Question
. Let T be a binary search tree. Suppose we want to include a field v.size, the number of items stored in the subtree of
. Let T be a binary search tree. Suppose we want to include a field v.size, the number of items stored in the subtree of v, at each node v.
a. Given T, describe an algorithm that will populate all the size fields in T. What is the running time of your algorithm?
b. Now suppose we make modifications to T by inserting or removing items. For each modification i.e., an insertion or a removal describe the modifications that have to be made to the size fields of the nodes in T. How much time will such modifications take?
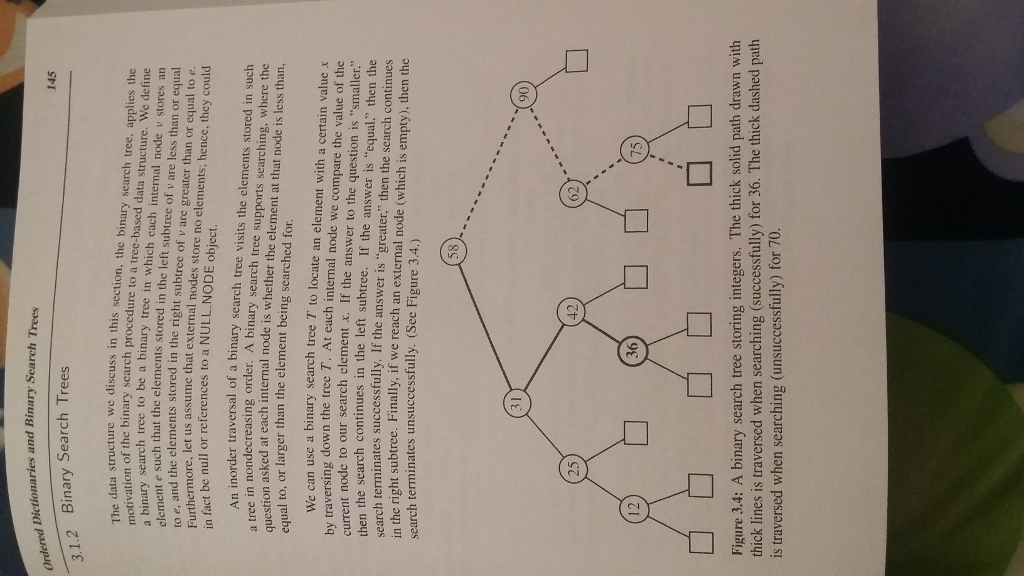 c. Using the binary search tree on Figure 3.4, insert an item with key equal to 52 and show the changes that have to be made on the size fields of the nodes in the tree. Now, remove the item with key equal to 75. Again, show the changes that have to be made on the size fields of the nodes in the tree.
c. Using the binary search tree on Figure 3.4, insert an item with key equal to 52 and show the changes that have to be made on the size fields of the nodes in the tree. Now, remove the item with key equal to 75. Again, show the changes that have to be made on the size fields of the nodes in the tree.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


