Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
koA= 0.1, kAo=0.9, dt=1 and using initial conditions corg,0=0, and caqu,0=10 derive the linear difference equations in matrix form for the concentration profiles of the
koA= 0.1, kAo=0.9, dt=1 and using initial conditions corg,0=0, and caqu,0=10 derive the linear difference equations in matrix form for the concentration profiles of the solute in both phases and then transfer them into eigenvaule/vector form 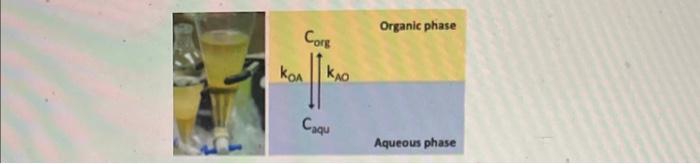

Organic phase Aqueous phase We can model the partitioning of the solute between the two phases based on a simple chemical equilibrium using the following differential equations: dtdCorg=kOACorg+kAOCaqudtdCCaqu=kOACorgkAOCaqu In these equations, Corg and Caqu are the concentrations of the solute in the organic and aqueous phases, respectively, while kOA is the rate of transferring from the organic phase to the aqueous phase and kAO is the reverse. Here we will use the following finite difference approximation to find an approximate solution to the system of ODEs: 1 y(t)tyn+1yn 

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


