JOURNAL ENTRY FOR:
Depreciation on the building for the month of January is calculated using the straight-line method. At the time the building was purchased, the company estimated a service life of 10 years and a residual value of $26,000. Prepare the adjusting journal entry for depreciation.
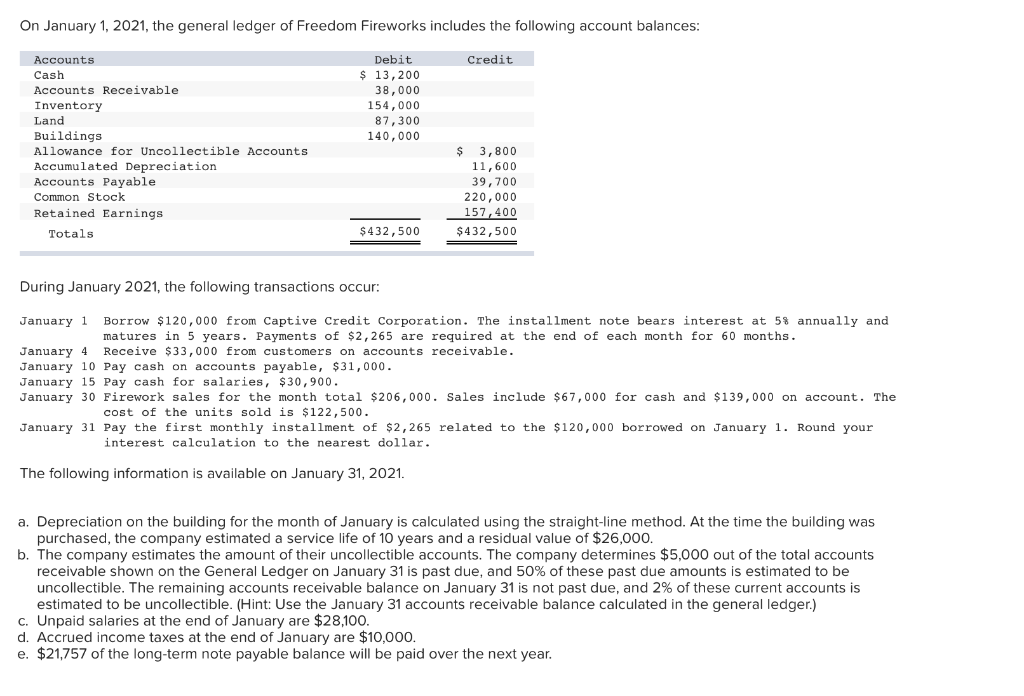
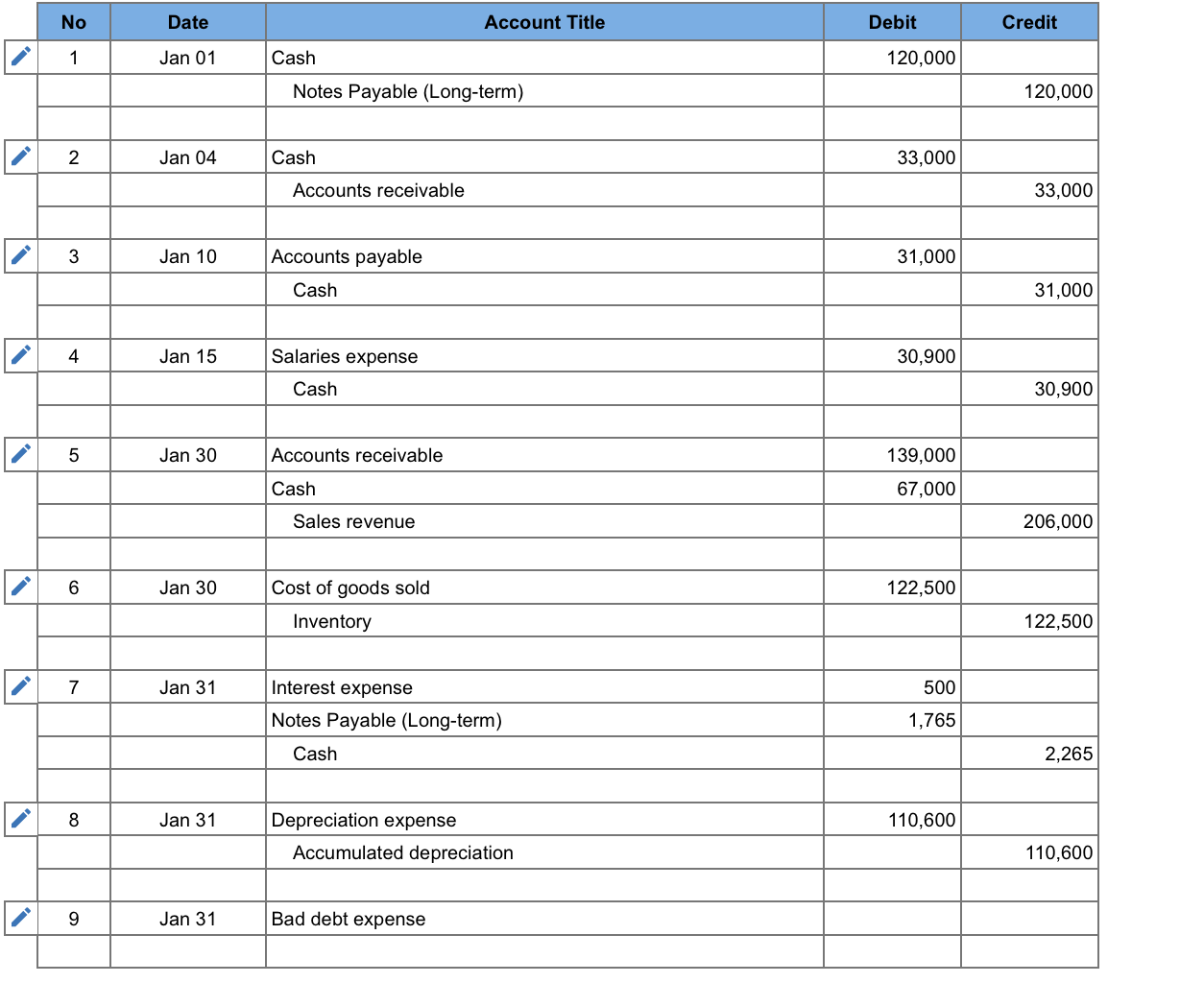
On January 1, 2021, the general ledger of Freedom Fireworks includes the following account balances: Credit Debit $ 13,200 38,000 154,000 87,300 140,000 Accounts Cash Accounts Receivable Inventory Land Buildings Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts Accumulated Depreciation Accounts Payable Common Stock Retained Earnings Totals $ 3,800 11,600 39,700 220,000 157,400 $432,500 $432,500 During January 2021, the following transactions occur: January 1 Borrow $120,000 from Captive Credit Corporation. The installment note bears interest at 5% annually and matures in 5 years. Payments of $2,265 are required at the end of each month for 60 months. January 4 Receive $33,000 from customers on accounts receivable. January 10 Pay cash on accounts payable, $31,000. January 15 Pay cash for salaries, $30,900. January 30 Firework sales for the month total $206,000. Sales include $67,000 for cash and $139,000 on account. The cost of the units sold is $122,500. January 31 Pay the first monthly installment of $2,265 related to the $120,000 borrowed on January 1. Round your interest calculation to the nearest dollar. The following information is available on January 31, 2021. a. Depreciation on the building for the month of January is calculated using the straight-line method. At the time the building was purchased, the company estimated a service life of 10 years and a residual value of $26,000. b. The company estimates the amount of their uncollectible accounts. The company determines $5,000 out of the total accounts receivable shown on the General Ledger on January 31 is past due, and 50% of these past due amounts is estimated to be uncollectible. The remaining accounts receivable balance on January 31 is not past due, and 2% of these current accounts is estimated to be uncollectible. (Hint: Use the January 31 accounts receivable balance calculated in the general ledger.) c. Unpaid salaries at the end of January are $28,100. d. Accrued income taxes at the end of January are $10,000. e. $21,757 of the long-term note payable balance will be paid over the next year. No Credit Date Jan 01 Account Title Cash Notes Payable (Long-term) Debit 120,000 120,000 2 Jan 04 33,000 Cash Accounts receivable 33,000 1 3 Jan 10 31,000 Accounts payable Cash 31,000 4 Jan 15 30,900 Salaries expense Cash 30,900 Jan 30 Accounts receivable Cash Sales revenue 139,000 67,000 206,000 Jan 30 122,500 Cost of goods sold Inventory 122,500 7 Jan 31 Interest expense Notes Payable (Long-term) Cash 500 1,765 2,265 8 Jan 31 110,600 Depreciation expense Accumulated depreciation 110,600 Jan 31 Bad debt expense








