I've been struggling to answer this question and wanted to see how it should be solved.
Conduct an energy balance around the Boiler- Digestor-Evaporator to determine the input coal flow (t/h), energy consumption (MW) and the CO2 emissions from the Boiler (t/year)


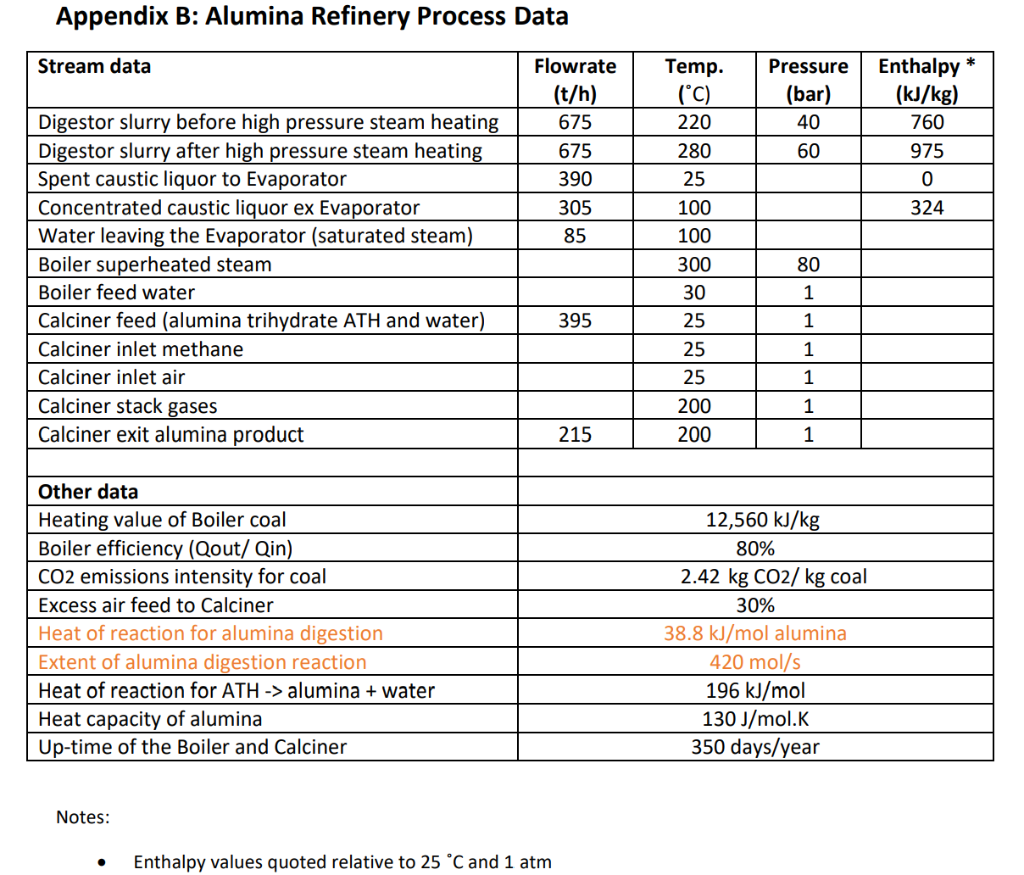
Bauxite Pre-treatment In preparation for digestion, bauxite ore is conveyed from an open stockpile to a series of grinding mills where the bauxite is ground from approx. 10mm particle size to 1mm. Fresh aqueous caustic solution ( NaOH/ water) is mixed with the bauxite in the grinding mills. Digestion The ground bauxite/ caustic mixture from the Pre-treatment unit then enters the Digestion unit. Here, the bauxite/ caustic mixture enters a series of digestion vessels together with the recycled spent caustic liquor coming from the Evaporator unit. In the Digestion vessels, the alumina (Al2O3) in the bauxite ore is fully dissolved in the caustic liquor at high temperature and high pressure (280C and 6,000kPa ) to form sodium aluminate according to the following reaction: Al2O3+2NaOH+3H2O2NaAl(OH)4 To reach this elevated temperature, the bauxite/ caustic slurry is first heated to approx. 200C via heat exchange with low-pressure steam coming from the flash tanks. The bauxite/ caustic slurry is then further heated to approx. 280C via heat exchange with high-pressure steam (approx. 310C ) produced in the on-site coal-fired Boiler. Flashed steam condensate leaves the Digestor and reports to the Mud Washing plant. The high-pressure steam condensate returns to the Boiler. The digested slurry from the Digestors is then cooled to approx. 100C in a series of flash tanks operating at successively lower pressures. As the slurry enters each flash tank, steam flashes off and is transferred back to the Digestion tanks to preheat the bauxite/ caustic slurry. In the final flash tank, the flashed steam is vented to atmosphere (blow-off steam). Clarification The cooled bauxite/ caustic slurry from the Digestion unit enters the Clarification unit. Here, the slurry enters a series of clarifiers or open-top thickening tanks operating at atmospheric pressure. The fine, red mud settles to the bottom of the clarifiers while the liquor containing the dissolved alumina (pregnant liquor) overflows the top of the clarifiers. The pregnant liquor is pumped to a series of filters to remove any remaining solids. The solids removed in the filters join the clarifier underflow and go to the mud washing circuit. Here the solids are washed with fresh process water to remove entrained caustic-alumina solution. The washed mud is then pumped to the waste red mud storage dams. The dirty wash water is recycled Precipitation The filtered, pregnant liquor from the Clarification unit enters the Precipitation unit. Here, the liquor enters a series of agitated, open-top precipitation tanks and crystals of alumina trihydrate (Al2O33H2O) form, according to the following reaction: 2NaAl(OH)4Al2O33H2O+2NaOH The crystals and solution then pass to a series of classifiers where the crystals settle from the solution and separate into three sizes: the primary classifiers collect the coarsest crystals which form the trihydrate product; the secondary and tertiary classifiers collect the fine crystals which return to the precipitators as seed crystal. The spent caustic solution from the precipitation tanks is then sent to the Evaporator. Evaporation The spent caustic solution from the Precipitation unit enters the Evaporator unit. Here, the caustic solution is heated in a steam-fired evaporator to concentrate the caustic solution which is then recycled back to the Digestion tanks. The evaporated water is sent to the mud washing plant. Calcination The coarse ATH crystals from the Precipitation unit are then conveyed to the Calcination unit. Here the crystals are washed with process water and then filtered to remove most of the free water. This water is pumped back to the mud washing plant. The filtered crystals then enter a gas-fired Calciner where the ATH crystals are subjected to extremely high temperatures (approx. 1100C ) to produce alumina, according to the following reaction: Al2O3.3H2OAl2O3+3H2O The fine, dry alumina powder exits the base of the Calciner, and is then cooled and conveyed to an on-site storage shed. The free and bound water exit the Calciner as exhaust gases. Utilities Fresh process water for the Mud Washing plant is pumped to the refinery site from the local Council water treatment plant. Natural gas (methane) for the Calciner is supplied through a gas pipeline from a local supplier. Coal for the Boiler is transported to the site from a local coal mine. High-pressure steam for the Digestor and the Evaporator is produced in an on-site, coal-fired Boiler. The Boiler operates in closed circuit; the steam condensate from the Digestor and Evaporator returns back as feedwater to the Boiler. Annandiv R. Alumina Dafiname Drarace nata Notes: - Enthalpy values quoted relative to 25C and 1 atm Bauxite Pre-treatment In preparation for digestion, bauxite ore is conveyed from an open stockpile to a series of grinding mills where the bauxite is ground from approx. 10mm particle size to 1mm. Fresh aqueous caustic solution ( NaOH/ water) is mixed with the bauxite in the grinding mills. Digestion The ground bauxite/ caustic mixture from the Pre-treatment unit then enters the Digestion unit. Here, the bauxite/ caustic mixture enters a series of digestion vessels together with the recycled spent caustic liquor coming from the Evaporator unit. In the Digestion vessels, the alumina (Al2O3) in the bauxite ore is fully dissolved in the caustic liquor at high temperature and high pressure (280C and 6,000kPa ) to form sodium aluminate according to the following reaction: Al2O3+2NaOH+3H2O2NaAl(OH)4 To reach this elevated temperature, the bauxite/ caustic slurry is first heated to approx. 200C via heat exchange with low-pressure steam coming from the flash tanks. The bauxite/ caustic slurry is then further heated to approx. 280C via heat exchange with high-pressure steam (approx. 310C ) produced in the on-site coal-fired Boiler. Flashed steam condensate leaves the Digestor and reports to the Mud Washing plant. The high-pressure steam condensate returns to the Boiler. The digested slurry from the Digestors is then cooled to approx. 100C in a series of flash tanks operating at successively lower pressures. As the slurry enters each flash tank, steam flashes off and is transferred back to the Digestion tanks to preheat the bauxite/ caustic slurry. In the final flash tank, the flashed steam is vented to atmosphere (blow-off steam). Clarification The cooled bauxite/ caustic slurry from the Digestion unit enters the Clarification unit. Here, the slurry enters a series of clarifiers or open-top thickening tanks operating at atmospheric pressure. The fine, red mud settles to the bottom of the clarifiers while the liquor containing the dissolved alumina (pregnant liquor) overflows the top of the clarifiers. The pregnant liquor is pumped to a series of filters to remove any remaining solids. The solids removed in the filters join the clarifier underflow and go to the mud washing circuit. Here the solids are washed with fresh process water to remove entrained caustic-alumina solution. The washed mud is then pumped to the waste red mud storage dams. The dirty wash water is recycled Precipitation The filtered, pregnant liquor from the Clarification unit enters the Precipitation unit. Here, the liquor enters a series of agitated, open-top precipitation tanks and crystals of alumina trihydrate (Al2O33H2O) form, according to the following reaction: 2NaAl(OH)4Al2O33H2O+2NaOH The crystals and solution then pass to a series of classifiers where the crystals settle from the solution and separate into three sizes: the primary classifiers collect the coarsest crystals which form the trihydrate product; the secondary and tertiary classifiers collect the fine crystals which return to the precipitators as seed crystal. The spent caustic solution from the precipitation tanks is then sent to the Evaporator. Evaporation The spent caustic solution from the Precipitation unit enters the Evaporator unit. Here, the caustic solution is heated in a steam-fired evaporator to concentrate the caustic solution which is then recycled back to the Digestion tanks. The evaporated water is sent to the mud washing plant. Calcination The coarse ATH crystals from the Precipitation unit are then conveyed to the Calcination unit. Here the crystals are washed with process water and then filtered to remove most of the free water. This water is pumped back to the mud washing plant. The filtered crystals then enter a gas-fired Calciner where the ATH crystals are subjected to extremely high temperatures (approx. 1100C ) to produce alumina, according to the following reaction: Al2O3.3H2OAl2O3+3H2O The fine, dry alumina powder exits the base of the Calciner, and is then cooled and conveyed to an on-site storage shed. The free and bound water exit the Calciner as exhaust gases. Utilities Fresh process water for the Mud Washing plant is pumped to the refinery site from the local Council water treatment plant. Natural gas (methane) for the Calciner is supplied through a gas pipeline from a local supplier. Coal for the Boiler is transported to the site from a local coal mine. High-pressure steam for the Digestor and the Evaporator is produced in an on-site, coal-fired Boiler. The Boiler operates in closed circuit; the steam condensate from the Digestor and Evaporator returns back as feedwater to the Boiler. Annandiv R. Alumina Dafiname Drarace nata Notes: - Enthalpy values quoted relative to 25C and 1 atm









