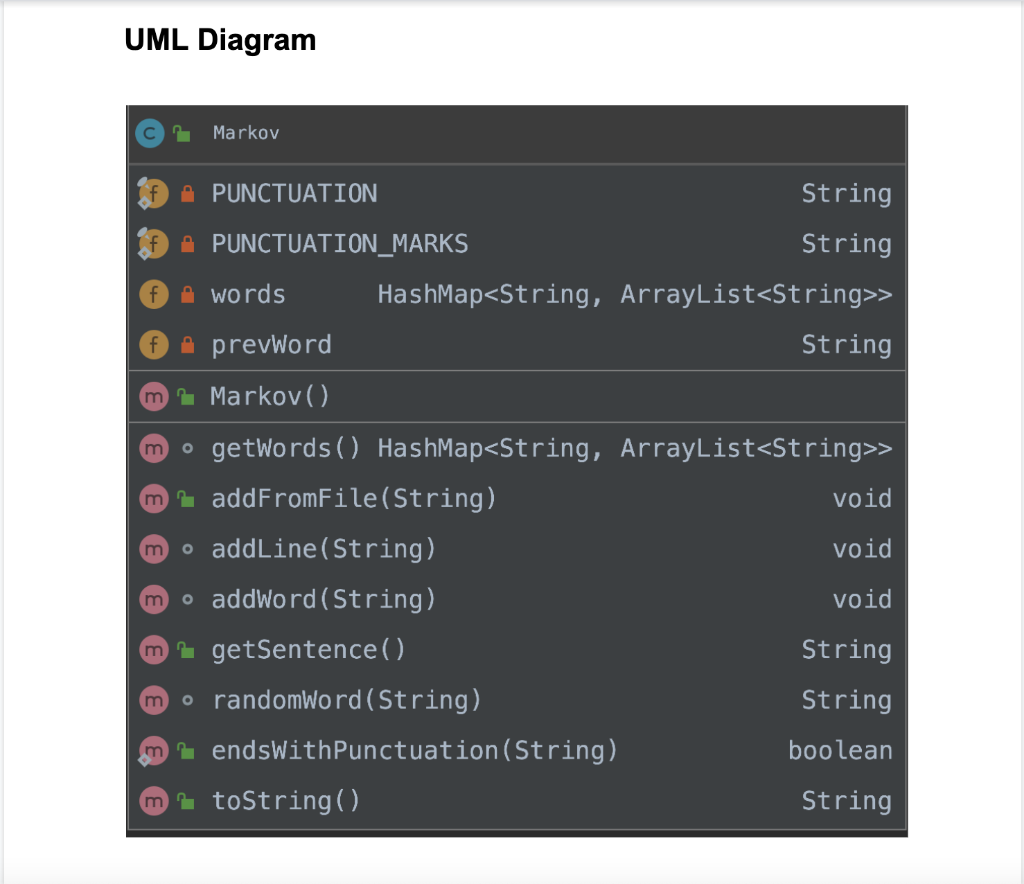



UML Diagram Markov A PUNCTUATION String A PUNCTUATION_MARKS String f words HashMap
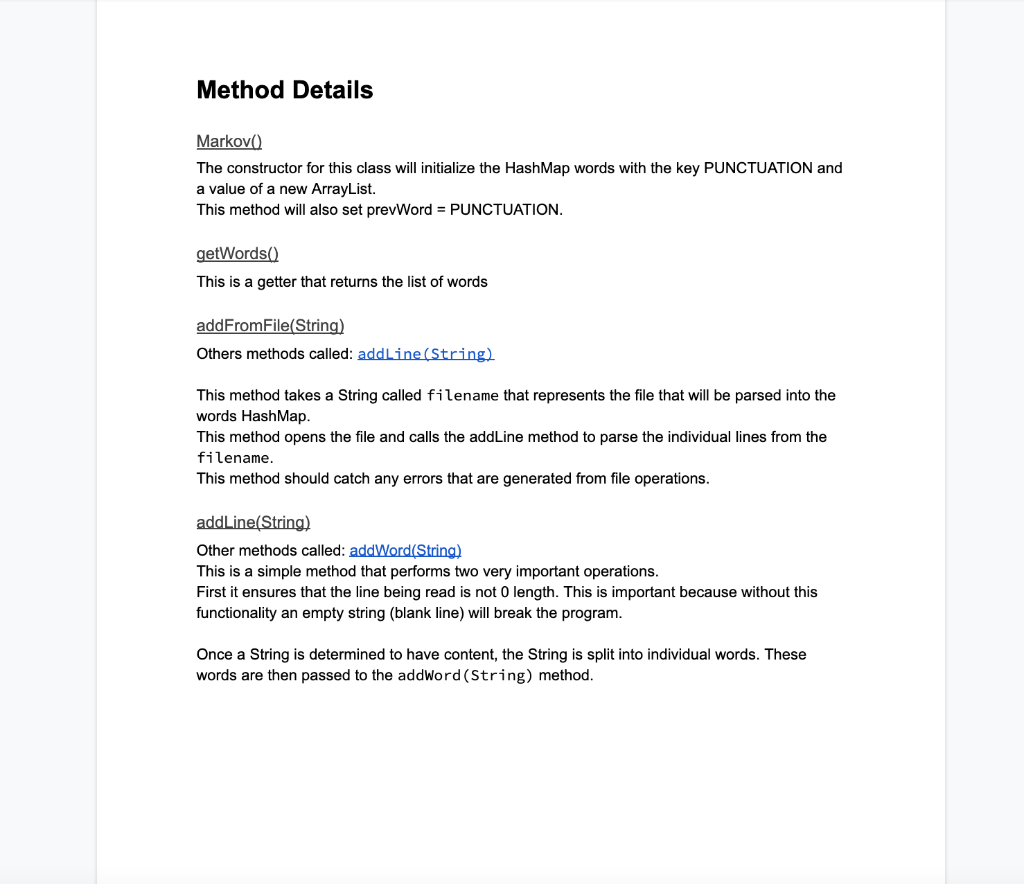
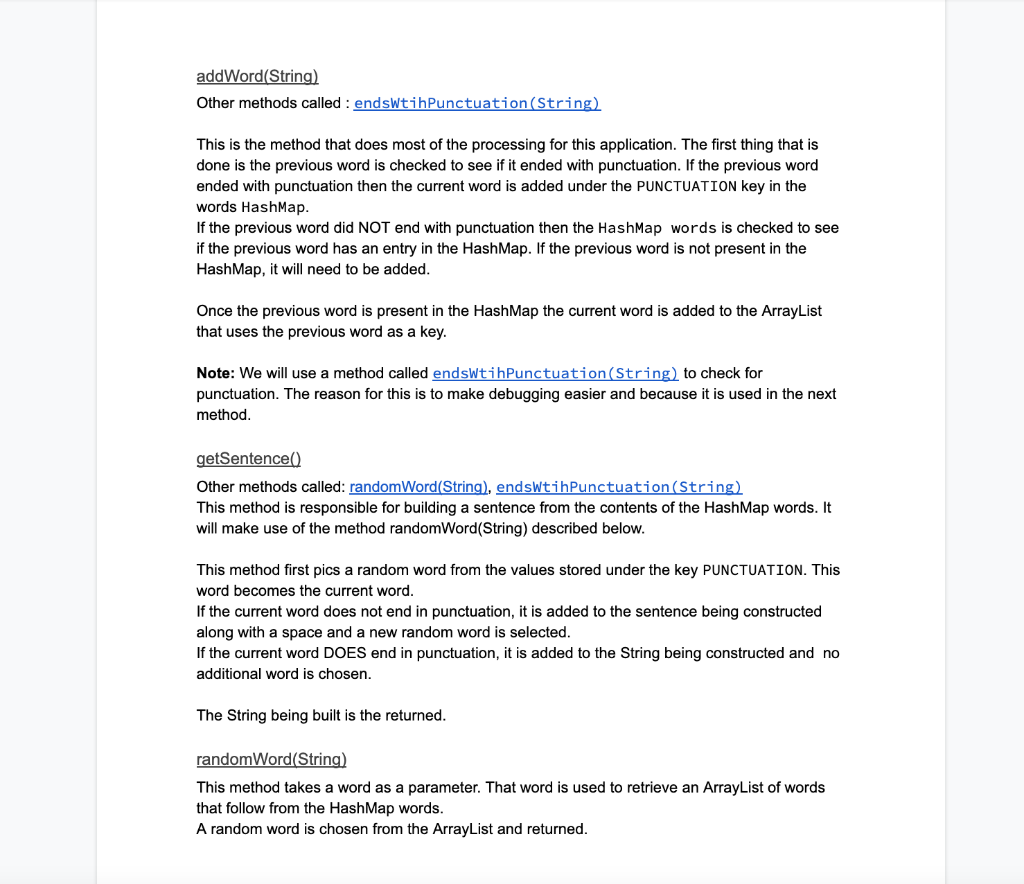
> f. prevword String m 2 Markov() m m o getWords () HashMap> m addFromFile(String) void addLine(String) void o addWord (String) void m 1 getSentence() String o randomword (String) String m endsWithPunctuation (String) boolean m 1 toString() String Field Details Constant Fields PUNCTUATION This field is used as a key to store words that end in punctuation. It is set to "_$" PUNCTUATION_MARKS This is used to store punctuation marks that we will look for in our words. Members HashMap> words This stores a list of all the words found in the text file as the key of the HashMap. The ArrayList is the list of words that directly follow the key. For example given the phrase: It is raining when it is cloudy. Our structure will looks something like the following: __$=[It], It=[is, is], is=[raining, cloudy], raining=[when], cloudy.=[] Another way to visualize this is as a json string: [ "it": {"is", "is"}, "is":{"raining", "cloudy."}, "raining": {"when"}, "When": {"it"}, "cloudy.":{} ] Note: It is important to ensure that ALL words are stored. Storing duplicates is a proxy for frequency. This way when we are selecting a word from our list it will, somewhat, match the frequency of the original document. String prevWord This will store the previous word that had been read from the text file. This is used to determine how to process the current word. If the previous word ended in something from PUNCTUATION_MARKS then this should be set to PUNCTUATION Method Details Markov() The constructor for this class will initialize the HashMap words with the key PUNCTUATION and a value of a new ArrayList. This method will also set prevWord = PUNCTUATION. getWords() This is a getter that returns the list of words addFromFile(String) Others methods called: addLine(String) This method takes a String called filename that represents the file that will be parsed into the words HashMap. This method opens the file and calls the addLine method to parse the individual lines from the filename. This method should catch any errors that are generated from file operations. addLine(String) Other methods called: addWord(String) This is a simple method that performs two very important operations. First it ensures that the line being read is not O length. This is important because without this functionality an empty string (blank line) will break the program. Once a String is determined to have content, the String is split into individual words. These words are then passed to the addWord (String) method. addWord(String) Other methods called : endsWtihPunctuation(String) This is the method that does most of the processing for this application. The first thing that is done is the previous word is checked to see if it ended with punctuation. If the previous word ended with punctuation then the current word is added under the PUNCTUATION key in the words HashMap. If the previous word did NOT end with punctuation then the HashMap words is checked to see if the previous word has an entry in the HashMap. If the previous word is not present in the HashMap, it will need to be added. Once the previous word is present in the HashMap the current word is added to the ArrayList that uses the previous word as a key. Note: We will use a method called endsWtihPunctuation(String) to check for punctuation. The reason for this is to make debugging easier and because it is used in the next method. getSentence() Other methods called: random Word(String), endsWtihPunctuation(String) This method is responsible for building a sentence from the contents of the HashMap words. It will make use of the method random Word(String) described below. This method first pics a random word from the values stored under the key PUNCTUATION. This word becomes the current word. If the current word does not end in punctuation, it is added to the sentence being constructed along with a space and a new random word is selected. If the current word DOES end in punctuation, it is added to the String being constructed and no additional word is chosen. The String being built is the returned. random Word(String) This method takes a word as a parameter. That word is used to retrieve an ArrayList of words that follow from the HashMap words. A random word is chosen from the ArrayList and returned. endsWith Punctuation(String) This method takes a String and checks if the last character of the String exists in PUNCTUATION_MARKS. If the last character does exist in PUNCTUATION_MARKS the method returns true, otherwise it returns false This method should also catch any errors that may occur when checking for punctuation. If an error is caught, print the word that caused the error along with an error message. This is unlikely to occur however, toString() The toString will return the toString of the HashMap words. Sample run 1 Called with spam.txt: spam.txt I like poptarts and 42 and spam. Will I get spam and poptarts for the holidays? I like spam poptarts! Main.java public static void main(String[] args) { Markov markov = new Markov(); markov.add FromFile("spam.txt"); System.out.println(markov); for (int i = 0; i > f. prevword String m 2 Markov() m m o getWords () HashMap> m addFromFile(String) void addLine(String) void o addWord (String) void m 1 getSentence() String o randomword (String) String m endsWithPunctuation (String) boolean m 1 toString() String Field Details Constant Fields PUNCTUATION This field is used as a key to store words that end in punctuation. It is set to "_$" PUNCTUATION_MARKS This is used to store punctuation marks that we will look for in our words. Members HashMap> words This stores a list of all the words found in the text file as the key of the HashMap. The ArrayList is the list of words that directly follow the key. For example given the phrase: It is raining when it is cloudy. Our structure will looks something like the following: __$=[It], It=[is, is], is=[raining, cloudy], raining=[when], cloudy.=[] Another way to visualize this is as a json string: [ "it": {"is", "is"}, "is":{"raining", "cloudy."}, "raining": {"when"}, "When": {"it"}, "cloudy.":{} ] Note: It is important to ensure that ALL words are stored. Storing duplicates is a proxy for frequency. This way when we are selecting a word from our list it will, somewhat, match the frequency of the original document. String prevWord This will store the previous word that had been read from the text file. This is used to determine how to process the current word. If the previous word ended in something from PUNCTUATION_MARKS then this should be set to PUNCTUATION Method Details Markov() The constructor for this class will initialize the HashMap words with the key PUNCTUATION and a value of a new ArrayList. This method will also set prevWord = PUNCTUATION. getWords() This is a getter that returns the list of words addFromFile(String) Others methods called: addLine(String) This method takes a String called filename that represents the file that will be parsed into the words HashMap. This method opens the file and calls the addLine method to parse the individual lines from the filename. This method should catch any errors that are generated from file operations. addLine(String) Other methods called: addWord(String) This is a simple method that performs two very important operations. First it ensures that the line being read is not O length. This is important because without this functionality an empty string (blank line) will break the program. Once a String is determined to have content, the String is split into individual words. These words are then passed to the addWord (String) method. addWord(String) Other methods called : endsWtihPunctuation(String) This is the method that does most of the processing for this application. The first thing that is done is the previous word is checked to see if it ended with punctuation. If the previous word ended with punctuation then the current word is added under the PUNCTUATION key in the words HashMap. If the previous word did NOT end with punctuation then the HashMap words is checked to see if the previous word has an entry in the HashMap. If the previous word is not present in the HashMap, it will need to be added. Once the previous word is present in the HashMap the current word is added to the ArrayList that uses the previous word as a key. Note: We will use a method called endsWtihPunctuation(String) to check for punctuation. The reason for this is to make debugging easier and because it is used in the next method. getSentence() Other methods called: random Word(String), endsWtihPunctuation(String) This method is responsible for building a sentence from the contents of the HashMap words. It will make use of the method random Word(String) described below. This method first pics a random word from the values stored under the key PUNCTUATION. This word becomes the current word. If the current word does not end in punctuation, it is added to the sentence being constructed along with a space and a new random word is selected. If the current word DOES end in punctuation, it is added to the String being constructed and no additional word is chosen. The String being built is the returned. random Word(String) This method takes a word as a parameter. That word is used to retrieve an ArrayList of words that follow from the HashMap words. A random word is chosen from the ArrayList and returned. endsWith Punctuation(String) This method takes a String and checks if the last character of the String exists in PUNCTUATION_MARKS. If the last character does exist in PUNCTUATION_MARKS the method returns true, otherwise it returns false This method should also catch any errors that may occur when checking for punctuation. If an error is caught, print the word that caused the error along with an error message. This is unlikely to occur however, toString() The toString will return the toString of the HashMap words. Sample run 1 Called with spam.txt: spam.txt I like poptarts and 42 and spam. Will I get spam and poptarts for the holidays? I like spam poptarts! Main.java public static void main(String[] args) { Markov markov = new Markov(); markov.add FromFile("spam.txt"); System.out.println(markov); for (int i = 0; i












