Question: Java Introduction This assignment will focus on Array Lists, Linked Lists, the List interface, and sets. A set is a collection of elements where duplicates
Java
Introduction
This assignment will focus on Array Lists, Linked Lists, the List interface, and sets. A set is a collection of elements where duplicates are not allowed and elements can appear in any order. Below is a diagram showing two sets, A and B, where each image shows a different set operation performed on A and B. The three operations are subtraction, union, and intersection.
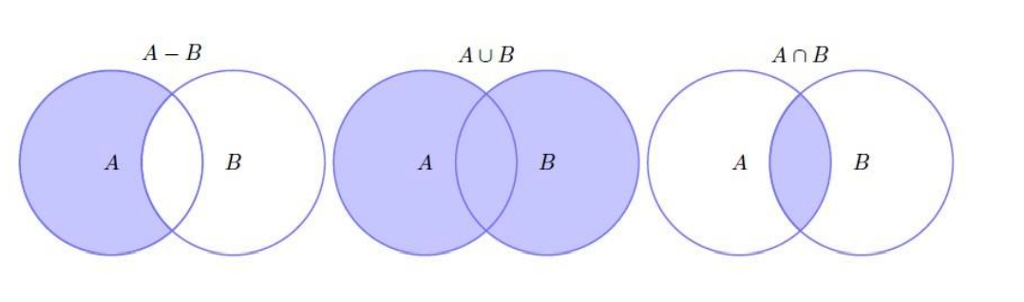
Assume set A and B hold Integers.
Set A = {1,2,3,4}
Set B = {4,5,6}
Subtraction
The left most diagram shows subtraction. The result is everything in set A minus anything in Set B.
A B = {1,2,3}
Union
The middle diagram show union. The result is everything in set A and everything in Set B. Remember, no duplicates are allowed.
A B = {1,2,3,4,5,6}
Intersection
The right most diagram shows intersection. The result is only elements that occurs in both sets.
A B = {4}
Program Specification
For this assignment, we will use Array Lists and Linked Lists that store Integer objects to represent our sets. We will assume that the sets created are well behaved, meaning no duplicates will occur. This means you will not have to check for this. But remember, sets can be still entered out of order.
What you need to do
I have provided a template for the Sets class, which will be a class of nothing but static methods and all parameters will be List objects. This means any class that implements the List interface can be passed to these methods. The methods you will have to write are:
public static boolean isElement(i , list)
o Search the passed in list for the passed in Integer i. If the Integer occurs in the list, return true, else return false.
Public static boolean isSubSet(list1, list2)
o Determine is list1 is a subset of list2 (list1 list2). For list1 to be a subset of list2, all elements that occur in list1 must occur in list2.
list1 = { 1 , 5 , 9 }
list2 = { 1 , 4 , 5 , 15 , 9 , 8 }
list1 is a subset of list2 because all of its elements occur in list2.
list1 = { 1 , 5 , 9 }
list2 = { 1 , 4 , 5 , 15 , 8 }
list1 is not a subset of list2 because 9 does not occur in list2.
public static boolean isSuperSet(list1, list2)
o Determine if list1 is a super set of list2 (list1 list2). For list1 to be a super set of list2, all elements in list2 must occur in list1.
list1 = { 1 , 4 , 5 , 15 , 9 , 8 }
list2 = { 1 , 5 , 9 }
list1 is a super set of list2 because all of list2s elements occur in list1.
list1 = { 1 , 4 , 15 , 9 , 8 }
list2 = { 1 , 5 , 9 }
list1 is not a superset because 5 occurs in list2 but not in list1.
public static List subtract(list1, list2)
o Perform the subtraction of the two lists as described above.
o Returns the result as a new List object in increasing sorted order.
public static List union(list1 , list2)
o Perform the union of the two lists as described above.
o Returns the result as a new List object in increasing sorted order.
public static List intersection(list1, list2)
o Perform the intersection of the two lists described above.
o Returns the result as a new List object in increasing sorted order.
Public static boolean equals(list1, list2)
o Determine if two sets are equal by checking if all elements in list1 occur in list2, and all elements in list2 occur in list1.
o Do not confuse this with the equals method of the Object class. This is not related an we are not overriding anything. Notice the parameters.
list1 = { 5 , 1 , 9 }
list2 = { 1 , 5 , 9 }
list1 and list2 are equal since both share the exact same elements.
public static List cartesianProduct(list1, list2)
o Perform the cartesian product of two lists. The cartesian product is creating all pairs between all elements in list1 and list2. The first element in each pair will be from list1.
list1 = { 1 , 4 }
list2 = { 2 , -6 , 4}
result = { (1,-6) , (1,2) , (1,4) , (4-6) , (4,2) , (4,4) }
o Before performing the Cartesian Prodcut, make sure each list is sorted.
o Include duplicate elements from opposite set. In the example, 4 occurs twice.
o Notice this method returns a List. Since Java does not support Tuples, we will mimic a pair by converting the pair of Integers to a String. The format is
"(,)"
Public static void sort(list)
o Sort the passed in list from smallest to largest values. You may use any sorting technique you wish.
o This method does not return anything, so the list passed in gets sorted.
---------------------------
Code Provided
Sets Class
import java.util.List;
public class Sets {
/**
* Check if passed in Integer is part of passed in List.
*
* @param i
* @param list
* @return booelan
*/
public static boolean isElement(Integer i, List list) {
//TODO
}
/**
* Check if list1 is a subset of list2.
* Subset means all elements in list1 must be in list2.
* If so return true, else return false.
*
* @param list1
* @param list2
* @return boolean
*/
public static boolean isSubset(List list1, List list2) {
//TODO
}
/**
* Check if list1 is a super set of list2.
* Super set means all elements in list2 must be in list1.
* Return true if so, false otherwise.
*
* @param list1
* @param list2
* @return boolean
*/
public static boolean isSuperSet(List list1, List list2) {
//TODO
}
/**
* Perform the union of list1 and list2.
* Union means take all elements from each List and combine them into one List.
* If duplicate elements, only include one of the element.
* For example, if 3 occurred in both Lists, the resulting List will only contain one 3.
* This method will return a new combined List that is sorted from smallest to largest.
*
* @param list1
* @param list2
* @return list
*/
public static List union(List list1, List list2){
//TODO
}
/**
* Perform intersection of list1 and list2.
* Intersection means to only include an element if it is in both Lists.
* This method will return a new interesected List that is sorted from smallest to largest.
*
* @param list1
* @param list2
* @return list
*/
public static List intersection(List list1,List list2){
//TODO
}
/**
* Perform subtract of sets. list1 - list2.
* The result will be a List that contains all elements in list1 minus any elements that also occur in list2.
* This method will return a new subtracted List that is sorted from smallest to largest.
*
* @param list1
* @param list2
* @return
*/
public static List subtract(List list1, List list2){
//TODO
}
/**
* Two lists are equal if all the elements in list1 occur in list2, and all elements in list2 occur in list1.
* Order does matter here.
*
* @param list1
* @param list2
* @return boolean
*/
public static boolean equals(List list1, List list2) {
//TODO
}
/**
* Perform the cartesian product of two lists.
* This method will store the result as a List that holds strings since Java does not allow Tuples.
* Both lists must be sorted before performing the cartesian product.
* Elements in list1 should be the first element in each product.
* If the either list is empty, return a empty List.
*
* See handout for example.
*
* @param list1
* @param list2
* @return list
*/
public static List cartesianProduct(List list1, List list2){
//TODO
}
/**
* Sort the list passed in from smallest to the larget.
* Notice, there is no return type, so this sorts the List in place.
*
* @param list
*/
public static void sort(List list) {
//TODO
}
}
-----------------------
JUnit Class




AUB An B AUB An B
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


