Question
Kleinberg, Ch. 2, Exercise 2 2) In the next set of questions, we consider a related cluster of definitions, which seek to formalize the idea
Kleinberg, Ch. 2, Exercise 2
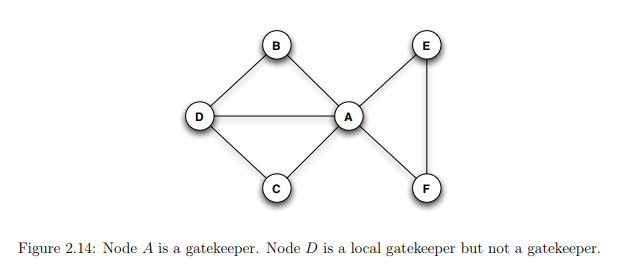
2) In the next set of questions, we consider a related cluster of definitions, which seek to formalize the idea that certain nodes can play a "gatekeeping" role in a network. The first definition is the following: we say that a node X is a if for some other two nodes Y and Z, every path from Y to Z passes through X. For example, in the graph in Figure 2.14, node A is a gatekeeper, since it lies for example on every path from B to E. (It also lies on every path between other pairs of nodes- for example, the pair D and E, as well as other pairs.)
This definition has a certain "global" flavor, since it requires that we think about paths in the full graph in order to decide whether a particular node is a gatekeeper. A more "local" version of this definition might involve only looking at the neighbors of a node. Here's a way to make this precise: we say that a node X is a local gatekeeper if there are two neighbors of X, say Y and Z, that are not connected by an edge. (That is, for X to be a local gatekeeper, thereshould be two nodes Y and Z so that Y and Z each have edges to X, but not to each other.) So for example, in Figure 2.14, node A is a local gatekeeper as well as being a gatekeeper; node D, on the other hand, is a local gatekeeper but not a gatekeeper. (Node D has neighbors B and C that are not connected by an edge; however, every pair of nodes-including B and C- can be connected by a path that does not go through D.)
So we have two new definitions: gatekeeper; and local gatekeeper. When faced with new mathematical definitions, a strategy that is often useful is to explore them first through examples, and then to access them at a more general level and try to relate them to other ideas and definitions. Let's try this in the next few questoins.
(a) Give an example (together with an explanation) of a graph in which more than half of all nodes are gatekeepers.
(b) Give an example (together with an explanation) of a graph in which there are no gatekeepers, but in which every node is a local gatekeeper.
Figure 2.14: Node A is a gatekeeper. Node D is a local gatekeeper but not a gatekeeperStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


