Job costing, normal and actual costing. Anderson Construction assembles residential houses. It uses a job-costing system with two direct-cost categories (direct materials and direct labor)
Job costing, normal and actual costing. Anderson Construction assembles residential houses. It uses a job-costing system with two direct-cost categories (direct materials and direct labor) and one indirect-cost pool (assembly support). Direct labor-hours is the allocation base for assembly support costs. In December 2013, Anderson budgets 2014 assembly-support costs to be $8,000,000 and 2014 direct laborhours to be 160,000. At the end of 2014, Anderson is comparing the costs of several jobs that were started and completed in 2014. 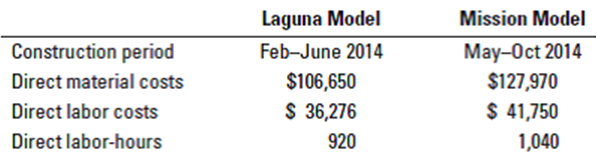 Direct materials and direct labor are paid for on a contract basis. The costs of each are known when direct materials are used or when direct labor-hours are worked. The 2014 actual assembly-support costs were $7,614,000, and the actual direct labor-hours were 162,000.
Direct materials and direct labor are paid for on a contract basis. The costs of each are known when direct materials are used or when direct labor-hours are worked. The 2014 actual assembly-support costs were $7,614,000, and the actual direct labor-hours were 162,000.
1. Compute the (a) budgeted indirect-cost rate and (b) actual indirect-cost rate. Why do they differ?
2. What are the job costs of the Laguna Model and the Mission Model using (a) normal costing and (b) actual costing?
3. Why might Anderson Construction prefer normal costing over actual costing?
Construction period Direct material costs Direct labor costs Direct labor-hours Laguna Model Feb-June 2014 $106,650 $ 36,276 920 Mission Model May-Oct 2014 $127,970 $ 41,750 1,040
Step by Step Solution
3.36 Rating (152 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Predetermined overhead rate Predetermined overhead rate is used to apply manufacturing overhead to work in process inventory Usually this predetermined overhead rate will be calculated at the beginnin...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


