Question
Java Program Help: Airport Queue Simulation Write a program for a queuing simulation for a small airport which only has one runway. Need help using
Java Program Help: Airport Queue Simulation
Write a program for a queuing simulation for a small airport which only has one runway. Need help using and creating the Java Queue Interface that is implemented using the Java Linked List. I have included the remaining requirements with the attached pictures.


/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
A driver that demonstrates the class WaitLine.
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
public class Driver {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WaitLine customerLine = new WaitLine();
// int duration, double arrivalProbability,int maxTransactionTime
customerLine.simulate(480, 0.01, 4);
// customerLine.simulate(20, 0.5, 5);
customerLine.displayResults();
System.out.println(" Done.");
} // end main
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
public class WaitLine {
private QueueInterface line;
private int numberOfArrivals;
private int numberServed;
private int totalTimeWaited;
public WaitLine() {
line = new LinkedBlockingQueue();
reset();
} // end default constructor
/**
* Simulates a waiting line with one serving agent.
*
* @param duration
* The number of simulated minutes
* @param arrivalProbability
* A real number between 0 and 1, and the probability that a customer
* arrives at a given time
* @param maxTransactionTime
* the longest transaction time for a customer
*/
public void simulate(int duration, double arrivalProbability, int maxTransactionTime) {
int transactionTimeLeft = 0;
for (int clock = 0; clock
if (Math.random()
numberOfArrivals++; // Random.nextInt(maxTransactionTime) + 1
int transactionTime = (int) (Math.random() * maxTransactionTime + 1);
Customer nextArrival = new Customer(clock, transactionTime, numberOfArrivals);
line.enqueue(nextArrival);
System.out.println("Customer " + numberOfArrivals + " enters line at time " + clock
+ ". Transaction time is " + transactionTime);
} // end if
if (transactionTimeLeft > 0)
transactionTimeLeft--;
else if (!line.isEmpty()) {
Customer nextCustomer = line.dequeue();
transactionTimeLeft = nextCustomer.getTransactionTime() - 1;
int timeWaited = clock - nextCustomer.getArrivalTime();
totalTimeWaited = totalTimeWaited + timeWaited;
numberServed++;
System.out.println("Customer " + nextCustomer.getCustomerNumber() + " begins service at time " + clock
+ ". Time waited is " + timeWaited);
} // end if
} // end for
} // end simulate
/** Displays summary results of the simulation. */
public void displayResults() {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Number served = " + numberServed);
System.out.println("Total time waited = " + totalTimeWaited);
double averageTimeWaited = ((double) totalTimeWaited) / numberServed;
System.out.println("Average time waited = " + averageTimeWaited);
int leftInLine = numberOfArrivals - numberServed;
System.out.println("Number left in line = " + leftInLine);
} // end displayResults
/** Initializes the simulation. */
public final void reset() {
line.clear();
numberOfArrivals = 0;
numberServed = 0;
totalTimeWaited = 0;
} // end reset
} // end WaitLine
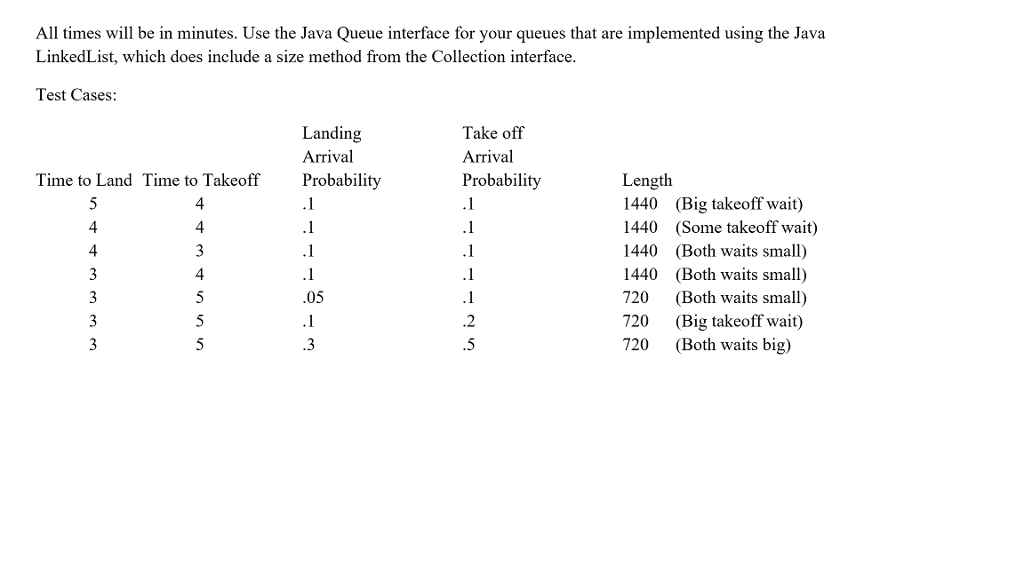
Write a queuing simulation for a small airport which has only one runway. Airplanes waiting to take off join a queue on the ground. Airplanes waiting to land join a queue in the air. Only one plane can be on the runway at a time. All planes in the air must land before any plane can take off. The amount of time to land a plane is constant. The amount of time for a plane to takeoff is also constant, not necessarily the same time as a landing. The algorithm on the back of this page and the class WaitLine which was emailed to you are a good start point for the algorithm Parameters Time to land a plane Time for takeoff Arrival rate for planes landing Arrival rate for planes taking off Length of time to be simulated. Output: Number of planes landed Number of plane that took off Average time a plane waited to take off Average time a plane waited to land Number of planes still waiting to take off Number of planes still waiting to land Write a queuing simulation for a small airport which has only one runway. Airplanes waiting to take off join a queue on the ground. Airplanes waiting to land join a queue in the air. Only one plane can be on the runway at a time. All planes in the air must land before any plane can take off. The amount of time to land a plane is constant. The amount of time for a plane to takeoff is also constant, not necessarily the same time as a landing. The algorithm on the back of this page and the class WaitLine which was emailed to you are a good start point for the algorithm Parameters Time to land a plane Time for takeoff Arrival rate for planes landing Arrival rate for planes taking off Length of time to be simulated. Output: Number of planes landed Number of plane that took off Average time a plane waited to take off Average time a plane waited to land Number of planes still waiting to take off Number of planes still waiting to landStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


