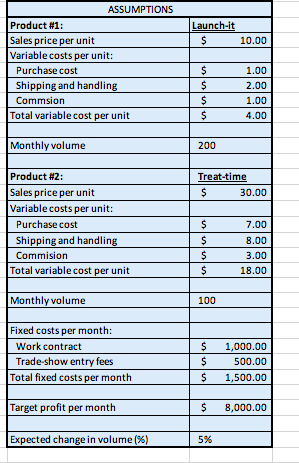


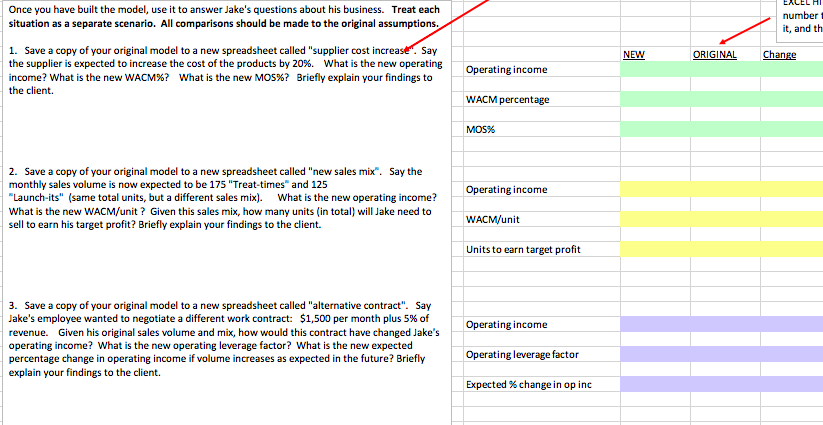
Launch-it $ 10.00 ASSUMPTIONS Product #1: Sales price per unit Variable costs per unit: Purchase cost Shipping and handling Commsion Total variable cost per unit uluun $ $ $ $ 1.00 2.00 1.00 4.00 Monthly volume 200 Treat-time 30.00 $ Product #2: Sales price per unit Variable costs per unit: Purchase cost Shipping and handling Commision Total variable cost per unit ulurumun $ $ $ $ 7.00 8.00 3.00 18.00 Monthly volume 100 Fixed costs per month: Work contract Trade show entry fees Total fixed costs per month un $ $ $ 1,000.00 500.00 1,500.00 Target profit per month $ 8,000.00 Expected change in volume (%) 5%6 Business Description After taking business classes, Jake, an avid dog-lover, decided to start selling unique pet supplies at trade shows. He has two products: Product 1: "Launch-it"- a tennis ball thrower that will sell for $10. Product 2: "Treat-time- an automatic treat dispenser that releases a treat when the dog places his paw on the pedal. The treat dispenser will sell for $30. Costs: Jake has hired an employee to work the trade show booths. The work contract is $1,000 per month plus a commission equal to 10% of revenue. Jake will also spend $500 per month on trade show entry fees. Jake is purchasing the products from a supplier in Mexico. Launch-its cost $1 each; Treat-times cost $7 each. Shipping and handling on the Launch-its will cost $2 each; Shipping and handling on the Treat-times, which are heavier, will cost $8 each. The shipping and handling costs will be paid by Jake, not the customer. Assume Jake expects to sell 200 Launch-its and 100 Treat-times during his first month of operations (une). Jake's financial goal is to earn an operating income of $8,000 per month. He believes volume may grow at a rate of 5% a month. 21 Complete the assumptions blue box based on the data about Jake's business. Identity and list all variable costs separately and all fixed costs separately before finding the total for each type of cost. 2. Complete the Product Analysis (yellow boxes) assuming Jake ONLY sells either Product #1 (Launch-its) OR Product 12 (Treat- times) 3) Complete the proforma CM Income Statement for the month of June (green box). HINT: On product line income statements such as this, the fixed costs are only listed in the total column. Make sure you also show the totals for all other line items. Finally. calculate the overall WACM% for the company. 4) Calculate the weighted average contribution margin (WAC) per unit (in orange box). 5) Use the WACM/unit to calculate the TOTAL number of units needed to breakeven (TOTAL column in the first gray box). THEN, calculate the number of EACH type of product needed to breakeven. Finally, calculate the sales revenue associated with this volume for EACH product, and then the sales revenue to breakeven in total 6) Use the WACM/unit to calculate the total number of units needed to achieve Jake's target profit TOTAL column in the second gray box). THEN, calculate the number of EACH type of product needed to achieve the target profit. Finally, calculate sales revenue associated with this volume for EACH product, and then the sales revenue in total 7) Calculate the Mos using June sales as the expected sales (purple box). Calculate the MOS in terms of sales revenue and as a percentage. Also calculate the current operating leverage factor (round to the nearest 2 decimal places) and use it to determine the expected percentage change in operating income stemming from an expected change in sales volume. 8) Change name of worksheet to "Original Assumptions". 9) Make sure you have cleaned up your worksheet using the formatting conventions listed above. 10) Go to the "Actvising client" worksheet and follow the directions found there. 11) Check to make sure you have done everything on the grading rubric. Upload your file to canvas when you are finished. number it, and th Once you have built the model, use it to answer Jake's questions about his business. Treat each situation as a separate scenario. All comparisons should be made to the original assumptions. 1. Save a copy of your original model to a new spreadsheet called "supplier cost increase". Say the supplier is expected to increase the cost of the products by 20%. What is the new operating income? What is the new WACM%? What is the new MOS%? Briefly explain your findings to the client. NEW ORIGINAL Change Operating income WACM percentage MOS% Operating income 2. Save a copy of your original model to a new spreadsheet called "new sales mix". Say the monthly sales volume is now expected to be 175 "Treat-times" and 125 "Launch-its" (same total units, but a different sales mix). What is the new operating income? What is the new WACM/unit? Given this sales mix, how many units (in total) will Jake need to sell to earn his target profit? Briefly explain your findings to the client. WACM/unit Units to earn target profit Operating income 3. Save a copy of your original model to a new spreadsheet called "alternative contract". Say Jake's employee wanted to negotiate a different work contract: $1,500 per month plus 5% of revenue. Given his original sales volume and mix, how would this contract have changed Jake's operating income? What is the new operating leverage factor? What is the new expected percentage change in operating income if volume increases as expected in the future? Briefly explain your findings to the client. Operating leverage factor Expected % change in op inc Launch-it $ 10.00 ASSUMPTIONS Product #1: Sales price per unit Variable costs per unit: Purchase cost Shipping and handling Commsion Total variable cost per unit uluun $ $ $ $ 1.00 2.00 1.00 4.00 Monthly volume 200 Treat-time 30.00 $ Product #2: Sales price per unit Variable costs per unit: Purchase cost Shipping and handling Commision Total variable cost per unit ulurumun $ $ $ $ 7.00 8.00 3.00 18.00 Monthly volume 100 Fixed costs per month: Work contract Trade show entry fees Total fixed costs per month un $ $ $ 1,000.00 500.00 1,500.00 Target profit per month $ 8,000.00 Expected change in volume (%) 5%6 Business Description After taking business classes, Jake, an avid dog-lover, decided to start selling unique pet supplies at trade shows. He has two products: Product 1: "Launch-it"- a tennis ball thrower that will sell for $10. Product 2: "Treat-time- an automatic treat dispenser that releases a treat when the dog places his paw on the pedal. The treat dispenser will sell for $30. Costs: Jake has hired an employee to work the trade show booths. The work contract is $1,000 per month plus a commission equal to 10% of revenue. Jake will also spend $500 per month on trade show entry fees. Jake is purchasing the products from a supplier in Mexico. Launch-its cost $1 each; Treat-times cost $7 each. Shipping and handling on the Launch-its will cost $2 each; Shipping and handling on the Treat-times, which are heavier, will cost $8 each. The shipping and handling costs will be paid by Jake, not the customer. Assume Jake expects to sell 200 Launch-its and 100 Treat-times during his first month of operations (une). Jake's financial goal is to earn an operating income of $8,000 per month. He believes volume may grow at a rate of 5% a month. 21 Complete the assumptions blue box based on the data about Jake's business. Identity and list all variable costs separately and all fixed costs separately before finding the total for each type of cost. 2. Complete the Product Analysis (yellow boxes) assuming Jake ONLY sells either Product #1 (Launch-its) OR Product 12 (Treat- times) 3) Complete the proforma CM Income Statement for the month of June (green box). HINT: On product line income statements such as this, the fixed costs are only listed in the total column. Make sure you also show the totals for all other line items. Finally. calculate the overall WACM% for the company. 4) Calculate the weighted average contribution margin (WAC) per unit (in orange box). 5) Use the WACM/unit to calculate the TOTAL number of units needed to breakeven (TOTAL column in the first gray box). THEN, calculate the number of EACH type of product needed to breakeven. Finally, calculate the sales revenue associated with this volume for EACH product, and then the sales revenue to breakeven in total 6) Use the WACM/unit to calculate the total number of units needed to achieve Jake's target profit TOTAL column in the second gray box). THEN, calculate the number of EACH type of product needed to achieve the target profit. Finally, calculate sales revenue associated with this volume for EACH product, and then the sales revenue in total 7) Calculate the Mos using June sales as the expected sales (purple box). Calculate the MOS in terms of sales revenue and as a percentage. Also calculate the current operating leverage factor (round to the nearest 2 decimal places) and use it to determine the expected percentage change in operating income stemming from an expected change in sales volume. 8) Change name of worksheet to "Original Assumptions". 9) Make sure you have cleaned up your worksheet using the formatting conventions listed above. 10) Go to the "Actvising client" worksheet and follow the directions found there. 11) Check to make sure you have done everything on the grading rubric. Upload your file to canvas when you are finished. number it, and th Once you have built the model, use it to answer Jake's questions about his business. Treat each situation as a separate scenario. All comparisons should be made to the original assumptions. 1. Save a copy of your original model to a new spreadsheet called "supplier cost increase". Say the supplier is expected to increase the cost of the products by 20%. What is the new operating income? What is the new WACM%? What is the new MOS%? Briefly explain your findings to the client. NEW ORIGINAL Change Operating income WACM percentage MOS% Operating income 2. Save a copy of your original model to a new spreadsheet called "new sales mix". Say the monthly sales volume is now expected to be 175 "Treat-times" and 125 "Launch-its" (same total units, but a different sales mix). What is the new operating income? What is the new WACM/unit? Given this sales mix, how many units (in total) will Jake need to sell to earn his target profit? Briefly explain your findings to the client. WACM/unit Units to earn target profit Operating income 3. Save a copy of your original model to a new spreadsheet called "alternative contract". Say Jake's employee wanted to negotiate a different work contract: $1,500 per month plus 5% of revenue. Given his original sales volume and mix, how would this contract have changed Jake's operating income? What is the new operating leverage factor? What is the new expected percentage change in operating income if volume increases as expected in the future? Briefly explain your findings to the client. Operating leverage factor Expected % change in op inc










