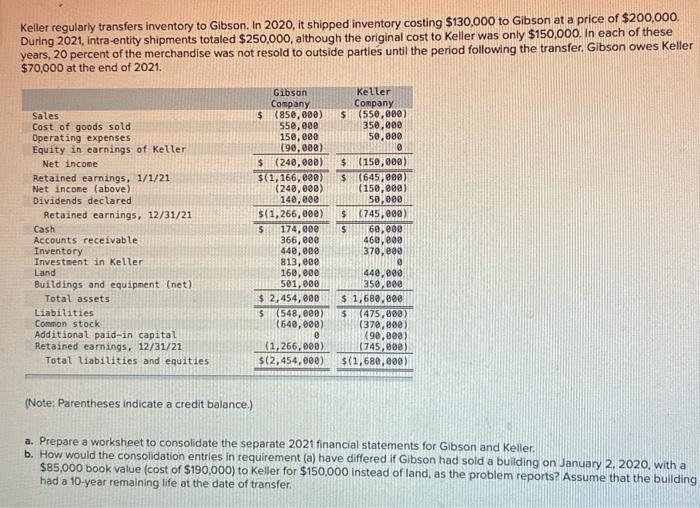
Keller regularly transfers inventory to Gibson. In 2020, it shipped inventory costing $130,000 to Gibson at a price of $200,000. During 2021, intra entity shipments totaled $250,000, although the original cost to Keller was only $150,000. In each of these years, 20 percent of the merchandise was not resold to outside parties until the period following the transfer. Gibson owes Keller $70,000 at the end of 2021. Sales Cost of goods sold Operating expenses Equity in earnings of Keller Net income Retained earnings, 1/1/21 Net income (above) Dividends declared Retained earnings, 12/31/21 Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Investment in Keller Land Buildings and equipment (net) Total assets Liabilities Common stock Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings, 12/31/21 Total liabilities and equities Gibson Company $ (858,000) 550,000 150,000 190,000) $ (240,000) ${1, 166,000) (240,000) 140,000 ${1,266,000) $ 174,000 366,000 440,000 813,000 160,000 501,000 $ 2,454,800 $ (548,800 (640,000) e (1,266,000) $(2,454,000) Keller Company $(550,000) 350,000 50,000 0 $ 150,000) $ 1645,800 (150,000 50,000 $ (745,000) $ 60,000 460,000 370,000 440,000 350.000 $ 1,680,000 $ (475,000) (378,000 (90,000) (745,000) $(1,680,000) (Note: Parentheses indicate a credit balance.) a. Prepare a worksheet to consolidate the separate 2021 financial statements for Gibson and Keller. b. How would the consolidation entries in requirement (a) have differed if Gibson had sold a building on January 2, 2020, with a $85,000 book value (cost of $190,000) to Keller for $150,000 instead of land, as the problem reports? Assume that the building had a 10-year remaining life at the date of transfer Keller regularly transfers inventory to Gibson. In 2020, it shipped inventory costing $130,000 to Gibson at a price of $200,000. During 2021, intra entity shipments totaled $250,000, although the original cost to Keller was only $150,000. In each of these years, 20 percent of the merchandise was not resold to outside parties until the period following the transfer. Gibson owes Keller $70,000 at the end of 2021. Sales Cost of goods sold Operating expenses Equity in earnings of Keller Net income Retained earnings, 1/1/21 Net income (above) Dividends declared Retained earnings, 12/31/21 Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Investment in Keller Land Buildings and equipment (net) Total assets Liabilities Common stock Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings, 12/31/21 Total liabilities and equities Gibson Company $ (858,000) 550,000 150,000 190,000) $ (240,000) ${1, 166,000) (240,000) 140,000 ${1,266,000) $ 174,000 366,000 440,000 813,000 160,000 501,000 $ 2,454,800 $ (548,800 (640,000) e (1,266,000) $(2,454,000) Keller Company $(550,000) 350,000 50,000 0 $ 150,000) $ 1645,800 (150,000 50,000 $ (745,000) $ 60,000 460,000 370,000 440,000 350.000 $ 1,680,000 $ (475,000) (378,000 (90,000) (745,000) $(1,680,000) (Note: Parentheses indicate a credit balance.) a. Prepare a worksheet to consolidate the separate 2021 financial statements for Gibson and Keller. b. How would the consolidation entries in requirement (a) have differed if Gibson had sold a building on January 2, 2020, with a $85,000 book value (cost of $190,000) to Keller for $150,000 instead of land, as the problem reports? Assume that the building had a 10-year remaining life at the date of transfer