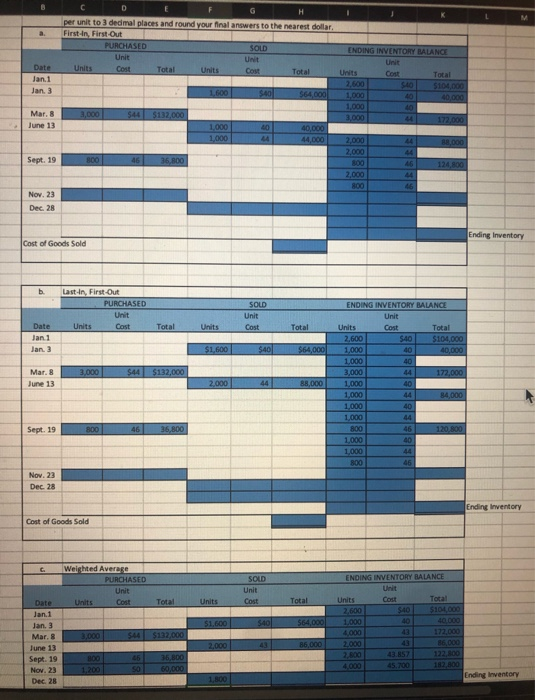
last-in, first-out method. LOG andix A) X a. P6-11B. Inventory Costing Methods-Perpetual Method Refer to the information in P6-4B and assume the perpetual inventory system is used. Required Assume that Glenn uses the first-in, first-out method. Compute the cost of goods sold for 2018 and the ending inventory balance at December 31, 2018, for product B. b. Assume that Glenn uses the last-in, first-out method. Compute the cost of goods sold for 2018 and the ending inventory balance at December 31, 2018, for product B. Assume that Glenn uses the weighted-average cost method. Compute the cost of goods sold for 2018 and the ending inventory balance at December 31, 2018, for product B. d. Assuming that Glenn sells items that quickly become obsolete, which of these three inventory costing methods would you choose to: 1. Reflect the likely goods flow through the business? 2. Minimize income tax for the period? 3. Report the largest amount of net income for the period? Explain your answers. c. a C D G H per unit to 3 dedmal places and round your final answers to the nearest dollar, First-In First Out PURCHASED SOLD Unit Unit Units Cost Total Units Cov Total Date Jan. 1 ENDING INVENTORY BALANCE Unit Units CORE Total $40 5104.000 1,000 40,000 1,000 40 3,000 172,000 Jan. 3 1,600 $40 $64.000 3,000 544 $132.000 Mar. 8 June 13 40 1,000 1,000 40,000 44,000 2.000 BR000 2.000 Sept. 19 800 46 36,800 800 2,000 124,800 46 44 46 Nov. 23 Dec. 28 Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Sold b Last-In First Out PURCHASED Unit Units Cast SOLD Unit Cost Total Units Total Date Jan 1 Jan. 3 $1,600 $40 $64,000 3,000 $44 $132,000 Mar. 8 June 13 2,000 44 88,000 ENDING INVENTORY BALANCE Unit Units Cost Total 2.600 540 $104,000 1.000 40 40,000 1,000 40 3,000 44 172.000 1,000 40 1,000 84.000 1.000 40 1,000 800 46 120.800 1,000 40 1,000 800 46 Sept. 19 800 46 36,800 Nov. 23 Dec. 28 Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Sold C ENDING INVENTORY BALANCE Weighted Average PURCHASED Unit Units Cost SOLD Unit Cost Total Units Total Cost $40 40 43 $1,600 5401 $64.000 Units 2.600 1.000 4,000 2000 2.800 3.000 Date Jan.1 Jan. 3 Mar. June 13 Sept. 19 Nov. 23 Dec. 28 $44 $132.000 Total $104,000 40.000 172.000 86.000 122.000 182,800 2,000 B6,000 36.800 43.857 800 1,200 46 SO 60,000 Ending Inventory 1.800 last-in, first-out method. LOG andix A) X a. P6-11B. Inventory Costing Methods-Perpetual Method Refer to the information in P6-4B and assume the perpetual inventory system is used. Required Assume that Glenn uses the first-in, first-out method. Compute the cost of goods sold for 2018 and the ending inventory balance at December 31, 2018, for product B. b. Assume that Glenn uses the last-in, first-out method. Compute the cost of goods sold for 2018 and the ending inventory balance at December 31, 2018, for product B. Assume that Glenn uses the weighted-average cost method. Compute the cost of goods sold for 2018 and the ending inventory balance at December 31, 2018, for product B. d. Assuming that Glenn sells items that quickly become obsolete, which of these three inventory costing methods would you choose to: 1. Reflect the likely goods flow through the business? 2. Minimize income tax for the period? 3. Report the largest amount of net income for the period? Explain your answers. c. a C D G H per unit to 3 dedmal places and round your final answers to the nearest dollar, First-In First Out PURCHASED SOLD Unit Unit Units Cost Total Units Cov Total Date Jan. 1 ENDING INVENTORY BALANCE Unit Units CORE Total $40 5104.000 1,000 40,000 1,000 40 3,000 172,000 Jan. 3 1,600 $40 $64.000 3,000 544 $132.000 Mar. 8 June 13 40 1,000 1,000 40,000 44,000 2.000 BR000 2.000 Sept. 19 800 46 36,800 800 2,000 124,800 46 44 46 Nov. 23 Dec. 28 Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Sold b Last-In First Out PURCHASED Unit Units Cast SOLD Unit Cost Total Units Total Date Jan 1 Jan. 3 $1,600 $40 $64,000 3,000 $44 $132,000 Mar. 8 June 13 2,000 44 88,000 ENDING INVENTORY BALANCE Unit Units Cost Total 2.600 540 $104,000 1.000 40 40,000 1,000 40 3,000 44 172.000 1,000 40 1,000 84.000 1.000 40 1,000 800 46 120.800 1,000 40 1,000 800 46 Sept. 19 800 46 36,800 Nov. 23 Dec. 28 Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Sold C ENDING INVENTORY BALANCE Weighted Average PURCHASED Unit Units Cost SOLD Unit Cost Total Units Total Cost $40 40 43 $1,600 5401 $64.000 Units 2.600 1.000 4,000 2000 2.800 3.000 Date Jan.1 Jan. 3 Mar. June 13 Sept. 19 Nov. 23 Dec. 28 $44 $132.000 Total $104,000 40.000 172.000 86.000 122.000 182,800 2,000 B6,000 36.800 43.857 800 1,200 46 SO 60,000 Ending Inventory 1.800