Question
Java. This is Dijkstra's algorithm problem in JAVA. I will type out the code below and post the question just so you will not get
Java. This is Dijkstra's algorithm problem in JAVA. I will type out the code below and post the question just so you will not get confused. Please help me, Im beyond stuck on this The class is already created and I just have to complete the methods with "TODO" comment on them, Please help. There is a psuedocode and hint, I'm not sure if you will need them. This is the link of the drive with all packages but the code I need to work on is below and also in the drive incase. Please help
https://drive.google.com/file/d/15mVL5ud8XHF_L1lQhmd7zfXBomQnO5pq/view?usp=sharing


Code:
package lib280.graph;
//import java.io.File;
//import java.io.IOException;
//import java.util.Scanner;
import lib280.base.Pair280;
import lib280.exception.InvalidArgument280Exception;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class NonNegativeWeightedGraphAdjListRep280 extends
WeightedGraphAdjListRep280 {
public NonNegativeWeightedGraphAdjListRep280(int cap, boolean d,
String vertexTypeName) {
super(cap, d, vertexTypeName);
}
public NonNegativeWeightedGraphAdjListRep280(int cap, boolean d) {
super(cap, d);
}
/**
* Replaces the current graph with a graph read from a data file.
*
* File format is a sequence of integers. The first integer is the total
* number of nodes which will be numbered between 1 and n.
*
* Remaining integers are treated as ordered pairs of (source, destination)
* indicies defining graph edges.
*
* @param fileName
* Name of the file from which to read the graph.
* @precond The weights on the edges in the data file fileName are non negative.
* @throws RuntimeException
* if the file format is incorrect, or an edge appears more than
* once in the input.
*/
@Override
public void setEdgeWeight(V v1, V v2, double weight) {
// Overriding this method to throw an exception if a weight is negative will cause
// super.initGraphFromFile to throw an exception when it tries to set a weight to
// something negative.
// Verify that the weight is non-negative
if(weight
// If it is, then just set the edge weight using the superclass method.
super.setEdgeWeight(v1, v2, weight);
}
@Override
public void setEdgeWeight(int srcIdx, int dstIdx, double weight) {
// Get the vetex objects associated with each index and pass off to the
// version of setEdgeWEight that accepts vertex objects.
this.setEdgeWeight(this.vertex(srcIdx), this.vertex(dstIdx), weight);
}
/**
* Implementation of Dijkstra's algorithm.
* @param startVertex Start vertex for the single-source shortest paths.
* @return An array of size G.numVertices()+1 in which offset k contains the shortest
* path from startVertex to k. Offset 0 is unused since vertex indices start
* at 1.
*/
public Pair280 shortestPathDijkstra(int startVertex) {
// TODO Implement this method
// Remove this return statement when you're ready -- it's a placeholder to prevent a compiler error.
return new Pair280(null, null);
}
// Given a predecessors array output from this.shortestPathDijkatra, return a string
// that represents a path from the start node to the given destination vertex 'destVertex'.
private static String extractPath(int[] predecessors, int destVertex) {
// TODO Implement this method
return ""; // Remove this when you're ready -- this is a placeholder to prevent a compiler error.
}
// Regression Test
public static void main(String args[]) {
NonNegativeWeightedGraphAdjListRep280 G = new NonNegativeWeightedGraphAdjListRep280(1, false);
if( args.length == 0)
G.initGraphFromFile("lib280-asn8/src/lib280/graph/weightedtestgraph.gra");
else
G.initGraphFromFile(args[0]);
System.out.println("Enter the number of the start vertex: ");
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int startVertex;
try {
startVertex = in.nextInt();
}
catch(InputMismatchException e) {
in.close();
System.out.println("That's not an integer!");
return;
}
if( startVertex G.numVertices() ) {
in.close();
System.out.println("That's not a valid vertex number for this graph.");
return;
}
in.close();
Pair280 dijkstraResult = G.shortestPathDijkstra(startVertex);
double[] finalDistances = dijkstraResult.firstItem();
//double correctDistances[] = {-1, 0.0, 1.0, 3.0, 23.0, 7.0, 16.0, 42.0, 31.0, 36.0};
int[] predecessors = dijkstraResult.secondItem();
for(int i=1; i
System.out.println("The length of the shortest path from vertex " + startVertex + " to vertex " + i + " is: " + finalDistances[i]);
// if( correctDistances[i] != finalDistances[i] )
// System.out.println("Length of path from to vertex " + i + " is incorrect; should be " + correctDistances[i] + ".");
// else {
System.out.println(extractPath(predecessors, i));
// }
}
}
}
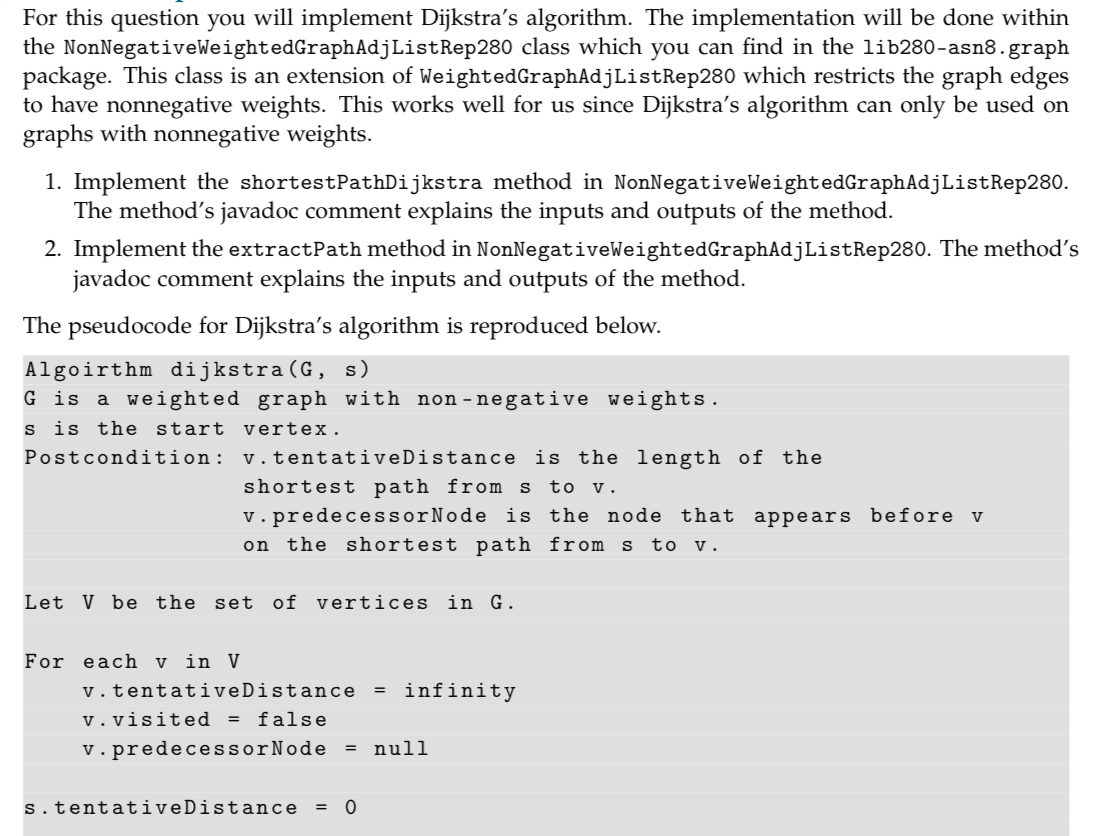
For this question you will implement Dijkstra's algorithm. The implementation will be done within the NonNegativeWeightedGraphAdjListRep280 class which you can find in the lib280-asn8.graph package. This class is an extension of WeightedGraphAdjListRep280 which restricts the graph edges to have nonnegative weights. This works well for us since Dijkstra's algorithm can only be used on graphs with nonnegative weights 1. Implement the shortestPathDijkstra method in NonNegativeWeightedGraphAdjListRep280. The method's javadoc comment explains the inputs and outputs of the method 2. Implement the extractPath method in NonNegativeWeightedGraphAdjListRep280. The method's javadoc comment explains the inputs and outputs of the method The pseudocode for Dijkstra's algorithm is reproduced below. Algoirthm dijkstra (G, s) G is a weighted graph with non-negative weights s is the start vertex. Postcondition: v.tentativeDistance is the length of the shortest path from s to v v.predecessorNode is the node that appears before v on the shortest path from s to v Let V be the set of vertices in G or each V in V v.tentativeDistance = infinity v.visited-false v.predecessorNode - nul s.tentativeDistance0 For this question you will implement Dijkstra's algorithm. The implementation will be done within the NonNegativeWeightedGraphAdjListRep280 class which you can find in the lib280-asn8.graph package. This class is an extension of WeightedGraphAdjListRep280 which restricts the graph edges to have nonnegative weights. This works well for us since Dijkstra's algorithm can only be used on graphs with nonnegative weights 1. Implement the shortestPathDijkstra method in NonNegativeWeightedGraphAdjListRep280. The method's javadoc comment explains the inputs and outputs of the method 2. Implement the extractPath method in NonNegativeWeightedGraphAdjListRep280. The method's javadoc comment explains the inputs and outputs of the method The pseudocode for Dijkstra's algorithm is reproduced below. Algoirthm dijkstra (G, s) G is a weighted graph with non-negative weights s is the start vertex. Postcondition: v.tentativeDistance is the length of the shortest path from s to v v.predecessorNode is the node that appears before v on the shortest path from s to v Let V be the set of vertices in G or each V in V v.tentativeDistance = infinity v.visited-false v.predecessorNode - nul s.tentativeDistance0Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


