Question
Laser beam divergence Object: Measuring the beam divergence angle and compare between laser diode and He-Ne laser . Apparatus: He Ne laser, pin hole, screen,
Laser beam divergence
Object:
Measuring the beam divergence angle and compare between laser diode and He-Ne
laser .
Apparatus:
He Ne laser, pin hole, screen, beam expander, diode laser.
Theory
one of the string features of most laser in that the output is in the form of in almost
parallel beam this is a very useful features for a number of application and can be
define it is the full angle of the opening beam it is measure in rad.
The relation between degree and rad. is 2n = 360 degree. And | rad = 57.3,
I mrad = 0.057 degree.
Can be measured the spot size from this relation:
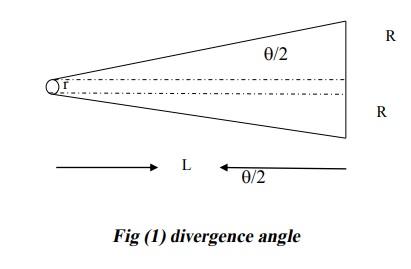
Tan (0/2) =(R-1r)/L.............Q))
Where R= radius of spot
And r= radius of aperture
And__L = the distance from laser and screen
The other feature of the laser is brightness it can be define as the power emitted per unit
solid angle. The emission sold angle (w) is:
waa. (2)
The beam brightness (B) is given by:
B = power /( area xsolid angle )
Since it mean that is very easy to collect emitting radiation and focus it on to a small area
using a fairly simple lens system a laser beam is not perfectly parallel this is not because
of a fault in laser design but is due to diffraction caused by the wave nature of light.
procedure
1- Determine (r) which represent the aperture of He Ne laser.
2- Place the screen supported by the magnetic mount directly in front of He Ne laser so
that the light from laser is perpendicularly incident on the screen.
3- Put He- Ne laser on the table make sure the area where the laser beam is pointing is
clear
4-increce the distance (L) from (1-6) M
5- Measure and record (on the data sheet) the distance of screen from laser (L)
6- Measure and record (on the data sheet) the distance of the beam (R) on the screen in
each mater.
7- Determine the exact diameter of the beam is difficult. Because the beam intensity is
reduced with 1/ (distance) 7. And over the beam across section it decay almost
exponentially (Gaussian shape) toward the edges. more accurate measurement is by
subtracting the laser beam diameter at the laser out pout ( d ) from the measure value
and call the new value ( D*)
8- Draw the graph of (D*) VS (L) a
9- Calculate (on the data sheet) the slope of the graph.
10- Calculate (on the data sheet) the angle divergence of the laser.
The slope = angle of the divergence (rad)
11- Repeat all steps with the beam expander.
12- Repeat all steps with the diode laser
| L(m) | R(mm) | r(mm) | 0(rad) |
| 1 | 3 | 2.5 | 0.928 |
| 2 | 3.5 | 2.5 | 0.926 |
| 3 | 3.75 | 2.5 | 0.76 |
| 4 | 4.5 | 2.5 | 0.934 |
| 5 | 4.5 | 2.5 | 0.76 |
| 6 |
Discussion
1- What the reason for the laser divergence?
2- Calculate the brightness of 3mw He-Ne laser and | cm in diameter?
3- The divergence of the laser beam after sending it through a telescope is 10 ~ rad
What is the diameter of the spot formed on the moon surface if the laser is directed
towards the earth? (The distance from earth to the moon is (3.8 10 *km)
(the laser beam diameter is 2mm).
R 0/2 R L 0/2 Fig (1) divergence angle R 0/2 R L 0/2 Fig (1) divergence angleStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


