Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
jus need to know what there problems or issues are and what recommendations you have fore them to fix the problems and a brief summary
jus need to know what there problems or issues are and what recommendations you have fore them to fix the problems and a brief summary 
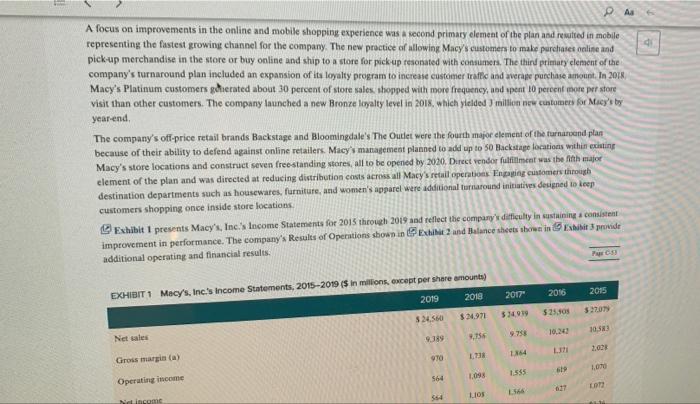
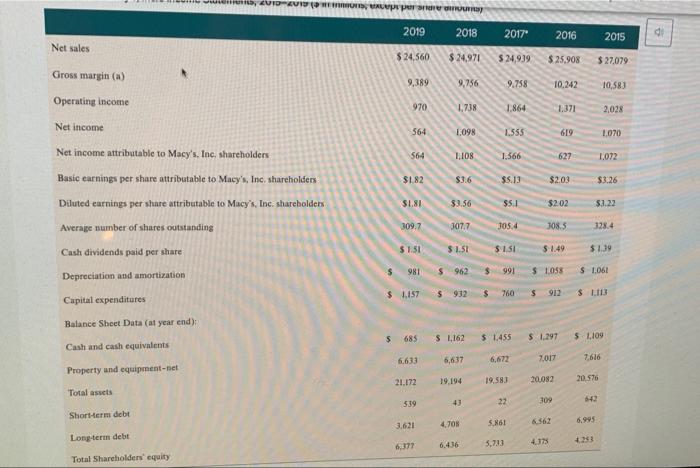
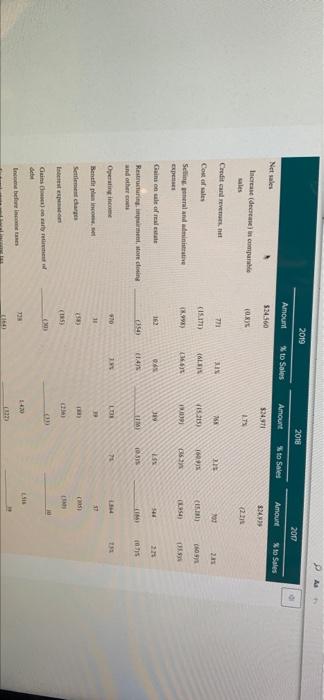
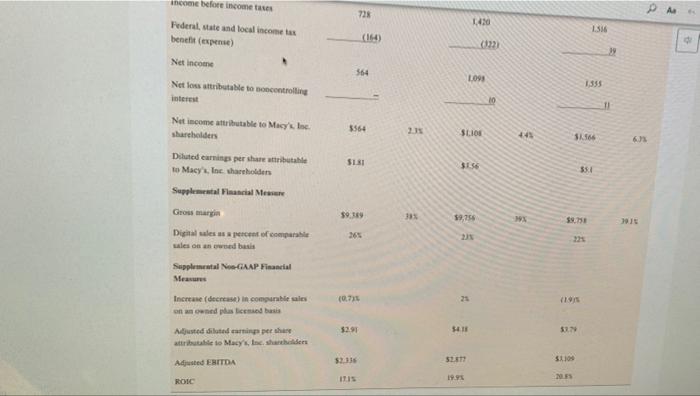
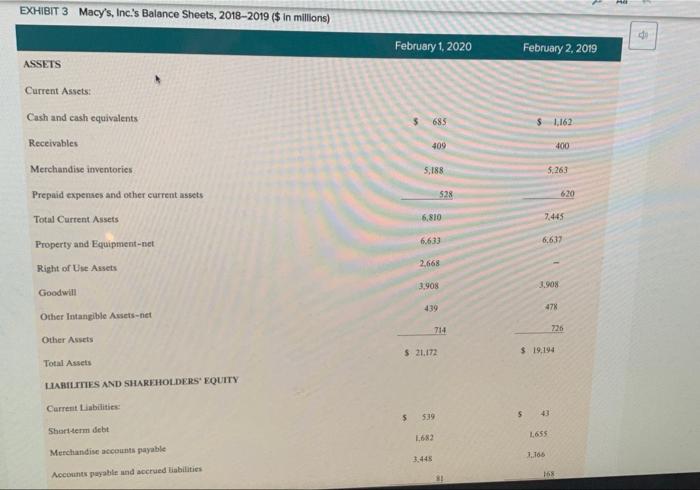
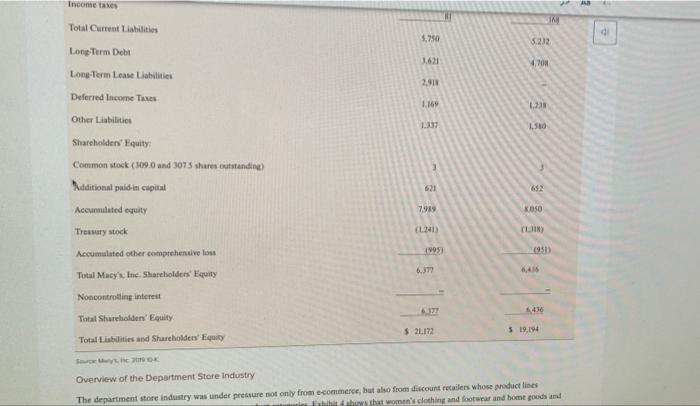
CASE 5 Macy's, Inc.: Will Its Strategy Allow It to Survive in the Changing Retail Sector? Alen Badal University of Liverpool John E. Gamble Texas AAM University Corpus Christi The retail landscape in the United States in early 2030 may have been best characterized rapidly changing with an certain future. The COVID-19 pandemic and stay at home orders by state and local governments had created unprecedented challenges for all retail traditional brickand mortar retailers had under pressure for alle decade. The color of shopping wearly every type of consumer good at Amazon or other online retailers had radically transformed the industry Consumer de continued to allow for Variations in strategy that allowed for distinctive ailer approaches to meeting expectation. But commentados even the most highly differentiated tailers to have an eine presence in addition to their prestigious brichardmeta location The change in consumer shopping preferences had especially impacted male departe. Nearly all shopping mall strong department store anchor to draw a number of shoppers who would rear specialized rettes during their visits to a mall The transition to online shopping and really damaged the business model malerier failed along with department stores, both of whom had experienced a declinentale per quare foot from me tratti Macy't. Inc had particularly led to adapt its best model to the online shopping with sales de cacher side its records $28.1 billion perd in 2014 in 2018. Macy turned our company were Gettetal the compro turnaround and transformation CEO to cart 2020, was in the year of his five time the company's business model and retail in the years the plan white which were for product and merchandising notions in ones that would startinanden med 100 additional stores per year. The company to implemented direct de filment model for the theme med tynd o May Translate ACCT-205-90-11 > The Oct The third element of the turnaround plan was to allow customers to order items online and pick up merchandise in a nearby store location PA Gennette also wished to expand the number of the company's off price Macy's Backstage stores from approximately 150 to more than 200. Macy's management had determined that the off price store locations were less vulnerable to competition from online retailers than its core Macy's stores. Expanding the company's loyalty plan to encourage repeat business, making online sales available through its new mobile app and better utilizing its stronges product categories like housewares and women's apparel to draw customers to its stores were less sweeping changes that rounded out the plan As of early-2020, the plan had produced few positive results with some analysts suggesting that the strategy was better aligned with PwC82 the retail environment of 2010 than of 2020. In February 2020, Macy's announced that it would close 125 store locations. By March 18 the company's COVID-19 response resulted in it closing all 775 store locations. The company began reopening stores on May 4 and expected to have 270 stores open by the 2020 Memorial Day Weekend. The combined effect of the company's ongoing poor performance and COVID 19 store closes was expected to result in a first quarter 2020 loss of $905 million to SL.1 billion Company Background Headquartered in Cincinnati, Ohio, Macy's, Inc. was the second largest department store chain with a market share of approximately 16,3 percent in 2020. The company operated about 551 Macy's department stores, 53 Bloomingdales, and 171 Bluemercury businesses in early 2020, and its retailing portfolio also included Bloomingdale's The Outlet, Macy's Backstage, and STORY and online businesses macys.com, bt oomingdales.com, and bluemercury.com. The company also licensed Bloomingdale's stores in Dubai and Kuwait for operation by Al Tayer Group Beginning in 2018, CEO Gennette and his chief lieutenants launched a five-point turnaround plan to improve the company's performance The Growth 50 initiative was focused on 50 Macy's department stores to revitalize in 2018, including store remodelsimproved customer service, and increased product assortment. The addition of STORY retail locations in 2018 supported sales growth for the company as well STORY locations were much smaller stores with an inventory assortment that was refreshed with new items every six to eight weeks. The value proposition of the STORY business was keyed to engaging consumers through an opportunity to interact with products and collaborate. The value proposition for The Market Macy's was similar, but entailed departments focated within select Macy's stores rather than operating as standalone locations. Revitalization of the customer experience at Bloomingdale's and Blumercury were also important elements of the turnaround efforts. Like cy's Bloomingdale's, the Bluemercury business operated standalone stores but also was comprised of store within-store locations inside stores. The Bluemercury division had achieved impressive sales growth for the company and an addition of 26 standalone locations Additionally. Bluemercury online sales increased by greater than 50 percent, accounting for double-digit increases in total sales. The Bluemercury division increased its private brands Lune Aster and M-6l, which accounted for greater than 10 percent of total sales al Bluemercury per company mencecand primary element of the plan and resulted in mobile d A focus on improvements in the online and mobile shopping experience was a second primary element of the plan and resulted in mobile representing the fastest growing channel for the company. The new practice of allowing Macy's customers to make purchases online and pickup merchandise in the store or buy online and ship to a store for pick up resonated with consumers. The third primaty element of the company's turnaround plan included an expansion of its loyalty program to increase customer traffic and average purchase amount. In 2018 Macy's Platinum customers generated about 30 percent of store sales shopped with more frequency, and spent 10 percent more per store visit than other customers. The company launched a new Bronze Jalty level in 2018, which yielded million new customers for Macy's by year-end The company's off-price retail brands Backstage and Bloomingdale's The Outlet were the fourth major element of the turnaround plan because of their ability to defend against online retailers. Macy's management planned to add up to 50 Backstage locations within eating Macy's store locations and construct seven freestanding stores, all to be opened by 2020. Derect vendor fulfillment was the fifth major element of the plan and was directed at reducing distribution costs across all Macy's retail operation Enging customers through destination departments such as housewares, furniture, and women's apparel were additional turnaround initiatives designed to keep customers shopping once inside store locations Exhibit 1 presents Macy's, Inc.'s Income Statements for 2015 through 2019 and reflect the company difficulty in sustaining consistent improvement in performance. The company's Results of Operations shown in Exhibit and Balance sheets shown in Exhibit provide additional operating and financial results, 2017" 2016 2015 EXHIBIT1 Macy's, Inc.'s Income Statements, 2015-2019 ($ in millions, except per share amounts) 2019 2018 52707 5245 $2.971 $25.50 $34019 102 Net sales 136 38 14 Gross margin(a) 69 LO 1.555 564 098 Operating income LOT LIOS 1566 Nincome VIORANS, VALSTS 2019 2018 2017" 2016 2015 Net sales $ 24,560 $ 24,971 $ 24,939 $ 25,908 $ 27.079 Gross margin(a) 9,389 9,756 9.758 10.242 10,583 Operating income 970 1,738 1.864 1.371 2,028 Net income 564 1.098 1.555 619 1,070 564 1108 1.566 627 1.072 $182 $3.6 $5.3 $2.03 $3.26 Net income attributable to Macy's, Inc. shareholders Basic earnings per share attributable to Macy's, Inc. shareholders Diluted earnings per share attributable to Macy's, Inc. shareholders Average number of shares outstanding SLI $3.56 $5.1 $2.02 $3.22 309.7 307.7 105.4 108.5 328.4 $ 1.51 Cash dividends paid per share $ 1.51 $15 $ 1.49 $ 139 $ 981 $ 962 $ 991 $ 1.058 $ 1.061 Depreciation and amortization $ 1.157 $932 $ 760 $ 912 $ 113 Capital expenditures Balance Sheet Data (at year end); 5 685 $ 1,162 $ 1.455 $ 1197 5 1,109 Cash and cash equivalents 6.633 6,637 6.672 7.017 7,616 Property and equipment-net 21.172 19.58 20.576 19.194 20,082 Total assets 539 43 22 309 542 Short-term debt 3.621 6,995 4.703 5.861 Long-term debt 6,377 6.436 3,733 4.33 31 Total Shareholders' equity 2019 2018 2017 . Amount % to Sales Amount to Sales Amour Net als to Sales 524560 $24.971 S249 Increase (decres sales OXY 2.72 Credit card 771 165 25 100 21 CIS (15215 TO (5) Cost of sales Selling med minste Expenses Gains on sale of all 1899) (369 256 162 0. " SS 94 (184) 1.4) Restructuring impairment are closing and other LUM 035 10 TIS 970 Operating income 1 9 Benefit plan income 11 17 Settlement changes 8 () Gain on my 3 Incombe income before income taxes 728 PAR 1430 Federal, state and local income bent (open) 1356 (164) 39 Net Income 364 L09 1355 Netloss attributable to controlling interest TI Net income attributable to Macy'sInc. shareholders 3564 2. SLIO 11.566 61 SISI 35 Diluted earnings per share the to Macy's. In shareholden Supplemental Financial Mesum Gross marge 39.389 385 59,256 20 Digitales es percent of comparable wales on and basis Supplementale GAAP Financial Measure Increase (decrease in comparable sais nowned plastic basis 07 23 $2.91 418 SUN Ajuste duted earning per she attribute to Macy's, Inc. shades SET 52.336 Adjusted EBITDA SU ROIC ITIS 19.95 EXHIBIT 3 Macy's, Inc.'s Balance Sheets, 2018-2019 ($ in millions) February 1, 2020 February 2, 2019 ASSETS Current Assets: Cash and cash equivalents 5 685 1.162 Receivables 409 400 5,188 5.263 Merchandise inventories Prepaid expenses and other current assets Total Current Assets 528 620 6,810 7,445 Property and Equipment-net 6,633 6,637 2.668 Right of Use Assets 3.908 31.908 Goodwill 439 478 Other Intangible Assets-net 714 726 Other Assets $ 21.172 $ 19,194 Total Assets LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY Current Liabilities: 5 539 5 Short-term debt 1.682 1655 Merchandise accounts payable 1.10 3.445 Accounts payable and accrued liabilities 81 Income taxes 16 Total Current Liabilities 3.750 5.22 3.631 Long Term Debt Long Term Lease Llabilities Deferred Income Taxes 2.911 1.16 Other Liabilities 1.50 Shareholders' Equity Common stock (3090 and 3075 shares outstanding) Additional paid in capital Accumulated equity 7919 KOSO Treasury Mock (1741 (LIN) 1950 Accumulated other comprehensive los 19053 6.377 Total Macy's Inc. Shareholders' Equity 4.455 Noncontrolling interest 6436 Total Shureholders' Equity S2L172 5 19.194 Total Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity Overview of the Department Store Industry The department store industry was under pressure not only from ecommerce, but also from discount retailers whose product lines Ich how that women's clothing and footwear and hot goods and Thread: USB Overview of the Department Store Industry The department store industry was under pressure not only from e-commerce, but also from discount retailers whose product lines encroached on traditional department store product categories. Exhibit 4 shows that women's clothing and footwear and home goods and appliances made up the two largest categories of products sold in department stores in 2019. Drugs and cosmetics made up the third largest category of department store sales in 2019. Men's clothing and footwear, children's clothing and footwear, nongrocery food items, and toys and hobbies were all products that could be purchased at supercenter discount retailers such as Walmart and Target or wholesale clubs such as Sam's or Costco. The proliferation of such product categories both online and available in brick-and-mortar stores required mall-based department stores to offer a highly differentiated experience or distinctive product line The shopping mall experience. The business model of online only retailers such as Amazon that involved low costs for land and Page 35 buildings, real estate leases, inventory, store furnishings and merchandise displays, and personnel put tremendous pricing pressure on brick and-mortar retailers. The low prices offered by many online retailers coupled with consumers' desire for the convenience of online shopping has dramatically altered the value proposition for shopping malls and resulting customer experience. Malls, which once were a popular place to visit, shop, and pass time, were challenged as the closings of prestigious anchor stores and specialty stores made shopping at a mall less exciting for consumers. Physical malls were also expensive to build and just as costly to remodel as many had been open for some time. The aging nature of many malls also decreased consumer desire to visit a mall. There were some locations that were characterized by extreme temperatures that made shopping indoors more appealing, such as the Mall of America in Minneapolis, Minnesota. The most viable malls in 2020 tended to be upscale outdoor lifestyle malls that featured beautiful architecture and landscaping along with a strong mix of aspirational luxury brands. The overall ambiance of such malls recreated the excitement of shopping in a mall that had been common in the 1970s and 1980s. Other malls that remained popular in 2020 were outdoor outlet malls that were located near major highways that provided deep discounts on such highly sought after brands as Gucci, North Face, Coach, Abercrombie & Fitch. Under Armour, Ralph Lauren Polo, and Tori Burch, Changing consumer demographics. A declining birthrate in the United States and many developed countries resulted in fewer shoppers for an increasing number of goods. The peak of the baby boom in 1957 saw 122.7 births per 1,000 U.S. women, while the US, birth rate in 2017 had fallen to 60.3 per 1,000 women. Baby boomers had driven sharp demand increases in industries and products such as mountain bikes. golf courses and equipment, SUVs and Harley-Davidson motorcycles in the 1980s and 1990s and still made up the largest group of consumers in 2020. By 2024, the 65 and older demographic in the United States was projected to exceed 65 million consumers. Older consumers maintained tremendous purchasing power resulting from decades of career advancements and savings. The 60-demographic was the most highly educated generation and wealthiest generation in U.S. history. Much of baby boomer spending was on the purchase of goods and services for their children and grandchildren, which drove sales of products for all age demographics. The impact of purchases by grandparents as gifts to children and grandchildren had given rise to the term "grandparent economy by many in the retail industry are also important consumer groups with approximately 40 million to 45 1 Page 3 CU Generation X and early and late-Millennial shoppers were also important consumer groups with approximately 40 million to 45 million consumers in the age groups aged 25-34, 35-44 and 45-54. The focus by consumers on convenience and low prices grew stronger P.56 as age demographies declined in age. Online shopping met the discount pricing and 24-hour availability and convenience desired by Millennial shoppers, Smartphone applications greatly enhanced the ability of consumers to make purchases from any location at any time of the day. Walmart had achieved considerable success in online and mobile selling by closely studied demographics when adding services like Jetblack personal shopping, buy-online-pickup-in-store and curbside pickup services. Walmart also recognized the desire of Generation X and Millennial shoppers to focus on quality and brand prestige even though low prices remained an important consideration in purchasing decisions. The acquisitions of Bonobos, Lord & Taylor, and Bobbi Brown were made by Walmart to improve the quality of products offered in its stores and online Retail sector growth and the impact of COVID-19. The retail trade sector had grown at an average annual rate of 0.7 percent in the years 2015-2020 to reach $5,3 trillion in industry revenues. In 2020, the US retail sector was made up of 2.8 million enterprises and employed 17.6 million Americans. Total wages in the industry exceeded $476 billion. The growth rate in retail trade had also allowed for a 3.1 percent increase in retailer profit margins in 2020 and an 8.9 percent increase in wages as a share of revenues in 2020. The onset of the coronavirus in early-2020 was projected to lead to a 3.3 percent decline in revenues for the entire 2020 calendar year as retailers were required to temporarily close stores. Also, the spike in unemployment resulting from COVID-19 stay at home orders and store closures was projected to result in an overall decrease in consumer spending which would harm the US department store industry and other consumer sectors Analysts believe that the retail sector would return to a strong 1.8 percent annual growth rate for 2021 through 2025 as COVID-19 became contained and mitigated. Industry revenues were projected to increase to nearly $5.9 trillion by 2025 The declining sales of the department store segment of the retail industry. The $100 billion department store segment of the retail sector had Inred for less well than retailers such as discount supercenters, wholesale clubs, and specialty retailers during the mid-2010s. While the entire retail sector had enjoyed a 0.7 percent annual growth rate between 2015 and 2020, the department store segment of the retail sector had declined Il percent annually during those years. The number of department stores declined 4.9 percent between 2015 and 2020, with COVID-19 hastening the decay of the industry with a projected 274 percent decline in department store revenues and a 32 percent decrease in profit margins for the industry segment. Analysts projected that the department store segment of the retail industry would continue to decline by 7.5 percent annually, falling from $100 billion in 2020 to $67.7 billion in 2025 Profiles of the Largest US Department Store Chains Targer Corporation Target Corporation was the largest U.S. department store chain in 2020 with a market share of 50.1 percent and 2019 sales of $50.1 billion Target has achieved explosive growth between 2015 and 2020, allowing its market share to increase from approximately 34 percent in 2015 to 50 percent in 2020. The company operated 1.868 stores across the United States and recorded sales of $78.1 billion in fiscal 2020. A large portion of the company's sales was comprised of groceries, which lowered its sales of department store items to $50.1 the comm's sales of department store items had declined at an annual rate of 2.2 percent between 2015 and 2020 AB 6 d . Profiles of the Largest U.S. Department Store Chains Target Corporation Target Corporation was the largest U.S. department store chain in 2020 with a market share of 50.1 percent and 2019 sales of $50.1 billion. Target has achieved explosive growth between 2015 and 2020, allowing its market share to increase from approximately 34 percent in 2015 to 50 percent in 2020. The company operated 1,868 stores across the United States and recorded sales of $78.1 billion in fiscal 2020. A large portion of the company's sales was comprised of groceries, which lowered its sales of department store items to $50.1 billion. In fact, the company's sales of department store items had declined at an annual rate of 2.2 percent between 2015 and 2020, The company had been able to increase overall sales in its supercenter locations through a reimaging plan that included store Page 5 remodeling projects and the introduction of perishable and nonperishable foods to more store locations. This introduction of grocery items produced a comparable store sales growth of 5 percent. Gains in every market category was achieved coupled with a record high earnings per share increases. Key clements of Target Corporation's retail strategy included: Becoming the first U.S. retailer to offer same day and drive-up fulfillment capabilities, coast-to-coast. Remodeled more than 400 store locations by 2019. In 2018, opened more than 24 small-store formats, with 30 more planned in 2019. in high-traffic urban locations and college campuses. Focused on better guest services increased minimum wage to S12/hour, raising again in 2019 to $13/hour, with a goal of $15/hour by the end of 2020, Focused on digital channels, where in 2018 comparable digital sales grew 36 percent Introduction of more brands, more than doubling a goal of more than a dozen in 2017, which was one reason Target Corporation was named by Fast Company as one of the world's most innovative companies. Nordstrom, Inc. Nordstrom Inc. was the third largest department store chain in the United States with 380 total stores in 2020. Nordstrom Inc, had a diverse mix of retailing formats with 136 fill-line Nordstrom department stores, 244 off-price Nordstrom Rack stores, and multiple e-commerce sites. The company's greatest store concentration of Nordstrom department stores was in California with 35 full price locations followed by Texas with 10. While Nordstrom was best known for its luxurious department stores, the company's innovative online retailing platforms accounted for 46 percent of Nordstrom Holdings' total sales of $15.1 billion. Haute Look was a rapidly growing online retailing site owned by Nordstrom Holdings that was an online private sales site. Truck Club was another personalized site that allowed men to purchase personalized clothing The company had other small-format online retailing sites such as The Black Tux that allowed men to order high quality, tailored taxes that could be tried on at home and returned for further alterations. The Black Tux rentals could also be taken to a Nordstrom department store for alterations The addition of specialty online retailing sites had allowed Nordstrom Holdings to achieve overall growth, its department store specific sales had declined by 5.8 percent annually between 2015 and 2020. The profitability of its department stores had also declined to less than a one percent margin in fiscal 2020. Sears Holdings Corporation Sears Holdings Corporation resulted from the 2005 merger between Sears Roebuck and Company and Kmart Holding Corporation. The merger produced a company with a network of approximately 1,000 Sears department stores and Kmart discount stores. Sears department stores were primarily mall-based, and Kmart locations were largely standalone stores. The merger was designed to strengthen two retail brands that had each been declining rapidly for decades. For nearly 100 years, Scars held commanding market shares in nearly every department store product category, from women's, men's, and children's apparel to large appliances and even automobile tires and batteries. Sears's loss of sales in the department store industry began in the 1980s as a result of poor strategic positioning that prevented it from effectively competing with cost lenders such as Walmart and Target or with mid-tier competitors such as Macy's or J.C. Penny. Similarly. Kmart had struggled since the 1980s to effectively compete against Walmart on price and merchandise availability. The introduction of the Walmart Supercenter in 1988 exposed problems at Kmart that included old, small store locations that were no longer located in high traffic shopping areas, supply chain inefficiencies and frequent out-of-stock store inventory, low employee morale, corrupe executive leadership, and a lack of price competitiveness. Scars Holdings filed Chapter 11 bankruptcy in 2018 to contend with its 21 percent annual sales decline, operating losses estimated at 6.7 percent of revenues, and outstanding $5 billion debt. Sears Holdings closed more than 500 store locations in the first year of its bankruptcy protection and operated only 182 stores in 2020. The company closed all stores in April 2020 because of the COVID-19 pandemic and had reopened 25 stores in May 2020. Page 3 J.C. Penny Company, Inc. J.C. Penny Company operated 846 store locations in the United States and Puerto Rico and achieved total revenues of $10.7 billion in fiscal 2019. The company's sales had declined steadily from a high of $20 billion in 2006 as a result of poor merchandising strategies and ineffective leadership. The company's descent accelerated during the Great Recession of the late-2000s as CEO Myron Ullman failed to adapt pricing to the diminished purchasing power of consumers suffering the effects of the recession. J.C. Penny's financial troubles grew worse under the leadership of former Apple CEO Ron Johnson who was hired in 2011 to turnaround the failing company CEO Johnson envisioned a J.C. Penny that would compete with more upscale retailers. His strategy was based on instinct and, without market testing. Johnson change the company's store designs, logo, advertisements, and pricing model to appeal to wealthier shoppers. Under Johnson, the company dropped its popular private label brands that were very profitable and had a loyal following among low and middle income customers. Johnson also ended J.C. Penny's history of using coupons and clearance sales to attract shoppers. By 2012, with sales plunging 25 percent and the company deeply in debt, it was clear that Johnson's strategy had failed to attract wealthy customers and had driven away its formerly loyal customers. In 2013.J.C. Penny turned to former CEO Ullman in to begin a turnaround plan and in 2015, selected Marvin Ellison as CEO. Ellison had Aa reopened 25 stores in May 2020. J.C. Penny Company, Inc. J.C. Penny Company operated 846 store locations in the United States and Puerto Rico and achieved PC total revenues of S10.7 billion in fiscal 2019. The company's sales had declined steadily from a high of $20 billion in 2006 as a result of poor merchandising strategies and ineffective leadership. The company's descent accelerated during the Great Recession of the late-2000s as CEO Myron Ullman failed to adapt pricing to the diminished purchasing power of consumers suffering the effects of the recession. IC Penny's financial troubles grew worse under the leadership of former Apple CEO Ron Johnson who was hired in 2011 to turnaround the failing company CEO Johnson envisioned a J.C. Penny that would compete with more upscale retailers. His strategy was based on instinct and, without market testing, Johnson change the company's store designs, logo, advertisements, and pricing model to appeal to wealthier shoppers. Under Johnson, the company dropped its popular private label brands that were very profitable and had a loyal following among low and middle income customers. Johnson also ended 1.C. Penny's history of using coupons and clearance sales to attract shoppers. By 2012, with sales plunging 25 percent and the company deeply in debt, it was clear that Johnson's strategy had failed to attract wealthy customers and had driven away its formerly loyal customers In 2013. J.C. Penny turned to former CEO Ullman in to begin a turnaround plan and in 2015, selected Marvin Ellison as CEO Ellison had led the appliance division at Home Depot and expected to position JC Penny to take advantage of the collapse of Sears to increase sales of appliances at J.C. Penny, The plan failed to achieve success with Ellison leaving to lead Lowe's. The company continued to struggle to develop a value proposition that resonated with consumers and filed for Chapter II bankruptcy in May 2020. The company's restructuring plan would involve the permanent closing of 30 percent of its store locations, but analysts believe it was quite possible that Penny would be liquidated and go out of business permanently, Macy's, Inc. Strategic Situation in Mid-2020 With the company reporting a year-over-year sales decline or more than 45 percent from approximately $5.5 billion in Q1 2019 to approximitely $3 billion in Q1 2020, there was tremendous uncertainty about the effectiveness of Macy's turnaround and its ability to absorb the impact of COVID-19 on the retail industry. However, in comments to analysts following the company's announcement of its first Quarter 2020 results, CEO Gennetle saw several bright spots. A portion of the company's loss in Q1 2020 was a result of a $300 million charge on inventory that would have been marked down as sale items if stores had been open. Also, CEO Gennette believed that the company would be able to right size its inventory during the second quarter of 2020 to reduce overhead. Macy's management was particularly encouraged by the company's 80 percent increase in online sales during the month of May 2020 as consumers were forced to shop online during stay-at-home orders. Gennette had commented to analysts that while sales might not stabilize until 2021 2022, the company would be able to retire $1 billion in debt by 2022. With so much unpredictability, coupled with changing consumer wants and needs, the retail arena was surely one that will continue to be a challenge moving forward CASE 5 Macy's, Inc.: Will Its Strategy Allow It to Survive in the Changing Retail Sector? Alen Badal University of Liverpool John E. Gamble Texas AAM University Corpus Christi The retail landscape in the United States in early 2030 may have been best characterized rapidly changing with an certain future. The COVID-19 pandemic and stay at home orders by state and local governments had created unprecedented challenges for all retail traditional brickand mortar retailers had under pressure for alle decade. The color of shopping wearly every type of consumer good at Amazon or other online retailers had radically transformed the industry Consumer de continued to allow for Variations in strategy that allowed for distinctive ailer approaches to meeting expectation. But commentados even the most highly differentiated tailers to have an eine presence in addition to their prestigious brichardmeta location The change in consumer shopping preferences had especially impacted male departe. Nearly all shopping mall strong department store anchor to draw a number of shoppers who would rear specialized rettes during their visits to a mall The transition to online shopping and really damaged the business model malerier failed along with department stores, both of whom had experienced a declinentale per quare foot from me tratti Macy't. Inc had particularly led to adapt its best model to the online shopping with sales de cacher side its records $28.1 billion perd in 2014 in 2018. Macy turned our company were Gettetal the compro turnaround and transformation CEO to cart 2020, was in the year of his five time the company's business model and retail in the years the plan white which were for product and merchandising notions in ones that would startinanden med 100 additional stores per year. The company to implemented direct de filment model for the theme med tynd o May Translate ACCT-205-90-11 > The Oct The third element of the turnaround plan was to allow customers to order items online and pick up merchandise in a nearby store location PA Gennette also wished to expand the number of the company's off price Macy's Backstage stores from approximately 150 to more than 200. Macy's management had determined that the off price store locations were less vulnerable to competition from online retailers than its core Macy's stores. Expanding the company's loyalty plan to encourage repeat business, making online sales available through its new mobile app and better utilizing its stronges product categories like housewares and women's apparel to draw customers to its stores were less sweeping changes that rounded out the plan As of early-2020, the plan had produced few positive results with some analysts suggesting that the strategy was better aligned with PwC82 the retail environment of 2010 than of 2020. In February 2020, Macy's announced that it would close 125 store locations. By March 18 the company's COVID-19 response resulted in it closing all 775 store locations. The company began reopening stores on May 4 and expected to have 270 stores open by the 2020 Memorial Day Weekend. The combined effect of the company's ongoing poor performance and COVID 19 store closes was expected to result in a first quarter 2020 loss of $905 million to SL.1 billion Company Background Headquartered in Cincinnati, Ohio, Macy's, Inc. was the second largest department store chain with a market share of approximately 16,3 percent in 2020. The company operated about 551 Macy's department stores, 53 Bloomingdales, and 171 Bluemercury businesses in early 2020, and its retailing portfolio also included Bloomingdale's The Outlet, Macy's Backstage, and STORY and online businesses macys.com, bt oomingdales.com, and bluemercury.com. The company also licensed Bloomingdale's stores in Dubai and Kuwait for operation by Al Tayer Group Beginning in 2018, CEO Gennette and his chief lieutenants launched a five-point turnaround plan to improve the company's performance The Growth 50 initiative was focused on 50 Macy's department stores to revitalize in 2018, including store remodelsimproved customer service, and increased product assortment. The addition of STORY retail locations in 2018 supported sales growth for the company as well STORY locations were much smaller stores with an inventory assortment that was refreshed with new items every six to eight weeks. The value proposition of the STORY business was keyed to engaging consumers through an opportunity to interact with products and collaborate. The value proposition for The Market Macy's was similar, but entailed departments focated within select Macy's stores rather than operating as standalone locations. Revitalization of the customer experience at Bloomingdale's and Blumercury were also important elements of the turnaround efforts. Like cy's Bloomingdale's, the Bluemercury business operated standalone stores but also was comprised of store within-store locations inside stores. The Bluemercury division had achieved impressive sales growth for the company and an addition of 26 standalone locations Additionally. Bluemercury online sales increased by greater than 50 percent, accounting for double-digit increases in total sales. The Bluemercury division increased its private brands Lune Aster and M-6l, which accounted for greater than 10 percent of total sales al Bluemercury per company mencecand primary element of the plan and resulted in mobile d A focus on improvements in the online and mobile shopping experience was a second primary element of the plan and resulted in mobile representing the fastest growing channel for the company. The new practice of allowing Macy's customers to make purchases online and pickup merchandise in the store or buy online and ship to a store for pick up resonated with consumers. The third primaty element of the company's turnaround plan included an expansion of its loyalty program to increase customer traffic and average purchase amount. In 2018 Macy's Platinum customers generated about 30 percent of store sales shopped with more frequency, and spent 10 percent more per store visit than other customers. The company launched a new Bronze Jalty level in 2018, which yielded million new customers for Macy's by year-end The company's off-price retail brands Backstage and Bloomingdale's The Outlet were the fourth major element of the turnaround plan because of their ability to defend against online retailers. Macy's management planned to add up to 50 Backstage locations within eating Macy's store locations and construct seven freestanding stores, all to be opened by 2020. Derect vendor fulfillment was the fifth major element of the plan and was directed at reducing distribution costs across all Macy's retail operation Enging customers through destination departments such as housewares, furniture, and women's apparel were additional turnaround initiatives designed to keep customers shopping once inside store locations Exhibit 1 presents Macy's, Inc.'s Income Statements for 2015 through 2019 and reflect the company difficulty in sustaining consistent improvement in performance. The company's Results of Operations shown in Exhibit and Balance sheets shown in Exhibit provide additional operating and financial results, 2017" 2016 2015 EXHIBIT1 Macy's, Inc.'s Income Statements, 2015-2019 ($ in millions, except per share amounts) 2019 2018 52707 5245 $2.971 $25.50 $34019 102 Net sales 136 38 14 Gross margin(a) 69 LO 1.555 564 098 Operating income LOT LIOS 1566 Nincome VIORANS, VALSTS 2019 2018 2017" 2016 2015 Net sales $ 24,560 $ 24,971 $ 24,939 $ 25,908 $ 27.079 Gross margin(a) 9,389 9,756 9.758 10.242 10,583 Operating income 970 1,738 1.864 1.371 2,028 Net income 564 1.098 1.555 619 1,070 564 1108 1.566 627 1.072 $182 $3.6 $5.3 $2.03 $3.26 Net income attributable to Macy's, Inc. shareholders Basic earnings per share attributable to Macy's, Inc. shareholders Diluted earnings per share attributable to Macy's, Inc. shareholders Average number of shares outstanding SLI $3.56 $5.1 $2.02 $3.22 309.7 307.7 105.4 108.5 328.4 $ 1.51 Cash dividends paid per share $ 1.51 $15 $ 1.49 $ 139 $ 981 $ 962 $ 991 $ 1.058 $ 1.061 Depreciation and amortization $ 1.157 $932 $ 760 $ 912 $ 113 Capital expenditures Balance Sheet Data (at year end); 5 685 $ 1,162 $ 1.455 $ 1197 5 1,109 Cash and cash equivalents 6.633 6,637 6.672 7.017 7,616 Property and equipment-net 21.172 19.58 20.576 19.194 20,082 Total assets 539 43 22 309 542 Short-term debt 3.621 6,995 4.703 5.861 Long-term debt 6,377 6.436 3,733 4.33 31 Total Shareholders' equity 2019 2018 2017 . Amount % to Sales Amount to Sales Amour Net als to Sales 524560 $24.971 S249 Increase (decres sales OXY 2.72 Credit card 771 165 25 100 21 CIS (15215 TO (5) Cost of sales Selling med minste Expenses Gains on sale of all 1899) (369 256 162 0. " SS 94 (184) 1.4) Restructuring impairment are closing and other LUM 035 10 TIS 970 Operating income 1 9 Benefit plan income 11 17 Settlement changes 8 () Gain on my 3 Incombe income before income taxes 728 PAR 1430 Federal, state and local income bent (open) 1356 (164) 39 Net Income 364 L09 1355 Netloss attributable to controlling interest TI Net income attributable to Macy'sInc. shareholders 3564 2. SLIO 11.566 61 SISI 35 Diluted earnings per share the to Macy's. In shareholden Supplemental Financial Mesum Gross marge 39.389 385 59,256 20 Digitales es percent of comparable wales on and basis Supplementale GAAP Financial Measure Increase (decrease in comparable sais nowned plastic basis 07 23 $2.91 418 SUN Ajuste duted earning per she attribute to Macy's, Inc. shades SET 52.336 Adjusted EBITDA SU ROIC ITIS 19.95 EXHIBIT 3 Macy's, Inc.'s Balance Sheets, 2018-2019 ($ in millions) February 1, 2020 February 2, 2019 ASSETS Current Assets: Cash and cash equivalents 5 685 1.162 Receivables 409 400 5,188 5.263 Merchandise inventories Prepaid expenses and other current assets Total Current Assets 528 620 6,810 7,445 Property and Equipment-net 6,633 6,637 2.668 Right of Use Assets 3.908 31.908 Goodwill 439 478 Other Intangible Assets-net 714 726 Other Assets $ 21.172 $ 19,194 Total Assets LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY Current Liabilities: 5 539 5 Short-term debt 1.682 1655 Merchandise accounts payable 1.10 3.445 Accounts payable and accrued liabilities 81 Income taxes 16 Total Current Liabilities 3.750 5.22 3.631 Long Term Debt Long Term Lease Llabilities Deferred Income Taxes 2.911 1.16 Other Liabilities 1.50 Shareholders' Equity Common stock (3090 and 3075 shares outstanding) Additional paid in capital Accumulated equity 7919 KOSO Treasury Mock (1741 (LIN) 1950 Accumulated other comprehensive los 19053 6.377 Total Macy's Inc. Shareholders' Equity 4.455 Noncontrolling interest 6436 Total Shureholders' Equity S2L172 5 19.194 Total Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity Overview of the Department Store Industry The department store industry was under pressure not only from ecommerce, but also from discount retailers whose product lines Ich how that women's clothing and footwear and hot goods and Thread: USB Overview of the Department Store Industry The department store industry was under pressure not only from e-commerce, but also from discount retailers whose product lines encroached on traditional department store product categories. Exhibit 4 shows that women's clothing and footwear and home goods and appliances made up the two largest categories of products sold in department stores in 2019. Drugs and cosmetics made up the third largest category of department store sales in 2019. Men's clothing and footwear, children's clothing and footwear, nongrocery food items, and toys and hobbies were all products that could be purchased at supercenter discount retailers such as Walmart and Target or wholesale clubs such as Sam's or Costco. The proliferation of such product categories both online and available in brick-and-mortar stores required mall-based department stores to offer a highly differentiated experience or distinctive product line The shopping mall experience. The business model of online only retailers such as Amazon that involved low costs for land and Page 35 buildings, real estate leases, inventory, store furnishings and merchandise displays, and personnel put tremendous pricing pressure on brick and-mortar retailers. The low prices offered by many online retailers coupled with consumers' desire for the convenience of online shopping has dramatically altered the value proposition for shopping malls and resulting customer experience. Malls, which once were a popular place to visit, shop, and pass time, were challenged as the closings of prestigious anchor stores and specialty stores made shopping at a mall less exciting for consumers. Physical malls were also expensive to build and just as costly to remodel as many had been open for some time. The aging nature of many malls also decreased consumer desire to visit a mall. There were some locations that were characterized by extreme temperatures that made shopping indoors more appealing, such as the Mall of America in Minneapolis, Minnesota. The most viable malls in 2020 tended to be upscale outdoor lifestyle malls that featured beautiful architecture and landscaping along with a strong mix of aspirational luxury brands. The overall ambiance of such malls recreated the excitement of shopping in a mall that had been common in the 1970s and 1980s. Other malls that remained popular in 2020 were outdoor outlet malls that were located near major highways that provided deep discounts on such highly sought after brands as Gucci, North Face, Coach, Abercrombie & Fitch. Under Armour, Ralph Lauren Polo, and Tori Burch, Changing consumer demographics. A declining birthrate in the United States and many developed countries resulted in fewer shoppers for an increasing number of goods. The peak of the baby boom in 1957 saw 122.7 births per 1,000 U.S. women, while the US, birth rate in 2017 had fallen to 60.3 per 1,000 women. Baby boomers had driven sharp demand increases in industries and products such as mountain bikes. golf courses and equipment, SUVs and Harley-Davidson motorcycles in the 1980s and 1990s and still made up the largest group of consumers in 2020. By 2024, the 65 and older demographic in the United States was projected to exceed 65 million consumers. Older consumers maintained tremendous purchasing power resulting from decades of career advancements and savings. The 60-demographic was the most highly educated generation and wealthiest generation in U.S. history. Much of baby boomer spending was on the purchase of goods and services for their children and grandchildren, which drove sales of products for all age demographics. The impact of purchases by grandparents as gifts to children and grandchildren had given rise to the term "grandparent economy by many in the retail industry are also important consumer groups with approximately 40 million to 45 1 Page 3 CU Generation X and early and late-Millennial shoppers were also important consumer groups with approximately 40 million to 45 million consumers in the age groups aged 25-34, 35-44 and 45-54. The focus by consumers on convenience and low prices grew stronger P.56 as age demographies declined in age. Online shopping met the discount pricing and 24-hour availability and convenience desired by Millennial shoppers, Smartphone applications greatly enhanced the ability of consumers to make purchases from any location at any time of the day. Walmart had achieved considerable success in online and mobile selling by closely studied demographics when adding services like Jetblack personal shopping, buy-online-pickup-in-store and curbside pickup services. Walmart also recognized the desire of Generation X and Millennial shoppers to focus on quality and brand prestige even though low prices remained an important consideration in purchasing decisions. The acquisitions of Bonobos, Lord & Taylor, and Bobbi Brown were made by Walmart to improve the quality of products offered in its stores and online Retail sector growth and the impact of COVID-19. The retail trade sector had grown at an average annual rate of 0.7 percent in the years 2015-2020 to reach $5,3 trillion in industry revenues. In 2020, the US retail sector was made up of 2.8 million enterprises and employed 17.6 million Americans. Total wages in the industry exceeded $476 billion. The growth rate in retail trade had also allowed for a 3.1 percent increase in retailer profit margins in 2020 and an 8.9 percent increase in wages as a share of revenues in 2020. The onset of the coronavirus in early-2020 was projected to lead to a 3.3 percent decline in revenues for the entire 2020 calendar year as retailers were required to temporarily close stores. Also, the spike in unemployment resulting from COVID-19 stay at home orders and store closures was projected to result in an overall decrease in consumer spending which would harm the US department store industry and other consumer sectors Analysts believe that the retail sector would return to a strong 1.8 percent annual growth rate for 2021 through 2025 as COVID-19 became contained and mitigated. Industry revenues were projected to increase to nearly $5.9 trillion by 2025 The declining sales of the department store segment of the retail industry. The $100 billion department store segment of the retail sector had Inred for less well than retailers such as discount supercenters, wholesale clubs, and specialty retailers during the mid-2010s. While the entire retail sector had enjoyed a 0.7 percent annual growth rate between 2015 and 2020, the department store segment of the retail sector had declined Il percent annually during those years. The number of department stores declined 4.9 percent between 2015 and 2020, with COVID-19 hastening the decay of the industry with a projected 274 percent decline in department store revenues and a 32 percent decrease in profit margins for the industry segment. Analysts projected that the department store segment of the retail industry would continue to decline by 7.5 percent annually, falling from $100 billion in 2020 to $67.7 billion in 2025 Profiles of the Largest US Department Store Chains Targer Corporation Target Corporation was the largest U.S. department store chain in 2020 with a market share of 50.1 percent and 2019 sales of $50.1 billion Target has achieved explosive growth between 2015 and 2020, allowing its market share to increase from approximately 34 percent in 2015 to 50 percent in 2020. The company operated 1.868 stores across the United States and recorded sales of $78.1 billion in fiscal 2020. A large portion of the company's sales was comprised of groceries, which lowered its sales of department store items to $50.1 the comm's sales of department store items had declined at an annual rate of 2.2 percent between 2015 and 2020 AB 6 d . Profiles of the Largest U.S. Department Store Chains Target Corporation Target Corporation was the largest U.S. department store chain in 2020 with a market share of 50.1 percent and 2019 sales of $50.1 billion. Target has achieved explosive growth between 2015 and 2020, allowing its market share to increase from approximately 34 percent in 2015 to 50 percent in 2020. The company operated 1,868 stores across the United States and recorded sales of $78.1 billion in fiscal 2020. A large portion of the company's sales was comprised of groceries, which lowered its sales of department store items to $50.1 billion. In fact, the company's sales of department store items had declined at an annual rate of 2.2 percent between 2015 and 2020, The company had been able to increase overall sales in its supercenter locations through a reimaging plan that included store Page 5 remodeling projects and the introduction of perishable and nonperishable foods to more store locations. This introduction of grocery items produced a comparable store sales growth of 5 percent. Gains in every market category was achieved coupled with a record high earnings per share increases. Key clements of Target Corporation's retail strategy included: Becoming the first U.S. retailer to offer same day and drive-up fulfillment capabilities, coast-to-coast. Remodeled more than 400 store locations by 2019. In 2018, opened more than 24 small-store formats, with 30 more planned in 2019. in high-traffic urban locations and college campuses. Focused on better guest services increased minimum wage to S12/hour, raising again in 2019 to $13/hour, with a goal of $15/hour by the end of 2020, Focused on digital channels, where in 2018 comparable digital sales grew 36 percent Introduction of more brands, more than doubling a goal of more than a dozen in 2017, which was one reason Target Corporation was named by Fast Company as one of the world's most innovative companies. Nordstrom, Inc. Nordstrom Inc. was the third largest department store chain in the United States with 380 total stores in 2020. Nordstrom Inc, had a diverse mix of retailing formats with 136 fill-line Nordstrom department stores, 244 off-price Nordstrom Rack stores, and multiple e-commerce sites. The company's greatest store concentration of Nordstrom department stores was in California with 35 full price locations followed by Texas with 10. While Nordstrom was best known for its luxurious department stores, the company's innovative online retailing platforms accounted for 46 percent of Nordstrom Holdings' total sales of $15.1 billion. Haute Look was a rapidly growing online retailing site owned by Nordstrom Holdings that was an online private sales site. Truck Club was another personalized site that allowed men to purchase personalized clothing The company had other small-format online retailing sites such as The Black Tux that allowed men to order high quality, tailored taxes that could be tried on at home and returned for further alterations. The Black Tux rentals could also be taken to a Nordstrom department store for alterations The addition of specialty online retailing sites had allowed Nordstrom Holdings to achieve overall growth, its department store specific sales had declined by 5.8 percent annually between 2015 and 2020. The profitability of its department stores had also declined to less than a one percent margin in fiscal 2020. Sears Holdings Corporation Sears Holdings Corporation resulted from the 2005 merger between Sears Roebuck and Company and Kmart Holding Corporation. The merger produced a company with a network of approximately 1,000 Sears department stores and Kmart discount stores. Sears department stores were primarily mall-based, and Kmart locations were largely standalone stores. The merger was designed to strengthen two retail brands that had each been declining rapidly for decades. For nearly 100 years, Scars held commanding market shares in nearly every department store product category, from women's, men's, and children's apparel to large appliances and even automobile tires and batteries. Sears's loss of sales in the department store industry began in the 1980s as a result of poor strategic positioning that prevented it from effectively competing with cost lenders such as Walmart and Target or with mid-tier competitors such as Macy's or J.C. Penny. Similarly. Kmart had struggled since the 1980s to effectively compete against Walmart on price and merchandise availability. The introduction of the Walmart Supercenter in 1988 exposed problems at Kmart that included old, small store locations that were no longer located in high traffic shopping areas, supply chain inefficiencies and frequent out-of-stock store inventory, low employee morale, corrupe executive leadership, and a lack of price competitiveness. Scars Holdings filed Chapter 11 bankruptcy in 2018 to contend with its 21 percent annual sales decline, operating losses estimated at 6.7 percent of revenues, and outstanding $5 billion debt. Sears Holdings closed more than 500 store locations in the first year of its bankruptcy protection and operated only 182 stores in 2020. The company closed all stores in April 2020 because of the COVID-19 pandemic and had reopened 25 stores in May 2020. Page 3 J.C. Penny Company, Inc. J.C. Penny Company operated 846 store locations in the United States and Puerto Rico and achieved total revenues of $10.7 billion in fiscal 2019. The company's sales had declined steadily from a high of $20 billion in 2006 as a result of poor merchandising strategies and ineffective leadership. The company's descent accelerated during the Great Recession of the late-2000s as CEO Myron Ullman failed to adapt pricing to the diminished purchasing power of consumers suffering the effects of the recession. J.C. Penny's financial troubles grew worse under the leadership of former Apple CEO Ron Johnson who was hired in 2011 to turnaround the failing company CEO Johnson envisioned a J.C. Penny that would compete with more upscale retailers. His strategy was based on instinct and, without market testing. Johnson change the company's store designs, logo, advertisements, and pricing model to appeal to wealthier shoppers. Under Johnson, the company dropped its popular private label brands that were very profitable and had a loyal following among low and middle income customers. Johnson also ended J.C. Penny's history of using coupons and clearance sales to attract shoppers. By 2012, with sales plunging 25 percent and the company deeply in debt, it was clear that Johnson's strategy had failed to attract wealthy customers and had driven away its formerly loyal customers. In 2013.J.C. Penny turned to former CEO Ullman in to begin a turnaround plan and in 2015, selected Marvin Ellison as CEO. Ellison had Aa reopened 25 stores in May 2020. J.C. Penny Company, Inc. J.C. Penny Company operated 846 store locations in the United States and Puerto Rico and achieved PC total revenues of S10.7 billion in fiscal 2019. The company's sales had declined steadily from a high of $20 billion in 2006 as a result of poor merchandising strategies and ineffective leadership. The company's descent accelerated during the Great Recession of the late-2000s as CEO Myron Ullman failed to adapt pricing to the diminished purchasing power of consumers suffering the effects of the recession. IC Penny's financial troubles grew worse under the leadership of former Apple CEO Ron Johnson who was hired in 2011 to turnaround the failing company CEO Johnson envisioned a J.C. Penny that would compete with more upscale retailers. His strategy was based on instinct and, without market testing, Johnson change the company's store designs, logo, advertisements, and pricing model to appeal to wealthier shoppers. Under Johnson, the company dropped its popular private label brands that were very profitable and had a loyal following among low and middle income customers. Johnson also ended 1.C. Penny's history of using coupons and clearance sales to attract shoppers. By 2012, with sales plunging 25 percent and the company deeply in debt, it was clear that Johnson's strategy had failed to attract wealthy customers and had driven away its formerly loyal customers In 2013. J.C. Penny turned to former CEO Ullman in to begin a turnaround plan and in 2015, selected Marvin Ellison as CEO Ellison had led the appliance division at Home Depot and expected to position JC Penny to take advantage of the collapse of Sears to increase sales of appliances at J.C. Penny, The plan failed to achieve success with Ellison leaving to lead Lowe's. The company continued to struggle to develop a value proposition that resonated with consumers and filed for Chapter II bankruptcy in May 2020. The company's restructuring plan would involve the permanent closing of 30 percent of its store locations, but analysts believe it was quite possible that Penny would be liquidated and go out of business permanently, Macy's, Inc. Strategic Situation in Mid-2020 With the company reporting a year-over-year sales decline or more than 45 percent from approximately $5.5 billion in Q1 2019 to approximitely $3 billion in Q1 2020, there was tremendous uncertainty about the effectiveness of Macy's turnaround and its ability to absorb the impact of COVID-19 on the retail industry. However, in comments to analysts following the company's announcement of its first Quarter 2020 results, CEO Gennetle saw several bright spots. A portion of the company's loss in Q1 2020 was a result of a $300 million charge on inventory that would have been marked down as sale items if stores had been open. Also, CEO Gennette believed that the company would be able to right size its inventory during the second quarter of 2020 to reduce overhead. Macy's management was particularly encouraged by the company's 80 percent increase in online sales during the month of May 2020 as consumers were forced to shop online during stay-at-home orders. Gennette had commented to analysts that while sales might not stabilize until 2021 2022, the company would be able to retire $1 billion in debt by 2022. With so much unpredictability, coupled with changing consumer wants and needs, the retail arena was surely one that will continue to be a challenge moving forward 












Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


