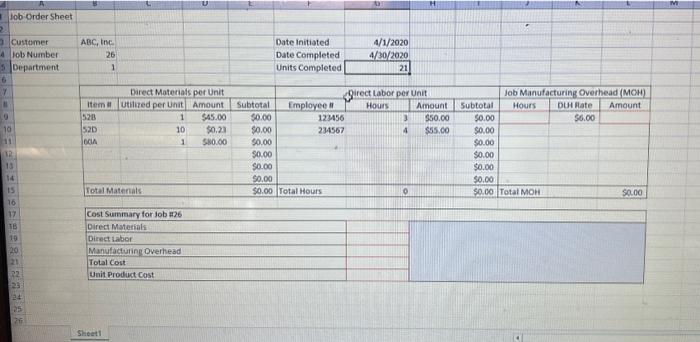
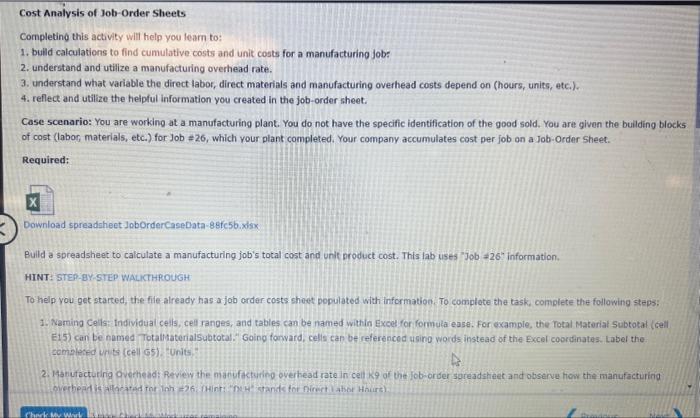
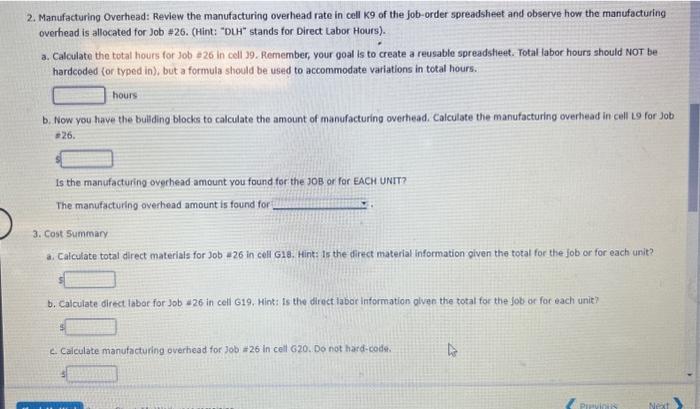
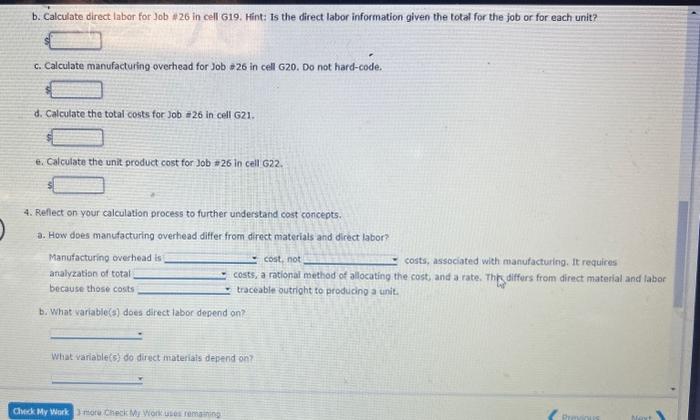
Job Order Sheet Sheeti Completing this activity will help you tearn to: 1. bulld calculations to find cumulative costs and unit costs for a manufacturing job: 2. understand and utilize a manufacturing overhead rate. 3. understand what variable the direct labor, direct materials and manufacturing overhead costs depend on (hours, units, etc.). 4. reflect and utilize the helpful information you created in the job-order isheet. Case scenario: You are working at a manufacturing plant. You do not have the specific identification of the good sold. You are given the building blocks of cost (labor, materials, etc.) for Job =26, which your plant completed. Your company accumulates cost per job on a Job-Order Sheet. Required: X7 Download spreadsheet-JobOrderCaseData-8efc5b.xdsx Build a spreadsheet to calculate a manufacturing job's total cost and unit product cost. This lab uses "Job. =26 " information. HINT: STEP-BY-STEP WALMTPOUGH To help you get started, the file already has a job order costs sheet populated with information, To complote the task, complete the following steps: 1. Naming Cells: Individual cella, cell ranges, and tables cam be named within Excel for formula ease. For example, the Total Matoriat subtotal (Gell E15) can be nemed TotalltaterialSubtotal." Going forvard, celis can be referenced usino words instead of the Excel coordinates. Label the complered urits (cell 65 ) runits,". 2. 1 tantactutiria overhead: Review the nianufakturipg overhead rate in celi k 9 of the lob-order soreadsh aet and observe hoiv the manufacturing 2. Manufacturing Overhead: Review the manufacturing overhead rate in cell K9 of the Job-order spreadsheet and observe how the manufacturing overhead is allocated for Job *26. (Hint: "DUH" stands for Direct Labor Hours). a. Calculate the total hours for 30b a 26 in cell 39. Remember, your goal is to create a reusable spreadsheet. Total labor hours should NOT be hardcoded (or typed in), but a formula should be used to accommodate variations in total hours. hours b. Now you have the bulding blocks to calculate the amount of manufacturing overhead. Calculate the manufacturing overhead in cell 19 for Job =26. Is the manufacturing overhead amount you found for the 30B or for EACH. UNIT? The manufacturing overhead amount is found for 3. Cost Summary a. Calculate total direct materials for Job 226 in cell G18. Hint: is the direct material information qiven the total for the fob or for each unit? b. Calculate direct labor for Job 226 in cell G19. Hint: is the direct labor information olven the total for the fob or for each unit? c. Caiculate manutacturing overhead for 30b=26 in cell 620 . Do not hard-cod9. b. Calculate direct labor for Job i26 in cell G19. Hint: is the direct labor information given the total for the job or for each unit? c. Calculate manufacturing overhead for Job $26 in cell 620 . Do not hard-code. d. Calculate the total costs for Job =26 in cell G21. e. Calculate the unit product cost for Job #26 in cell G22. 4. Reflect on your calculation process to further understand cost concepts. a. How does manufacturing overhead differ from direct materials and direct labor? Manufacturing erehead is cost, not costs, associated with manufacturing. It requires analyzation of total costs, a rational method of allocating the cost, and a rate. This diffors from direct material and labor because those costs traceable outright to producing a unit. b. What variable(s) does direct labor depend on? What variable(s) do direct materiais depend on? 4. Reflect on your calculation proccss to further understand cost concepts. a. How does manufacturing overhead differ from direct materials and direct labor? Manufacturing overhati is cost, not costs, associated with manufacturing. it requires analyzation of total costs, a rational mathod of allocating the cest, and a rate. This differs from direct material and labor because those costs tracenble cutright to producing a unit. b. What variable(s) does direct labor depend on? What variablef(s) do direct materials depend on? What variable(s) does manufacturing overhead depend on? c. What information can you gleam from the job-cost spreadsheet? What is the most expensive part of the job? least expensive? Is the most expensive part of manufacturing this job. it accounts for about Wo of the job's cost The least expensive part of this manufacturing Job is 5. Explain how job cost sheets are used to evaluate and control costs. The ingut in the box beiow will not be graded, bur may be reviewed and ronsitfered by your instructor. b. What variable(s) does direct labor depend on? What variable(s) do direct materials depend on? What variable(s) does manufacturing overhead depend on? c. What information can you gleam from the job-cost spreadsheet? What is the most expensive part of the job? least expensive? is the most expensive part of manufacturing this job. It accounts for about The least expensive part of this manufacturing job is It is about \% of the job's cost. 5. Explain how job cost sheets are used to evaluate and control costs. The input in the box below will not be graded, but may be reviewed and considered by your instructor. Job Order Sheet Sheeti Completing this activity will help you tearn to: 1. bulld calculations to find cumulative costs and unit costs for a manufacturing job: 2. understand and utilize a manufacturing overhead rate. 3. understand what variable the direct labor, direct materials and manufacturing overhead costs depend on (hours, units, etc.). 4. reflect and utilize the helpful information you created in the job-order isheet. Case scenario: You are working at a manufacturing plant. You do not have the specific identification of the good sold. You are given the building blocks of cost (labor, materials, etc.) for Job =26, which your plant completed. Your company accumulates cost per job on a Job-Order Sheet. Required: X7 Download spreadsheet-JobOrderCaseData-8efc5b.xdsx Build a spreadsheet to calculate a manufacturing job's total cost and unit product cost. This lab uses "Job. =26 " information. HINT: STEP-BY-STEP WALMTPOUGH To help you get started, the file already has a job order costs sheet populated with information, To complote the task, complete the following steps: 1. Naming Cells: Individual cella, cell ranges, and tables cam be named within Excel for formula ease. For example, the Total Matoriat subtotal (Gell E15) can be nemed TotalltaterialSubtotal." Going forvard, celis can be referenced usino words instead of the Excel coordinates. Label the complered urits (cell 65 ) runits,". 2. 1 tantactutiria overhead: Review the nianufakturipg overhead rate in celi k 9 of the lob-order soreadsh aet and observe hoiv the manufacturing 2. Manufacturing Overhead: Review the manufacturing overhead rate in cell K9 of the Job-order spreadsheet and observe how the manufacturing overhead is allocated for Job *26. (Hint: "DUH" stands for Direct Labor Hours). a. Calculate the total hours for 30b a 26 in cell 39. Remember, your goal is to create a reusable spreadsheet. Total labor hours should NOT be hardcoded (or typed in), but a formula should be used to accommodate variations in total hours. hours b. Now you have the bulding blocks to calculate the amount of manufacturing overhead. Calculate the manufacturing overhead in cell 19 for Job =26. Is the manufacturing overhead amount you found for the 30B or for EACH. UNIT? The manufacturing overhead amount is found for 3. Cost Summary a. Calculate total direct materials for Job 226 in cell G18. Hint: is the direct material information qiven the total for the fob or for each unit? b. Calculate direct labor for Job 226 in cell G19. Hint: is the direct labor information olven the total for the fob or for each unit? c. Caiculate manutacturing overhead for 30b=26 in cell 620 . Do not hard-cod9. b. Calculate direct labor for Job i26 in cell G19. Hint: is the direct labor information given the total for the job or for each unit? c. Calculate manufacturing overhead for Job $26 in cell 620 . Do not hard-code. d. Calculate the total costs for Job =26 in cell G21. e. Calculate the unit product cost for Job #26 in cell G22. 4. Reflect on your calculation process to further understand cost concepts. a. How does manufacturing overhead differ from direct materials and direct labor? Manufacturing erehead is cost, not costs, associated with manufacturing. It requires analyzation of total costs, a rational method of allocating the cost, and a rate. This diffors from direct material and labor because those costs traceable outright to producing a unit. b. What variable(s) does direct labor depend on? What variable(s) do direct materiais depend on? 4. Reflect on your calculation proccss to further understand cost concepts. a. How does manufacturing overhead differ from direct materials and direct labor? Manufacturing overhati is cost, not costs, associated with manufacturing. it requires analyzation of total costs, a rational mathod of allocating the cest, and a rate. This differs from direct material and labor because those costs tracenble cutright to producing a unit. b. What variable(s) does direct labor depend on? What variablef(s) do direct materials depend on? What variable(s) does manufacturing overhead depend on? c. What information can you gleam from the job-cost spreadsheet? What is the most expensive part of the job? least expensive? Is the most expensive part of manufacturing this job. it accounts for about Wo of the job's cost The least expensive part of this manufacturing Job is 5. Explain how job cost sheets are used to evaluate and control costs. The ingut in the box beiow will not be graded, bur may be reviewed and ronsitfered by your instructor. b. What variable(s) does direct labor depend on? What variable(s) do direct materials depend on? What variable(s) does manufacturing overhead depend on? c. What information can you gleam from the job-cost spreadsheet? What is the most expensive part of the job? least expensive? is the most expensive part of manufacturing this job. It accounts for about The least expensive part of this manufacturing job is It is about \% of the job's cost. 5. Explain how job cost sheets are used to evaluate and control costs. The input in the box below will not be graded, but may be reviewed and considered by your instructor