java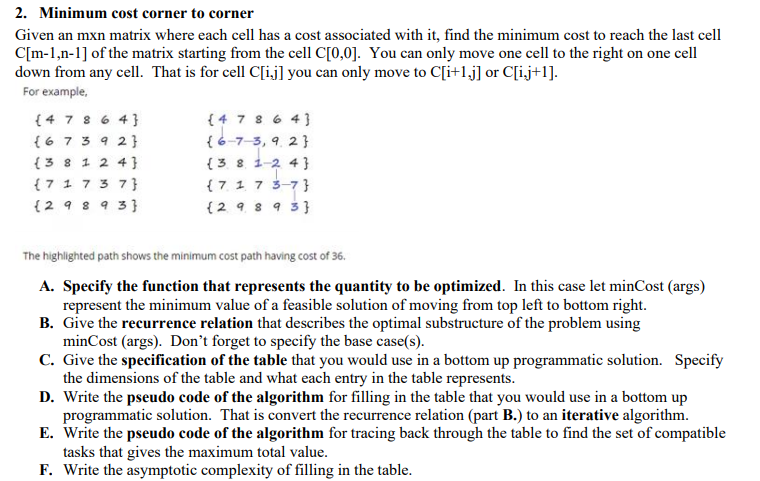
2. Minimum cost corner to corner Given an mxn matrix where each cell has a cost associated with it, find the minimum cost to reach the last cell C[m-1.n-1) of the matrix starting from the cell C[0,0]. You can only move one cell to the right on one cell down from any cell. That is for cell C[i,j] you can only move to C[i+1.j] or C[i,j+1]. For example, { 4 786 43 { 47 864 {6 7 3 9 2} {6-7-3, 9.2 { 3 8 1 2 4] {381-243 {7 1 7 3 73 {71 73-7} {29 89 33 {29893} The highlighted path shows the minimum cost path having cost of 36. A. Specify the function that represents the quantity to be optimized. In this case let minCost (args) represent the minimum value of a feasible solution of moving from top left to bottom right. B. Give the recurrence relation that describes the optimal substructure of the problem using minCost (args). Don't forget to specify the base case(s). C. Give the specification of the table that you would use in a bottom up programmatic solution. Specify the dimensions of the table and what each entry in the table represents. D. Write the pseudo code of the algorithm for filling in the table that you would use in a bottom up programmatic solution. That is convert the recurrence relation (part B.) to an iterative algorithm. E. Write the pseudo code of the algorithm for tracing back through the table to find the set of compatible tasks that gives the maximum total value. F. Write the asymptotic complexity of filling in the table. 2. Minimum cost corner to corner Given an mxn matrix where each cell has a cost associated with it, find the minimum cost to reach the last cell C[m-1.n-1) of the matrix starting from the cell C[0,0]. You can only move one cell to the right on one cell down from any cell. That is for cell C[i,j] you can only move to C[i+1.j] or C[i,j+1]. For example, { 4 786 43 { 47 864 {6 7 3 9 2} {6-7-3, 9.2 { 3 8 1 2 4] {381-243 {7 1 7 3 73 {71 73-7} {29 89 33 {29893} The highlighted path shows the minimum cost path having cost of 36. A. Specify the function that represents the quantity to be optimized. In this case let minCost (args) represent the minimum value of a feasible solution of moving from top left to bottom right. B. Give the recurrence relation that describes the optimal substructure of the problem using minCost (args). Don't forget to specify the base case(s). C. Give the specification of the table that you would use in a bottom up programmatic solution. Specify the dimensions of the table and what each entry in the table represents. D. Write the pseudo code of the algorithm for filling in the table that you would use in a bottom up programmatic solution. That is convert the recurrence relation (part B.) to an iterative algorithm. E. Write the pseudo code of the algorithm for tracing back through the table to find the set of compatible tasks that gives the maximum total value. F. Write the asymptotic complexity of filling in the table







