Question
* Java Only * This is for CS101 class. If you answer the questions accordingly, I would be glad. Thank you in advance. Introduction As
* Java Only *
This is for CS101 class. If you answer the questions accordingly, I would be glad. Thank you in advance.
Introduction
As programs get longer, managing them becomes increasingly difficult. That's where methods come in handy. In essence, a method is just a named collection of statements. Once declared, a method can be invoked any number of times. This lab will give you practice creating and using (static) methods.
Documenting your code

You can do this assignment in a single project within your lab06 workspace.
- print a table that shows the "raw" calculations for the Taylor series expansion of sin(x), where x is read from the user. Your table should have columns for the term number n, and for (-1)^n, x^(2n+1), (2n+1)!, the term itself computed from these values, and the sum of the preceding terms with this one, i.e. the current approximation to sin(x). The term number n should go from 0 up to, say, 10.
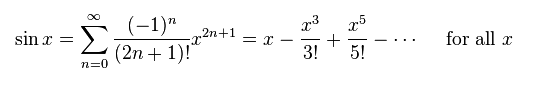
- obviously computing sin(x) like this results in significant errors and is very inefficient! A better approach is to compute each term from the previous one (hint: think how can you compute x^5/5! from x^3/3! ). Implement sin(x) as a method using this approach and test it by comparing its answers with those from Math.sin(x).
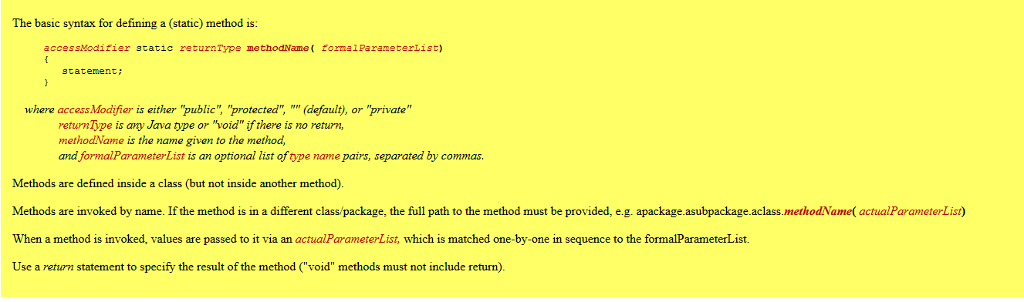
The basic syntax for defining a (static) method is: accessModifier static returnType methodName( formalParameterList) gtatement where access.Modifier is either "public" "protected", "" (default), or "private" returnTipe is ary Java type or "void" if there is no return, methodName is the name given to the method, and formalParameterList is an optional list of ope name pairs, separated by commas Methods are defined inside a class (but not inside another method) Methods are invoked by name. If the method is in a different class/package, the full path to the method must be provided, e.g. apackage.asubpackage.aclass.methodNamel actualParameterList) When a method is invoked, values are passed to it via an actualParameterList, which is matched one-by-one in sequence to the formalParameterList. Use a return statement to specify the result of the method ("void" methods must not include return)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


