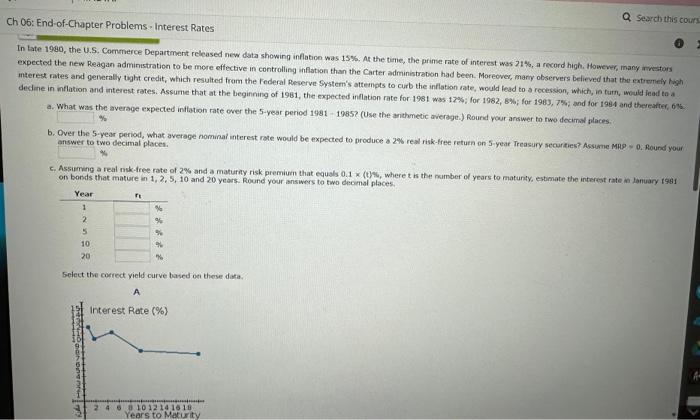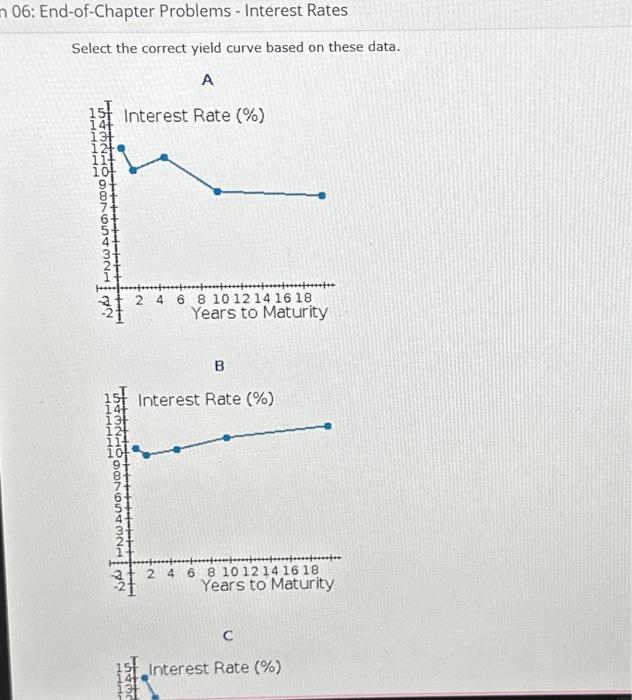
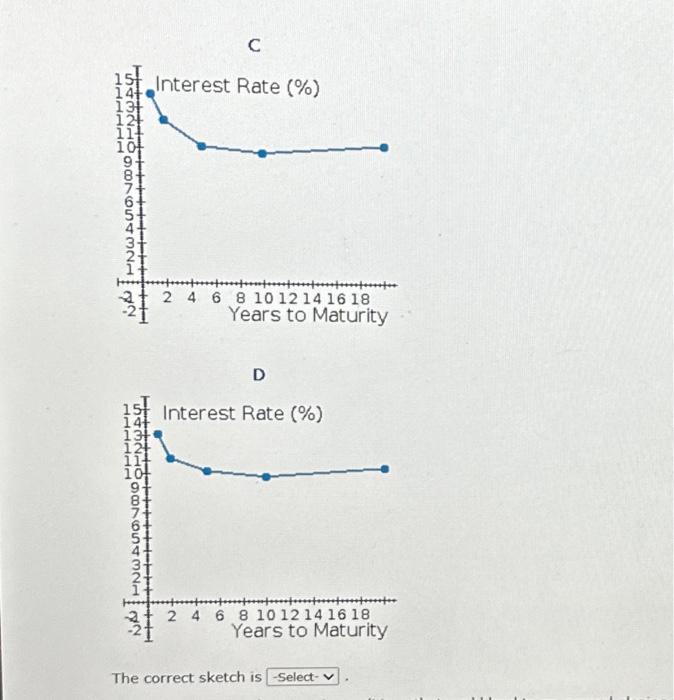

late 1980, the U.S. Commerce Department released new data showing inflation was 15%, At the time, the prime rate of interest was 21%, a record high, However, many ansators xpected the new Reagan administration to be more effective in controlling inflation than the Carter administration had been. Moreover, many observers believed that the eatremely hoh therest rates and generally toght credit, which resulted from the Federal Beserve System's attempts to curb the inflation rate, would lead to a rocessian, which, is turn, unculd iead to a a. What was the average expected inflation rate over the 5 -year period 1981 - 1985 ? (Use the arithmetic average.) Round vour answer to fwo decimal places: b. Over the 5 -year period, what average nominai interest rote would be expected to produce a 2% real risk-free return on 5-year Treasury securties? Assume Mpg = 0. Alound your answer ton two decimal places. c. Assuming a real nsk-free rate of 2% and a maturiny risk premium that equals 0.1 (t)s, where t is the number of years to maturity, estimate the interest rate in tanuary t98. on bonds that mature in 1,2,5,10 and 20 years. Round your answers to two decimal places. Select the correct yield curve based oe these data. The correct sketch is d. Describe the general economic conditions that could lead to an upward-sloping yeld curve. 1. An upward sloping yield curve is indicative of a period where inflation is expected to increase, and since the Map increases with years, the yeld curve slopes up. Durng a recession, the yield curve typically slopes upward, because inflation and consequently short term interest rates are currently low, yec people expect inflation and interest rates to rise as the economy comes out of the recession. 11. An upward skoping yeld curve is indicative of a perict where inflation is not expected to trend either up or down, but since the MRP increases with years, the vield curve slopes up. During a recession, the vield curve typically slopes up steeply, because inflation and canseciently short term interest rates are currently low, yet people expect inflation and interest rates to rise as the economy comes out of the recession. 1II. An upward sloping yield curve is indicative of a period where inflation is expected to decrease, but since the Map increases with years, the yield curve slopes up. During a recession, the yeld curve typically slopes up steeply, because infiation and consequently short-term interest rates are currently high, yet people expect inflation and interest rates to fall as the economy comes out of the recession. IV. An upward sloping yield curve is indicative of a period where inflation is expected to decrease, but since the MRP decreases with years, the yield curve slopes up. During a recession, the yeld curve typically slopes dewnward, because inflation and consequenely short-term interest rates are cumently high, yet people expect inflation and interest rates to fall as the econorry comes out of the recession. V. An upward sloping yield curve is indicative of a period where inflation is not expected to trend either up or down, but since the MRP increases with years, the yield carve slopes up. During a recession, the yield curve typically slopes up steeply, because inflation and consecuently short term interest rates are currently high, yet people expect inflation and interest rates to fall as the economy comes out of the recession. the factors that are likely to affect the curve. Does your answer here makn you question the yield ourve you drew in part C? 1. If inflation rates are expected to be constant, then the expectations theory holds that the yield curve should be horiontat. However, in this evene a is likely that would be more nearty nomal; that is, the long-term end of the curve would be rased. II. If inllation rates are expected to be canstant, then the expectasions theory holds that the vebt arve should be vertical. Hewever, in this event it is bikely that maturity isk premioms would be applied to long term bonds because of the greater nokv of holding long tem rather than short term bonds. Therefore, the vieid curve woudt be more nearly normal; that is, the lang-term end of the curve would te sloped to the right: would be more nearly normal; that in, the long term end of the curvit would be rased. IV. If inflation rates are expected to be constent, then the expectaturis theory holds that the viels curve should be upward soping thomever, n this event it is lkely that maturity risk premuirns would not be appled to long term bonds because of the lower naks of holding long term rather than short term bonds. Therefore, the vield. curve would be more nearly normal; that in, the lang term end of the curve would be henzontal. Select the correct yield curve based on these data