Question
Java WeightedGraph: package ch10.graphs; import ch04.queues.*; public class WeightedGraph implements WeightedGraphInterface { public static final int NULL_EDGE = 0; private static final int DEFCAP =
Java
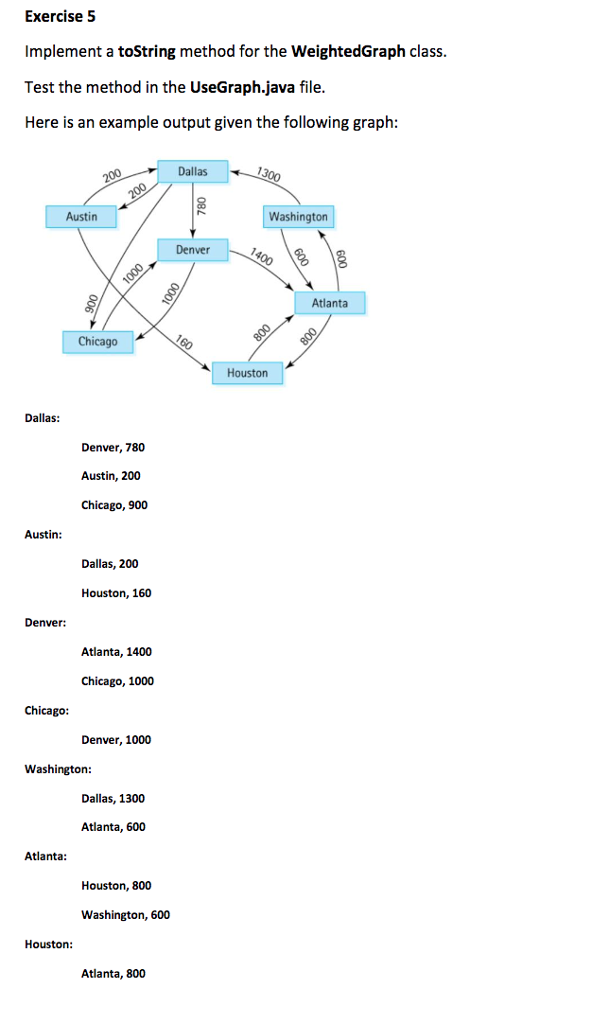
WeightedGraph:
package ch10.graphs;
import ch04.queues.*;
public class WeightedGraph
public WeightedGraph() // Instantiates a graph with capacity DEFCAP vertices. { numVertices = 0; maxVertices = DEFCAP; vertices = (T[]) new Object[DEFCAP]; marks = new boolean[DEFCAP]; edges = new int[DEFCAP][DEFCAP]; } public WeightedGraph(int maxV) // Instantiates a graph with capacity maxV. { numVertices = 0; maxVertices = maxV; vertices = (T[]) new Object[maxV]; marks = new boolean[maxV]; edges = new int[maxV][maxV]; }
public boolean isEmpty() // Returns true if this graph is empty; otherwise, returns false. { }
public boolean isFull() // Returns true if this graph is full; otherwise, returns false. { }
public void addVertex(T vertex) // Preconditions: This graph is not full. // vertex is not already in this graph. // vertex is not null. // // Adds vertex to this graph. { vertices[numVertices] = vertex; for (int index = 0; index
public boolean hasVertex(T vertex) // Returns true if this graph contains vertex; otherwise, returns false. { } private int indexIs(T vertex) // Returns the index of vertex in vertices. { int index = 0; while (!vertex.equals(vertices[index])) index++; return index; }
public void addEdge(T fromVertex, T toVertex, int weight) // Adds an edge with the specified weight from fromVertex to toVertex. { int row; int column; row = indexIs(fromVertex); column = indexIs(toVertex); edges[row][column] = weight; }
public int weightIs(T fromVertex, T toVertex) // If edge from fromVertex to toVertex exists, returns the weight of edge; // otherwise, returns a special null-edge value. { int row; int column; row = indexIs(fromVertex); column = indexIs(toVertex); return edges[row][column]; }
public QueueInterface public void clearMarks() // Unmarks all vertices. { } public void markVertex(T vertex) // Marks vertex. { } public boolean isMarked(T vertex) // Returns true if vertex is marked; otherwise, returns false. { } public T getUnmarked() // Returns an unmarked vertex if any exist; otherwise, returns null. { } public boolean edgeExists(T vertex1, T vertex2) // Preconditions: vertex1 and vertex2 are in the set of vertices // // Return value = (vertex1, vertex2) is in the set of edges { return (edges[indexIs(vertex1)][indexIs(vertex2)] != NULL_EDGE); } public boolean removeEdge(T vertex1, T vertex2) // Preconditions: vertex1 and vertex2 are in the set of vertices // // Return value = true if edge was in the graph (and has been removed) // = false if edge was not in the graph { boolean existed = edgeExists(vertex1, vertex2); edges[indexIs(vertex1)][indexIs(vertex2)] = NULL_EDGE; return existed; } } UseGraph.java: package ch10.apps; import ch04.queues.*; import ch02.stacks.*; import ch10.graphs.*; import ch09.priorityQueues.*; import support.Flight; public class UseGraph { private static void shortestPaths(WeightedGraphInterface PriQueueInterface System.out.println("Last Vertex Destination Distance"); System.out.println("------------------------------------"); do { flight = pq.dequeue(); if (!graph.isMarked(flight.getToVertex())) { graph.markVertex(flight.getToVertex()); System.out.println(flight); flight.setFromVertex(flight.getToVertex()); minDistance = flight.getDistance(); vertexQueue = graph.getToVertices(flight.getFromVertex()); while (!vertexQueue.isEmpty()) { vertex = vertexQueue.dequeue(); if (!graph.isMarked(vertex)) { newDistance = minDistance + graph.weightIs(flight.getFromVertex(), vertex); saveFlight = new Flight(flight.getFromVertex(), vertex, newDistance); pq.enqueue(saveFlight); } } } } while (!pq.isEmpty()); System.out.println(); System.out.println("The unreachable vertices are:"); vertex = graph.getUnmarked(); while (vertex != null) { System.out.println(vertex); graph.markVertex(vertex); vertex = graph.getUnmarked(); } System.out.println(); } private static boolean isPathDF(WeightedGraphInterface private static boolean isPathBF(WeightedGraphInterface // Returns true if a path exists on graph, from startVertex to endVertex; // otherwise returns false. Uses breadth-first search algorithm. { QueueInterface graph.clearMarks(); graph.markVertex(startVertex); queue.enqueue(startVertex); do { currVertex = queue.dequeue(); System.out.println(currVertex); if (currVertex.equals(endVertex)) found = true; else { vertexQueue = graph.getToVertices(currVertex); while (!vertexQueue.isEmpty()) { adjVertex = vertexQueue.dequeue(); if (!graph.isMarked(adjVertex)) { graph.markVertex(adjVertex); queue.enqueue(adjVertex); } } } } while (!queue.isEmpty() && !found); return found; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create and analyze grph in Figure 10.3 System.out.println("Creating graph in figure 10.3"); WeightedGraphInterface graph.addVertex(s0); graph.addVertex(s1); graph.addVertex(s2); graph.addVertex(s3); graph.addVertex(s4); graph.addVertex(s5); graph.addVertex(s6); graph.addEdge(s0, s5, 800); graph.addEdge(s0, s6, 600); graph.addEdge(s1, s3, 200); graph.addEdge(s1, s5, 160); graph.addEdge(s2, s4, 1000); graph.addEdge(s3, s1, 200); graph.addEdge(s3, s2, 900); graph.addEdge(s3, s4, 780); graph.addEdge(s4, s0, 1400); graph.addEdge(s4, s2, 1000); graph.addEdge(s5, s0, 800); graph.addEdge(s6, s0, 600); graph.addEdge(s6, s3, 1300); boolean result; System.out.println("Determining path using depth first ..."); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s1 + " to " + s2); result = isPathDF(graph, s1, s2); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s1 + " to " + s6); result = isPathDF(graph, s1, s6); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s3 + " to " + s1); result = isPathDF(graph, s3, s1); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s0 + " to " + s4); result = isPathDF(graph, s0, s4); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s6 + " to " + s3); result = isPathDF(graph, s6, s3); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s6 + " to " + s1); result = isPathDF(graph, s6, s1); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(); System.out.println("Determining path using breadth first ..."); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s1 + " to " + s2); result = isPathBF(graph, s1, s2); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s1 + " to " + s6); result = isPathBF(graph, s1, s6); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s3 + " to " + s1); result = isPathBF(graph, s3, s1); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s0 + " to " + s4); result = isPathBF(graph, s0, s4); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s6 + " to " + s3); result = isPathBF(graph, s6, s3); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s6 + " to " + s1); result = isPathBF(graph, s6, s1); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(); System.out.println("Shortest paths starting at " + s6); shortestPaths(graph, s6); System.out.println(); System.out.println(); System.out.println("Shortest paths starting at " + s4); shortestPaths(graph, s4); System.out.println(); System.out.println(); // Create and analyze graph in Figure 10.x System.out.println("Creating graph in figure 10.x"); graph = new WeightedGraph graph.addVertex(s0); graph.addVertex(s1); graph.addVertex(s2); graph.addVertex(s3); graph.addVertex(s4); graph.addVertex(s5); graph.addVertex(s6); graph.addEdge(s0, s5, 800); graph.addEdge(s0, s6, 600); graph.addEdge(s1, s3, 200); graph.addEdge(s1, s5, 160); graph.addEdge(s2, s4, 1000); graph.addEdge(s3, s1, 200); graph.addEdge(s3, s2, 900); graph.addEdge(s3, s4, 780); graph.addEdge(s4, s0, 1400); graph.addEdge(s4, s2, 1000); graph.addEdge(s5, s0, 800); graph.addEdge(s6, s0, 600); // graph.addEdge(s6, s3, 1300); System.out.println("Determining path using depth first ..."); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s1 + " to " + s2); result = isPathDF(graph, s1, s2); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s1 + " to " + s6); result = isPathDF(graph, s1, s6); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s6 + " to " + s5); result = isPathDF(graph, s6, s5); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s6 + " to " + s3); result = isPathDF(graph, s6, s3); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s6 + " to " + s1); result = isPathDF(graph, s6, s1); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(); System.out.println("Determining path using breadth first ..."); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s1 + " to " + s2); result = isPathBF(graph, s1, s2); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s1 + " to " + s6); result = isPathBF(graph, s1, s6); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s6 + " to " + s5); result = isPathBF(graph, s6, s5); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s6 + " to " + s3); result = isPathBF(graph, s6, s3); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(s6 + " to " + s1); result = isPathBF(graph, s6, s1); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(); System.out.println(); System.out.println("Shortest paths starting at " + s6); shortestPaths(graph, s6); System.out.println(); System.out.println(); System.out.println("Shortest paths starting at " + s4); shortestPaths(graph, s4); System.out.println(); } }
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


