Summarise this lecture concisely in your own words within 350 words Learning Outcomes (1 of 3) Discuss common applications of computers and information systems Explain
Summarise this lecture concisely in your own words within 350 words
Learning Outcomes (1 of 3)
Discuss common applications of computers and information systems
Explain the differences between computer literacy and information literacy
Define transaction-processing systems
Define management information systems
Learning Outcomes (2 of 3)
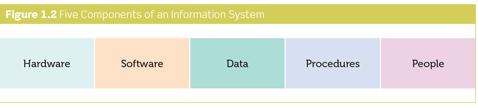
Describe the four major components of an information system
Discuss the differences between data and information
Explain the importance and applications of information systems in functional areas of a business
Learning Outcomes (3 of 3)
Discuss how information technologies are used to gain a competitive advantage
Explain the Five Forces Model and strategies for gaining a competitive advantage
Review the IT job market
Summarize the future outlook of information systems
What is an Information System?
Computers and Information Systems
Many uses
Reduce costs
Gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace
Online classes
Grocery and retail stores
Telecommuting
Social networking
Video sharing
Computer Literacy and Information Literacy (1 of 2)
Computer literacy
Skill in using productivity software, as well as having a basic knowledge of hardware and software, the Internet, and collaboration tools and technologies
Software examples: word processors, spreadsheets, database management systems, and presentation software
Computer Literacy and Information Literacy (2 of 2)
Information literacy: understanding the role of information in generating and using business intelligence (BI)
BI provides historical, current, and predictive views of business operations and environments and gives organizations a competitive advantage in the marketplace
The Beginning: Transaction-Processing Systems
Transaction-processing systems (TPSs)
Focus on data collection and processing
Used for cost reduction
Applied to structured tasks (e.g., record keeping, simple clerical operations, and inventory control)
Require minimal human involvement when automated
Management Information System (1 of 2)
Management information system (MIS)
Organized integration of hardware and software technologies, data, processes, and human elements
Designed to produce timely, integrated, relevant, accurate, and useful information for decision-making
Management Information System (2 of 2)
Designing tasks
Define the system’s objectives
Collect and analyze data
Provide information in a useful format for decision-making purposes
MIS applications
Used in both private and public sectors
Data (1 of 2)
Data component of an information system
Considered the input to the system
Sources of data
Internal: sales and personnel records
External: customers, competitors, suppliers, government agencies, financial institutions, labor and population statistics, as well as economic conditions
Data (2 of 2)
Has a time orientation
Past data: performance reports
Current data: operational reports
Can be collected in different forms
Disaggregated data: helps analyze sales by product, territory, or salesperson
Aggregated data: useful for reporting overall performance during a sales quarter
Database
Collection of relevant data organized in a series of integrated files
Essential for the success of any information system
Database management system (DBMS)
Used to create, organize, and manage databases
Reduces personnel time needed to gather, process, and interpret data manually
Process
Generates the most useful type of information for making decisions
Transaction-processing reports
Models for decision analysis that can be built into the system or accessed from external sources
Information (1 of 3)
Consists of facts analyzed by the process component and is an output of an information system
Usefulness qualities
Timeliness
Integration with other data and information
Consistency and accuracy
Relevance
Information (2 of 3)
Needs to provide either a base for users to explore different options or insight into tasks
Usefulness is affected by the information system’s user interface
Graphical user interfaces (GUIs) are used because they are flexible and easy
Information (3 of 3)
Systems should produce information in different formats, including graphics, tables, and exception reports
Increases likelihood of users understanding and being able to use the information
Users need to be able to make use of informal information when solving problems
Refer to text for examples
Using Information Systems and Information Technologies
Information technologies
The Internet
Computer networks
Database systems
Point-of-sale (POS) systems
Radio-frequency-identification (RFID) tags
The Importance of Information Systems (1 of 5)
Timely, relevant, and accurate information is a critical tool
Enhance a company’s competitive position in the marketplace
Manage the four Ms of resources
Manpower, machinery, materials, and money
The Importance of Information Systems (2 of 5)
Personnel information system (PIS) or human resource information system (HRIS)
Designed to provide information that helps decision makers in personnel carry out tasks effectively
Logistics information system (LIS)
Designed to reduce the cost of transporting materials while maintaining safe and reliable delivery
The Importance of Information Systems (3 of 5)
Manufacturing information system (MFIS)
Used to manage manufacturing resources
Reduce manufacturing costs
Increase product quality
Improve inventory decisions
The Importance of Information Systems (4 of 5)
Financial information system (FIS)
Used to provide information to financial executives in a timely manner
Marketing information system (MKIS)
Used to improve marketing decisions
Provides timely, accurate, and integrated information about the marketing mix
Price, promotion, place, and product
The Importance of Information Systems (5 of 5)
Marketing technology tools
Business, Web, and mobile analytics
E-mail marketing
Search engine marketing
Mobile technologies
Marketing automation
Using Information Technologies for a Competitive Advantage (1 of 3)
Michael Porter: three strategies for successfully competing in the marketplace
Overall cost leadership
Differentiation
Focus
Using Information Technologies for a Competitive Advantage (2 of 3)
Information systems
Help organizations reduce the cost of products and services
Help bottom-line and top-line strategies
Use enterprise systems to create an efficient and effective link between suppliers and consumers
Using Information Technologies for a Competitive Advantage (3 of 3)
Differentiation strategies
Making products and services different from competitors
Focus strategies
Focusing on specific market segments to achieve a cost or differentiation advantage
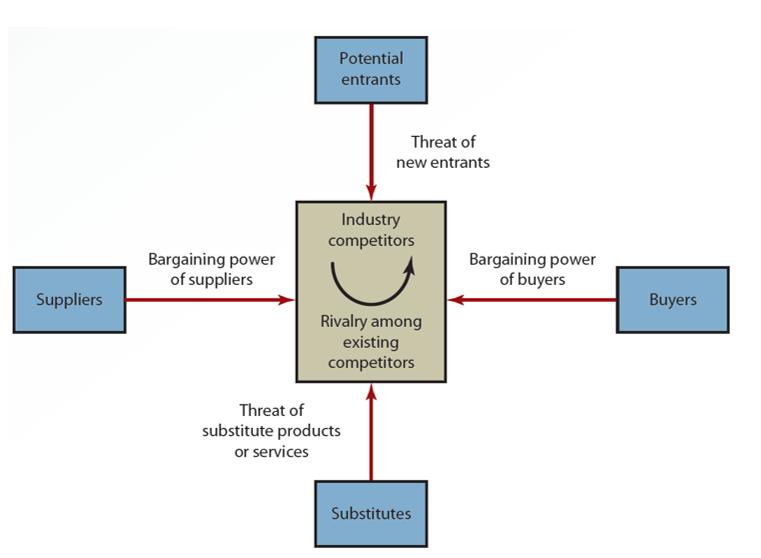
Porter’s Five Forces Model: Understanding the Business Environment (1 of 3)
Analyzes a firm’s position in the marketplace and how information systems can make it more competitive
Five forces
Buyer power
Supplier power
Threat of substitute products or services
Threat of new entrants
Rivalry among existing competitors
Exhibit: The Five Forces Model
Porter’s Five Forces Model (2 of 3)
Buyer power
High when customers have many choices and low when customers have few choices
Supplier power
High when customers have fewer options and low when customers have more options
Threat of substitute products or services
High when many alternatives to an organization’s products and services are available
Porter’s Five Forces Model (3 of 3)
Threat of new entrants
Low when duplicating a company’s product or service is difficult
Focus strategies are used to ensure that the threat remains low
Rivalry among existing competitors
High when competitors occupy the same marketplace position
Low when there are few competitors
The IT Job Market (1 of 5)
Categories of IT jobs
Operations and help desk
Programming
Systems design
Web design and Web hosting
Network design and maintenance
Database design and maintenance
Robotics and artificial intelligence
The IT Job Market (2 of 5)
Chief technology officer (CTO)/chief information officer (CIO)
Oversees long-range planning and monitors new developments that can affect a company’s success
Chief privacy officer (CPO)
Responsible for managing risks and business impacts of privacy laws and policies
The IT Job Market (3 of 5)
Manager of information systems services
Responsible for managing hardware, software, and personnel in the information systems department
Systems analyst
Responsible for the design and implementation of information systems
Should have a sound understanding of business systems and functional areas within a business organization
The IT Job Market (4 of 5)
Network administrator
Oversees a company’s internal and external network systems
Provides network and cybersecurity
Database administrator (DBA)
Responsible for database design and implementation
Required to have knowledge and understanding of data warehouses and data-mining tools
The IT Job Market (5 of 5)
Computer programmer
Writes programs or software segments that allow the information system to perform a specific task
Webmaster
Designs and maintain the organization’s Web site
Have been in high demand owing to the popularity of e-commerce applications
Outlook for the Future (1 of 3)
Predictions for the future
Hardware and software costs will decline
Artificial intelligence and related technologies will improve and expand
Computer literacy and networking technology will improve
Personal computers will improve in power and quality
Internet growth will continue
Outlook for the Future (2 of 3)
Computer criminals will become more sophisticated
Protecting personal information will become more difficult
Outlook for the Future (3 of 3)
Some of the trends that should continue
Ubiquitous computing and the Internet of Things (IoT)
3D printing, pervasive analytics, context aware computing, smart machines and devices, and cloud computing
Software defined applications and infrastructures
Security
Increased applications of augmented and virtual reality
Summary
Computers and information systems are used to reduce costs and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace
Information systems are designed to collect data, process it, and deliver timely, relevant, and useful information for making dec
Figure 1.2 Flve Components of an Information System Hardware Software Data Procedures People Figure 1.2 Flve Components of an Information System Hardware Software Data Procedures People
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (166 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started