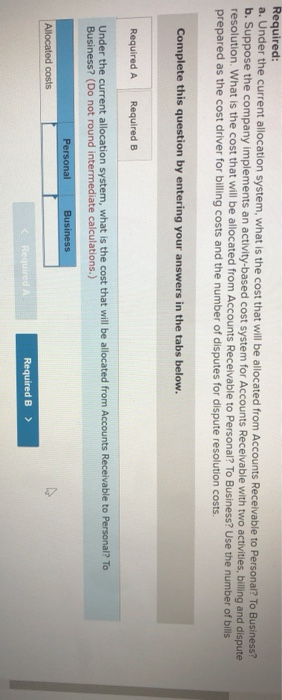
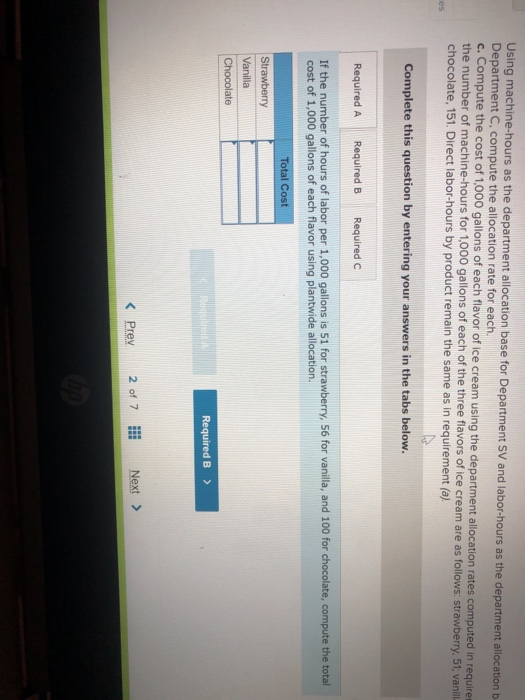
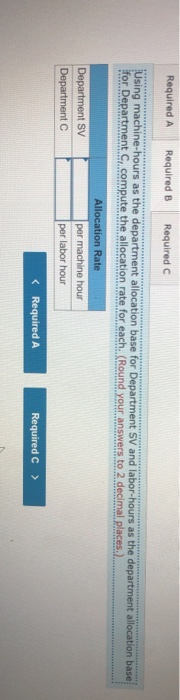
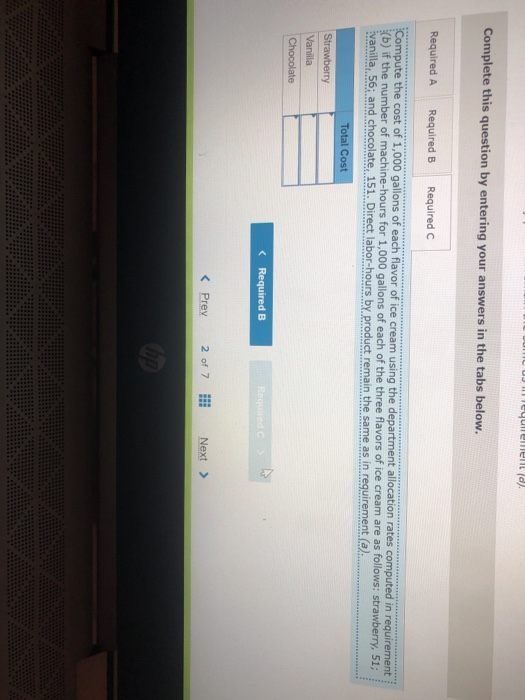
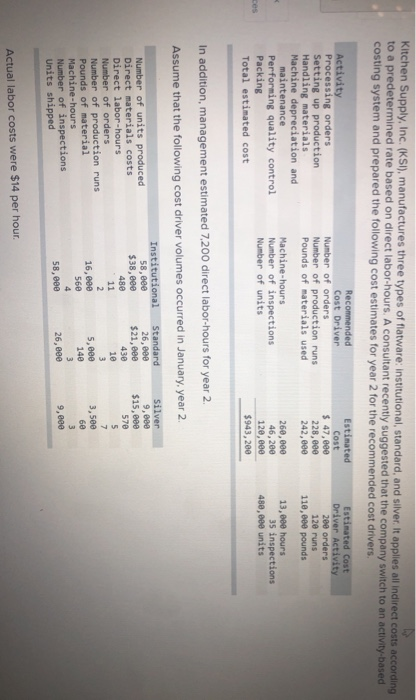
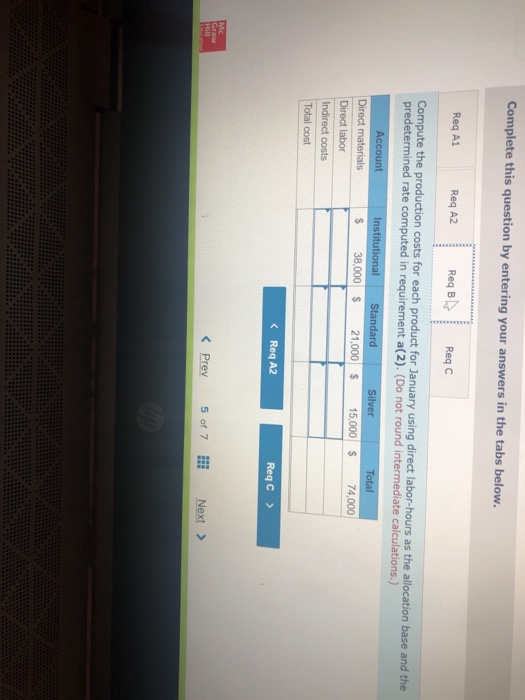
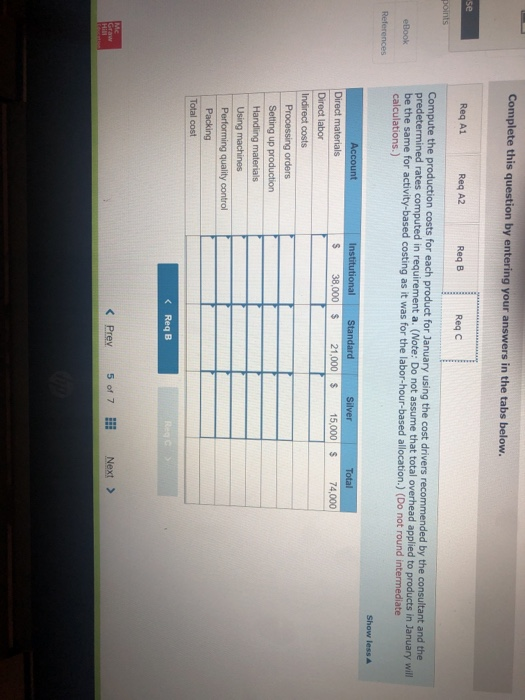
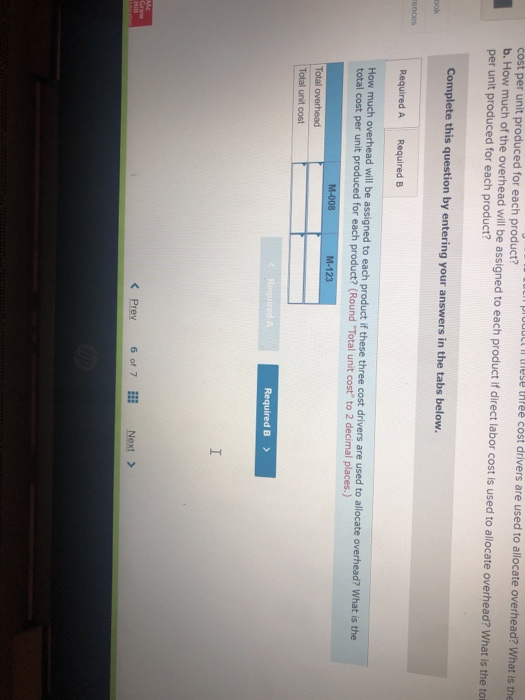
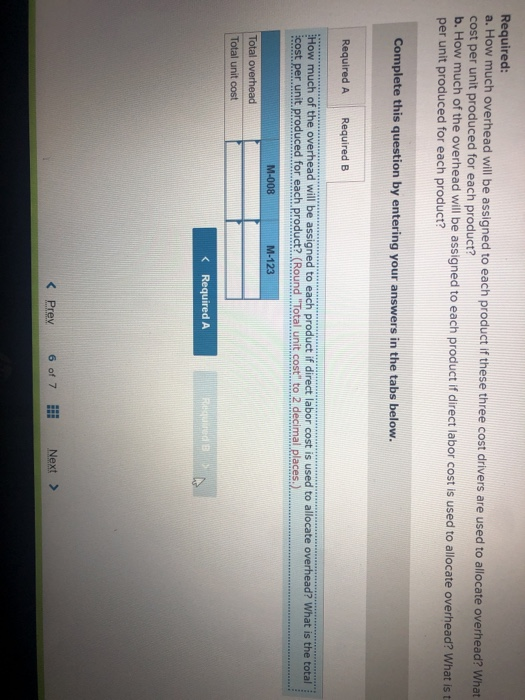
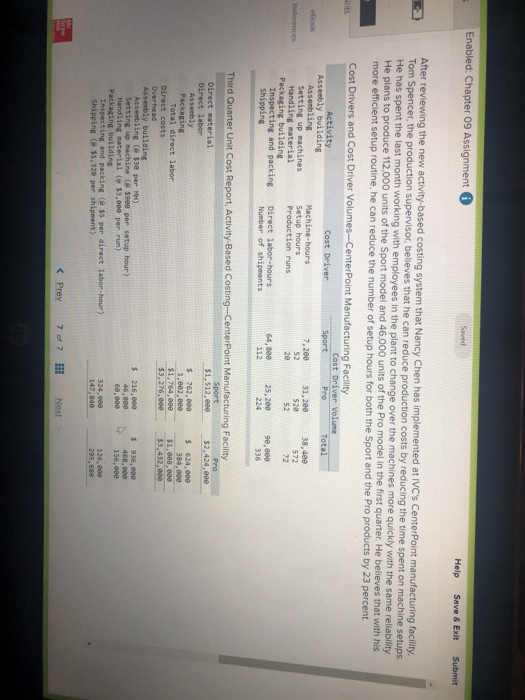
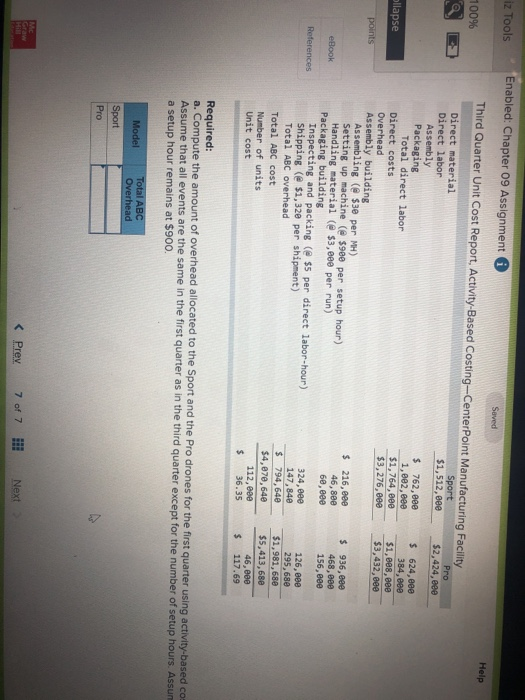
John's Custom Computer Shop (JCCS) assembles computers for both individual and corporate customers. The company is organized into two divisions: Personal and Business. Once a computer is built, it is shipped to the customer. Billing for all customers is handled by the corporate Accounts Receivable Department Accounts Receivable performs two major activities: billing and dispute resolution Billing refers to preparing and sending the bills as well as processing the payments. Dispute resolution occurs when a customer refuses to pay, usually due to an error in billing, The costs of the Accounts Receivable Department are allocated to the two divisions based on the number of bills prepared. Kyle, the manager of the Business division, has complained that the allocated costs from Accounts Receivable are beginning to make the business division look unprofitable and has asked you to recommend some changes to the allocation system. If he agrees with your recommendation, he will pass them on to the chief financial officer Data on costs and activities in the Accounts Receivable Department follow. Number of bills prepared Number of disputes Personal 600 60 Business 400 15 Total 1,800 75 The Accounts Receivable Department incurred the following costs during the year. Billing Dispute resolution Total $ 45,00 37,500 $82,500 Required: a. Under the current allocation system, what is the cost that will be allocated from Accounts Receivable to Personal? To Business? b. Suppose the company implements an activity-based cost system for Accounts Receivable with two activities, billing and dispute resolution. What is the cost that will be allocated from Accounts Receivable to Personal? To Business? Use the number of bills prepared as the cost driver for billing costs and the number of disputes for dispute resolution costs. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Under the current allocation system, what is the cost that will be allocated from Accounts Receivable to Personal? To Business? (Do not round intermediate calculations.) Personal Business Allocated costs Required A Required B > Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Suppose the company implements an activity-based cost system for Accounts Receivable with two activities, billing and dispute resolution. What is the cost that will be allocated from Accounts Receivable to Personal? To Business? Use the number of bills prepared as the cost driver for billing costs and the number of disputes for dispute resolution costs. Personal Business Billing Dispute resolution Required A Required B Required Using machine-hours as the department allocation base for Department SV and labor-hours as the department allocation base for Department C compute the allocation rate for each. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.). Department SV Department Allocation Rate per machine hour per labor hour JJ egunemend). Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Required Compute the cost of 1,000 gallons of each flavor of ice cream using the department allocation rates computed in requirement (b) if the number of machine-hours for 1,000 gallons of each of the three flavors of ice cream are as follows: strawberry, 51; vanilla, 56; and chocolate, 151. Direct labor-hours by product remain the same as in requirement (a). Total Cost Strawberry Vanilla Chocolate McNulty, Inc., produces desks and chairs. A new CFO has just been hired and announces a new policy that if a product cannot earn a margin of at least 40 percent, it will be dropped. The margin is computed as product gross profit divided by reported product cost. Manufacturing overhead for year 1 totaled $765,000. Overhead is allocated to products based on direct labor cost. Data for year 1 show the following Sales revenue Direct materials Direct labor Chairs $1,368,900 589,000 170,000 Desks $2,465,000 850,000 340,000 Required: a-1. Based on the CFO's new policy, calculate the profit margin for both chairs and desks. a-2. Which of the two products should be dropped? b. Regardless of your answer in requirement (a), the CFO decides at the beginning of year 2 to drop the chair product. The company cost analyst estimates that overhead without the chairline will be $700,000. The revenue and costs for desks are expected to be the same as last year. What is the estimated margin for desks in year 2? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A1 Req A2 ReqB Based on the CFO's new policy, calculate the profit margin for both chairs and desks. Profit Margin % Chairs Desks % a-2. Which of the two products should be dropped? b. Regardless of your answer in requirement (a), the CFO decides at the beginning of year 2 to cost analyst estimates that overhead without the chair line will be $700,000. The revenue and same as last year. What is the estimated margin for desks in year 2? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A1 Req A2 Req B Which of the two products should be dropped? O Chairs O Desks ho Next > lp Kitchen Supply, Inc. (KSI), manufactures three types of flatware: institutional standard, and silver. It applies all Indirect costs according to a predetermined rate based on direct labor-hours. A consultant recently suggested that the company switch to an activity-based costing system and prepared the following cost estimates for year 2 for the recommended cost drivers. Recommended Cost Driver Number of orders Number of production runs Pounds of materials used Estimated Cost $ 47,000 228,000 242, eee Estimated cost Driver Activity 289 orders 120 runs 110,000 pounds Activity Processing orders Setting up production Handling materials Machine depreciation and maintenance Performing quality control Packing Total estimated cost Machine-hours Number of inspections Number of units 260,000 46,200 120, eee $943,200 13,000 hours 35 inspections 480,000 units In addition, management estimated 7,200 direct labor-hours for year 2. Assume that the following cost driver volumes occurred in January, year 2. Standard 26, $21,000 430 Number of units produced Direct materials costs Direct labor-hours Number of orders Number of production runs Pounds of material Machine-hours Number of inspections Units shipped Institutional 58, eee $38, eee 480 11 2 16,800 560 4 58,eee le 3 5,000 14e 3 26, eee Silver 9,000 $15,000 570 5 7 3,5ec 6e 3 9, eee Actual labor costs were $14 per hour. Required: Help Save & Exit Sub a. (1) Compute a predetermined overhead rate for year 2 for each cost driver using the estimated costs and estimated cost driver units prepared by the consultant. (2) Compute a predetermined rate for year 2 using direct labor-hours as the allocation base. b. Compute the production costs for each product for January using direct labor-hours as the allocation base and the predetermined rate computed in requirement a(2) c. Compute the production costs for each product for January using the cost drivers recommended by the consultant and the predetermined rates computed in requirement a. (Note: Do not assume that total overhead applied to products in January will be the same for activity-based costing as it was for the labor-hour-based allocation.) Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A1 Req A2 ReqB Reqc Compute a predetermined overhead rate for year 2 for each cost driver using the estimated costs and estimated cost driver units prepared by the consultant. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Activity Processing orders Setting up production Handling materials Using machines Performing quality control Packing Rate per order per run per pound per machine hour per inspection per unit c. Compute the production costs for each product for January using the cost drivers recommended by the consultant predetermined rates computed in requirement a. (Note: Do not assume that total overhead applied to products in Jan same for activity-based costing as it was for the labor-hour-based allocation.) Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A1 Reg A2 ReqB Reqc Compute a predetermined rate for year 2 using direct labor-hours as the allocation base. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Predetermined rate per direct labor-hour Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A1 Reg A2 Reg Reqc Compute the production costs for each product for January using direct labor-hours as the allocation base and the predetermined rate computed in requirement a(2). (Do not round intermediate calculations.) Account Institutional Standard Silver Total Direct materials $ 38,000 $ 21,000 $ 15,000 $ 74,000 Direct labor Indirect costs Total cost Me Graw Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. se Reg A1 Reg A2 ReqB Reqc points Book Compute the production costs for each product for January using the cost drivers recommended by the consultant and the predetermined rates computed in requirement a. (Note: Do not assume that total overhead applied to products in January will be the same for activity-based costing as it was for the labor-hour-based allocation.) (Do not round intermediate calculations.) Show less References Institutional Standard $ 38,000 $ 21,000 $ Silver 15,000 $ Total 74,000 Account Direct materials Direct labor Indirect costs Processing orders Setting up production Handling materials Using machines Performing quality control Packing Total cost Doaktown Products manufactures fishing equipment for recreational uses. The Miramichi plant produces the company's two versions of a special reel used for river fishing. The two models are the M-008, a basic reel, and the M-123, a new and improved version. Cost accountants at company headquarters have prepared costs for the two reels for the most recent period. The plant manager is concerned. The cost report does not coincide with her intuition about the relative costs of the two models. She has asked you to review the cost accounting and help her prepare a response to headquarters. Manufacturing overhead is currently assigned to products based on their direct labor costs. For the most recent month, manufacturing overhead was $335,200. During that time, the company produced 14 700 units of the M-008 and 2,500 units of the M-123. The direct costs of production were as follows M-008 M-123 Total Direct materials $ 117,600 $100,000 $ 217,600 Direct labor 117,600 50,000 167,600 ins Book References Management determined that overhead costs are caused by three cost drivers. These drivers and their costs for last year were as follows Cost Driver Number of machine-hours Number of production runs Number of inspections Total overhead Costs $160, 700 80,000 94,500 $335,200 Activity Level M-008 M-123 1,000 9,000 10 3e 10 40 Total 10,000 40 Se Required: a. How much overhead will be assigned to each product if these three cost drivers are used to allocate overhead? What is the total cost per unit produced for each product? b. How much of the overhead will be assigned to each product if direct labor cost is used to allocate overhead? What is the total cost per unit produced for each product? puullir lese three cost drivers are used to allocate overhead? What is the cost per unit produced for each product? b. How much of the overhead will be assigned to each product if direct labor cost is used to allocate overhead? What is the to per unit produced for each product? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. OOK Tences Required A Required B How much overhead will be assigned to each product if these three cost drivers are used to allocate overhead? What is the total cost per unit produced for each product? (Round "Total unit cost" to 2 decimal places.) M-008 M-123 Total overhead Total unit cost Requited Required B > Mc Graw HI Required: a. How much overhead will be assigned to each product if these three cost drivers are used to allocate overhead? What cost per unit produced for each product? b. How much of the overhead will be assigned to each product if direct labor cost is used to allocate overhead? What ist per unit produced for each product? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B How much of the overhead will be assigned to each product if direct labor cost is used to allocate overhead? What is the total cost per unit produced for each product? (Round "Total unit cost" to 2 decimal places.) M-008 M-123 Total overhead Total unit cost Enabled: Chapter 09 Assignment Saved Help Save & Exit Submit After reviewing the new activity-based costing system that Nancy Chen has implemented at VC's CenterPoint manufacturing facility. Tom Spencer, the production supervisor, believes that he can reduce production costs by reducing the time spent on machine setups. He has spent the last month working with employees in the plant to change over the machines more quickly with the same reliability. He plans to produce 112,000 units of the Sport model and 46,000 units of the Pro model in the first quarter. He believes that with his more efficient setup routine, he can reduce the number of setup hours for both the Sport and the Pro products by 23 percent Cost Drivers and Cost Driver Volumes-CenterPoint Manufacturing Facility Cost Driver Volume Activity Cost Driver Sport Pro Total Assembly building Assembling Machine-hours 7,200 31, 2ee 38,400 Setting up machines Setup hours 520 572 Handling material Production runs 52 72 Packaging building Inspecting and packing Direct labor-hours 64,800 25,200 9e, eee Shipping Number of shipments 112 224 336 Book References 52 20 Third Quarter Unit Cost Report Activity-Based Costing-CenterPoint Manufacturing Facility Sport Pro Direct material $1,512, eee $2,424,000 Direct labor Assembly $ 762,000 $ 624,000 Packaging 1,282.600 384.000 Total direct labor $1,764,000 $1,688,000 Direct costs $3,276.000 $3,432,000 Overhead Assembly building Assembling ($30 per ) $ 216,000 $ 936.000 Setting up machine ( 5900 per setup hour) 46,800 468,000 Handling material (@ $3,000 per run) 60.000 156,000 Packaging building Inspecting and packing (e $5 per direct labor-hour) 324.ee 126,000 Shipping ( 31,320 per shipment) 147,840 295,680 Me Graw H Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Suppose the company implements an activity-based cost system for Accounts Receivable with two activities, billing and dispute resolution. What is the cost that will be allocated from Accounts Receivable to Personal? To Business? Use the number of bills prepared as the cost driver for billing costs and the number of disputes for dispute resolution costs. Personal Business Billing Dispute resolution Required A Required B Required Using machine-hours as the department allocation base for Department SV and labor-hours as the department allocation base for Department C compute the allocation rate for each. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.). Department SV Department Allocation Rate per machine hour per labor hour JJ egunemend). Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Required Compute the cost of 1,000 gallons of each flavor of ice cream using the department allocation rates computed in requirement (b) if the number of machine-hours for 1,000 gallons of each of the three flavors of ice cream are as follows: strawberry, 51; vanilla, 56; and chocolate, 151. Direct labor-hours by product remain the same as in requirement (a). Total Cost Strawberry Vanilla Chocolate McNulty, Inc., produces desks and chairs. A new CFO has just been hired and announces a new policy that if a product cannot earn a margin of at least 40 percent, it will be dropped. The margin is computed as product gross profit divided by reported product cost. Manufacturing overhead for year 1 totaled $765,000. Overhead is allocated to products based on direct labor cost. Data for year 1 show the following Sales revenue Direct materials Direct labor Chairs $1,368,900 589,000 170,000 Desks $2,465,000 850,000 340,000 Required: a-1. Based on the CFO's new policy, calculate the profit margin for both chairs and desks. a-2. Which of the two products should be dropped? b. Regardless of your answer in requirement (a), the CFO decides at the beginning of year 2 to drop the chair product. The company cost analyst estimates that overhead without the chairline will be $700,000. The revenue and costs for desks are expected to be the same as last year. What is the estimated margin for desks in year 2? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A1 Req A2 ReqB Based on the CFO's new policy, calculate the profit margin for both chairs and desks. Profit Margin % Chairs Desks % a-2. Which of the two products should be dropped? b. Regardless of your answer in requirement (a), the CFO decides at the beginning of year 2 to cost analyst estimates that overhead without the chair line will be $700,000. The revenue and same as last year. What is the estimated margin for desks in year 2? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A1 Req A2 Req B Which of the two products should be dropped? O Chairs O Desks ho Next > lp Kitchen Supply, Inc. (KSI), manufactures three types of flatware: institutional standard, and silver. It applies all Indirect costs according to a predetermined rate based on direct labor-hours. A consultant recently suggested that the company switch to an activity-based costing system and prepared the following cost estimates for year 2 for the recommended cost drivers. Recommended Cost Driver Number of orders Number of production runs Pounds of materials used Estimated Cost $ 47,000 228,000 242, eee Estimated cost Driver Activity 289 orders 120 runs 110,000 pounds Activity Processing orders Setting up production Handling materials Machine depreciation and maintenance Performing quality control Packing Total estimated cost Machine-hours Number of inspections Number of units 260,000 46,200 120, eee $943,200 13,000 hours 35 inspections 480,000 units In addition, management estimated 7,200 direct labor-hours for year 2. Assume that the following cost driver volumes occurred in January, year 2. Standard 26, $21,000 430 Number of units produced Direct materials costs Direct labor-hours Number of orders Number of production runs Pounds of material Machine-hours Number of inspections Units shipped Institutional 58, eee $38, eee 480 11 2 16,800 560 4 58,eee le 3 5,000 14e 3 26, eee Silver 9,000 $15,000 570 5 7 3,5ec 6e 3 9, eee Actual labor costs were $14 per hour. Required: Help Save & Exit Sub a. (1) Compute a predetermined overhead rate for year 2 for each cost driver using the estimated costs and estimated cost driver units prepared by the consultant. (2) Compute a predetermined rate for year 2 using direct labor-hours as the allocation base. b. Compute the production costs for each product for January using direct labor-hours as the allocation base and the predetermined rate computed in requirement a(2) c. Compute the production costs for each product for January using the cost drivers recommended by the consultant and the predetermined rates computed in requirement a. (Note: Do not assume that total overhead applied to products in January will be the same for activity-based costing as it was for the labor-hour-based allocation.) Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A1 Req A2 ReqB Reqc Compute a predetermined overhead rate for year 2 for each cost driver using the estimated costs and estimated cost driver units prepared by the consultant. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Activity Processing orders Setting up production Handling materials Using machines Performing quality control Packing Rate per order per run per pound per machine hour per inspection per unit c. Compute the production costs for each product for January using the cost drivers recommended by the consultant predetermined rates computed in requirement a. (Note: Do not assume that total overhead applied to products in Jan same for activity-based costing as it was for the labor-hour-based allocation.) Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A1 Reg A2 ReqB Reqc Compute a predetermined rate for year 2 using direct labor-hours as the allocation base. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Predetermined rate per direct labor-hour Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A1 Reg A2 Reg Reqc Compute the production costs for each product for January using direct labor-hours as the allocation base and the predetermined rate computed in requirement a(2). (Do not round intermediate calculations.) Account Institutional Standard Silver Total Direct materials $ 38,000 $ 21,000 $ 15,000 $ 74,000 Direct labor Indirect costs Total cost Me Graw Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. se Reg A1 Reg A2 ReqB Reqc points Book Compute the production costs for each product for January using the cost drivers recommended by the consultant and the predetermined rates computed in requirement a. (Note: Do not assume that total overhead applied to products in January will be the same for activity-based costing as it was for the labor-hour-based allocation.) (Do not round intermediate calculations.) Show less References Institutional Standard $ 38,000 $ 21,000 $ Silver 15,000 $ Total 74,000 Account Direct materials Direct labor Indirect costs Processing orders Setting up production Handling materials Using machines Performing quality control Packing Total cost Doaktown Products manufactures fishing equipment for recreational uses. The Miramichi plant produces the company's two versions of a special reel used for river fishing. The two models are the M-008, a basic reel, and the M-123, a new and improved version. Cost accountants at company headquarters have prepared costs for the two reels for the most recent period. The plant manager is concerned. The cost report does not coincide with her intuition about the relative costs of the two models. She has asked you to review the cost accounting and help her prepare a response to headquarters. Manufacturing overhead is currently assigned to products based on their direct labor costs. For the most recent month, manufacturing overhead was $335,200. During that time, the company produced 14 700 units of the M-008 and 2,500 units of the M-123. The direct costs of production were as follows M-008 M-123 Total Direct materials $ 117,600 $100,000 $ 217,600 Direct labor 117,600 50,000 167,600 ins Book References Management determined that overhead costs are caused by three cost drivers. These drivers and their costs for last year were as follows Cost Driver Number of machine-hours Number of production runs Number of inspections Total overhead Costs $160, 700 80,000 94,500 $335,200 Activity Level M-008 M-123 1,000 9,000 10 3e 10 40 Total 10,000 40 Se Required: a. How much overhead will be assigned to each product if these three cost drivers are used to allocate overhead? What is the total cost per unit produced for each product? b. How much of the overhead will be assigned to each product if direct labor cost is used to allocate overhead? What is the total cost per unit produced for each product? puullir lese three cost drivers are used to allocate overhead? What is the cost per unit produced for each product? b. How much of the overhead will be assigned to each product if direct labor cost is used to allocate overhead? What is the to per unit produced for each product? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. OOK Tences Required A Required B How much overhead will be assigned to each product if these three cost drivers are used to allocate overhead? What is the total cost per unit produced for each product? (Round "Total unit cost" to 2 decimal places.) M-008 M-123 Total overhead Total unit cost Requited Required B > Mc Graw HI Required: a. How much overhead will be assigned to each product if these three cost drivers are used to allocate overhead? What cost per unit produced for each product? b. How much of the overhead will be assigned to each product if direct labor cost is used to allocate overhead? What ist per unit produced for each product? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B How much of the overhead will be assigned to each product if direct labor cost is used to allocate overhead? What is the total cost per unit produced for each product? (Round "Total unit cost" to 2 decimal places.) M-008 M-123 Total overhead Total unit cost Enabled: Chapter 09 Assignment Saved Help Save & Exit Submit After reviewing the new activity-based costing system that Nancy Chen has implemented at VC's CenterPoint manufacturing facility. Tom Spencer, the production supervisor, believes that he can reduce production costs by reducing the time spent on machine setups. He has spent the last month working with employees in the plant to change over the machines more quickly with the same reliability. He plans to produce 112,000 units of the Sport model and 46,000 units of the Pro model in the first quarter. He believes that with his more efficient setup routine, he can reduce the number of setup hours for both the Sport and the Pro products by 23 percent Cost Drivers and Cost Driver Volumes-CenterPoint Manufacturing Facility Cost Driver Volume Activity Cost Driver Sport Pro Total Assembly building Assembling Machine-hours 7,200 31, 2ee 38,400 Setting up machines Setup hours 520 572 Handling material Production runs 52 72 Packaging building Inspecting and packing Direct labor-hours 64,800 25,200 9e, eee Shipping Number of shipments 112 224 336 Book References 52 20 Third Quarter Unit Cost Report Activity-Based Costing-CenterPoint Manufacturing Facility Sport Pro Direct material $1,512, eee $2,424,000 Direct labor Assembly $ 762,000 $ 624,000 Packaging 1,282.600 384.000 Total direct labor $1,764,000 $1,688,000 Direct costs $3,276.000 $3,432,000 Overhead Assembly building Assembling ($30 per ) $ 216,000 $ 936.000 Setting up machine ( 5900 per setup hour) 46,800 468,000 Handling material (@ $3,000 per run) 60.000 156,000 Packaging building Inspecting and packing (e $5 per direct labor-hour) 324.ee 126,000 Shipping ( 31,320 per shipment) 147,840 295,680 Me Graw H