Question
Leander Office Products Inc. produces and sells small storage and organizational products for office use. During the first month of operations, the products sold well.
Leander Office Products Inc. produces and sells small storage and organizational products for office use. During the first month of operations, the products sold well. Andrea Leander, the owner of the company, was surprised to see a loss for the month on her income statement. This statement was prepared by a local bookkeeping service recommended to her by her bank manager. The statement follows: LEANDER OFFICE PRODUCTS INC. Income Statement Sales (57,200 units) $ 354,640 Variable expenses: Variable cost of goods sold* $ 154,440 Variable selling and administrative expenses 64,064 218,504 Contribution margin 136,136 Fixed expenses: Fixed manufacturing overhead 131,100 Fixed selling and administrative expenses 28,028 159,128 Operating loss $ (22,992 ) *Consists of direct materials, direct labour, and variable manufacturing overhead. Leander is discouraged over the loss shown for the month, particularly since she had planned to use the statement to encourage investors to purchase stock in the new company. A friend who is an accountant insists that the company should be using absorption costing rather than variable costing. He argues that if absorption costing had been used, the company would probably have reported a profit for the month. Selected cost data relating to the product and to the first month of operations follow: Units produced 71,250 Units sold 57,200 Variable costs per unit: Direct materials $ 1.22 Direct labour $ 1.24 Variable manufacturing overhead $ 0.24 Variable selling and administrative expenses $ 1.12
Prepare an income statement for the month using absorption costing. (Do not leave any empty spaces; input a 0 wherever it is required.)
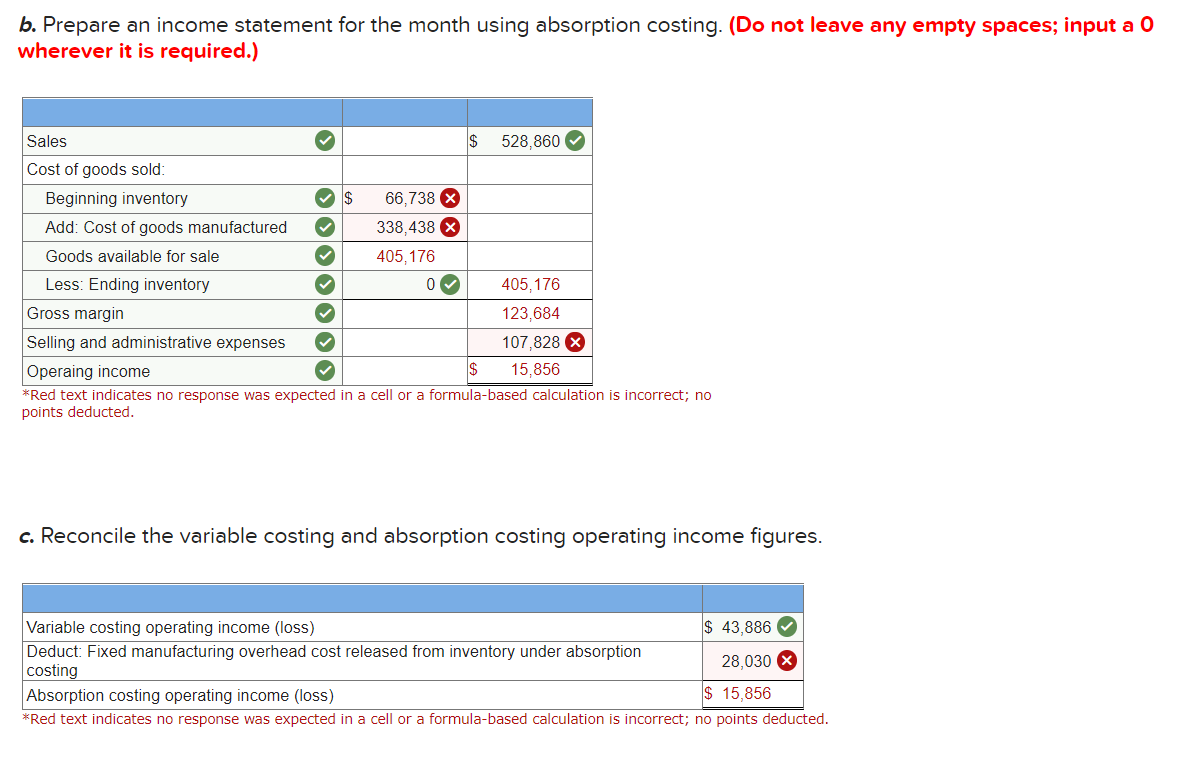
b. Prepare an income statement for the month using absorption costing. (Do not leave any empty spaces; input a 0 wherever it is required.) Sales $ 528,860 Cost of goods sold: Beginning inventory $ 66,738 X Add: Cost of goods manufactured 338,438 X Goods available for sale 405,176 Less: Ending inventory 0 405,176 Gross margin 123,684 Selling and administrative expenses 107,828 X Operaing income $ 15,856 *Red text indicates no response was expected in a cell or a formula-based calculation is incorrect; no points deducted. c. Reconcile the variable costing and absorption costing operating income figures. Variable costing operating income (loss) $ 43,886 Deduct: Fixed manufacturing overhead cost released from inventory under absorption 28,030 costing Absorption costing operating income (loss) $ 15,856 *Red text indicates no response was expected in a cell or a formula-based calculation is incorrect; no points deducted
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


