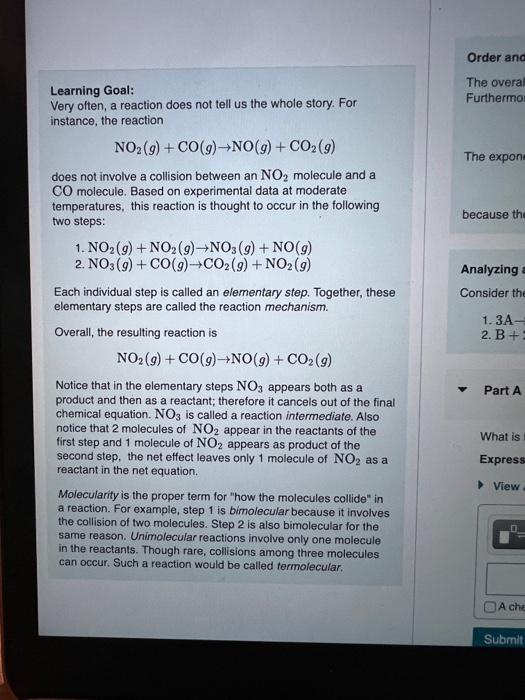
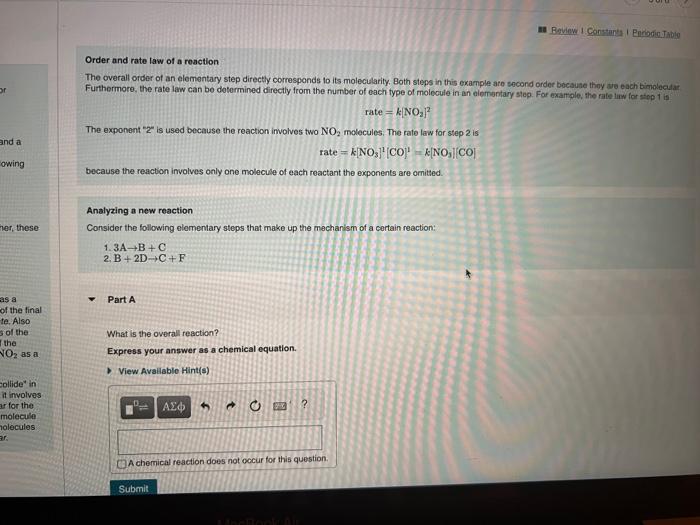
Learning Goal: Very often, a reaction does not tell us the whole story. For instance, the reaction NO2(g)+CO(g)NO(g)+CO2(g) does not involve a collision between an NO2 molecule and a CO molecule. Based on experimental data at moderate temperatures, this reaction is thought to occur in the following two steps: 1. NO2(g)+NO2(g)NO3(g)+NO(g) 2. NO3(g)+CO(g)CO2(g)+NO2(g) Each individual step is called an elementary step. Together, these elementary steps are called the reaction mechanism. Overall, the resulting reaction is The overal Furthermo Overall, the resulting reaction is NO2(g)+CO(g)NO(g)+CO2(g) Notice that in the elementary steps NO3 appears both as a product and then as a reactant; therefore it cancels out of the final chemical equation. NO3 is called a reaction intermediate. Also notice that 2 molecules of NO2 appear in the reactants of the first step and 1 molecule of NO2 appears as product of the second step, the net effect leaves only 1 molecule of NO2 as a reactant in the net equation. Molecularity is the proper term for "how the molecules collide" in a reaction. For example, step 1 is bimolecular because it involves the collision of two molecules. Step 2 is also bimolecular for the same reason. Unimolecular reactions involve only one molecule in the reactants. Though rare, collisions among three molecules can occur. Such a reaction would be called termolecular. Order and rate law of a reaction The overall order of an elementary step directly corresponds to its molecularity. Both steps in this example are second order becaute thny aie each bimolecular Furthermore, the rate law can bo dotermined directly from the fumber of each type of molocule in an alemantary step. For exartple, the rate liix for siop 1 is rate=k[NO2]2 The exponent 2 is used because the reaction involves two NO2 molecules, The tate law for step 2 is rate=k[NO3]1[CO1k[NO3][CO] because the reaction involves only one molecule of each reactant the exponents are omitted. Analyzing a new reaction Consider the following elementary steps that make up the mechanism of a certain reaction: 1.3A+B+C2.B+2DC+F Part A What is the overall reaction? Express your answer as a chemical equation. Which species is a reaction intermediate? View Available Hint(s) A B C D F What is the rate law for step 1 of this reaction? Express your answer in standard MasteringChemistry notation. For example, if the rate law is k[A][C]3 type k+[A]][C]3. View Available Hint(s) Rate = Part D What is the rate law for step 2 of this reaction? Express your answer in standard MasteringChemistry notation. For example, if the rate law is k[A][C]3 type k[A][C]3. View Available Hint(s) Rate