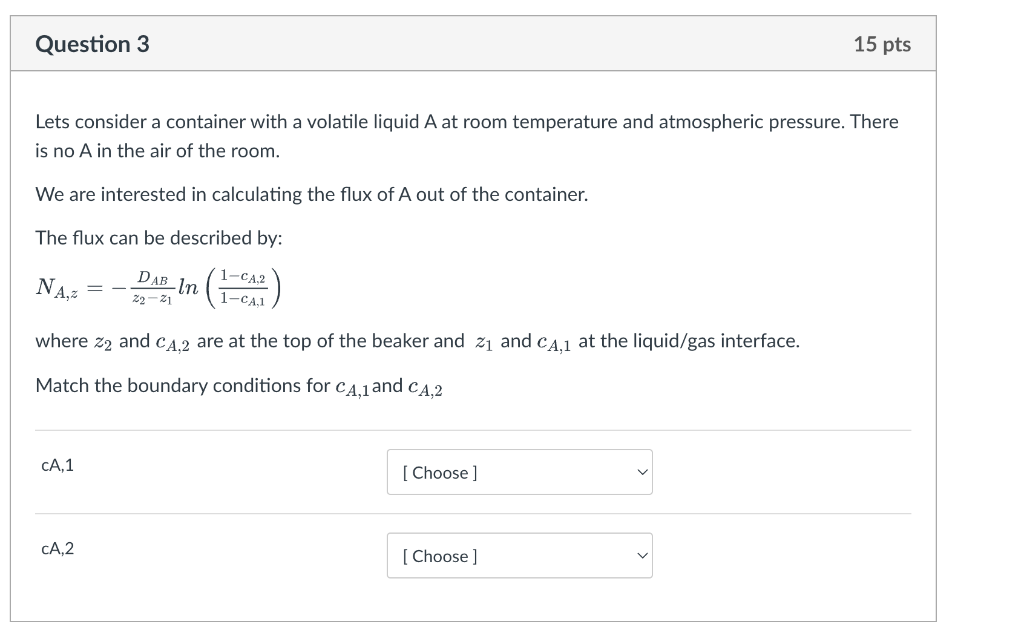
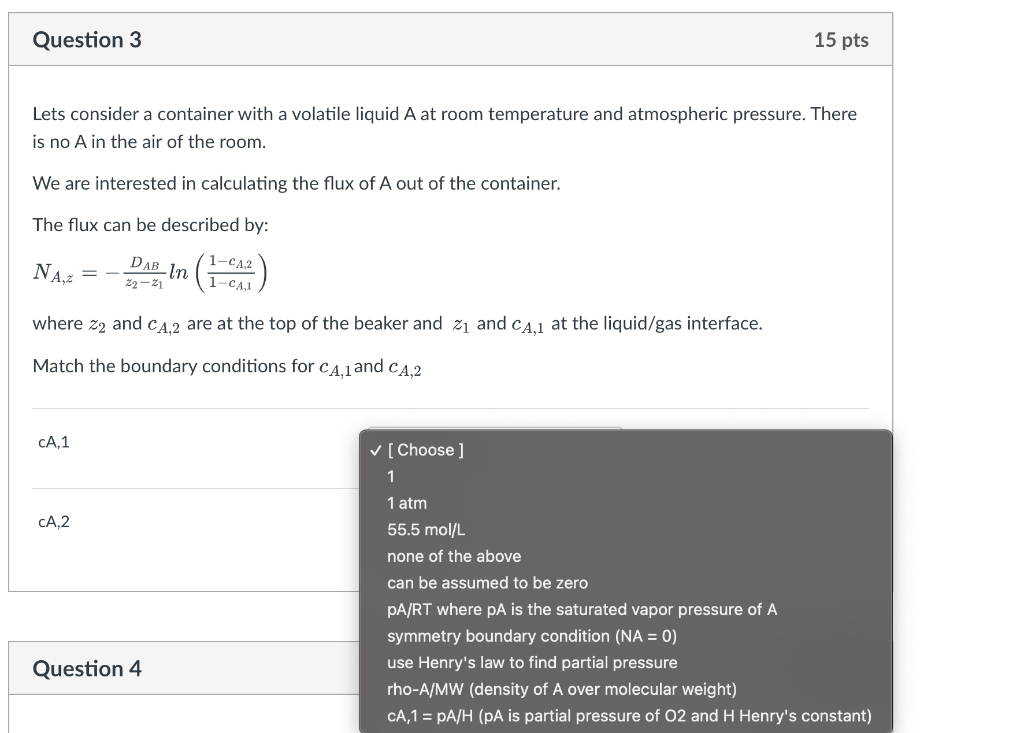
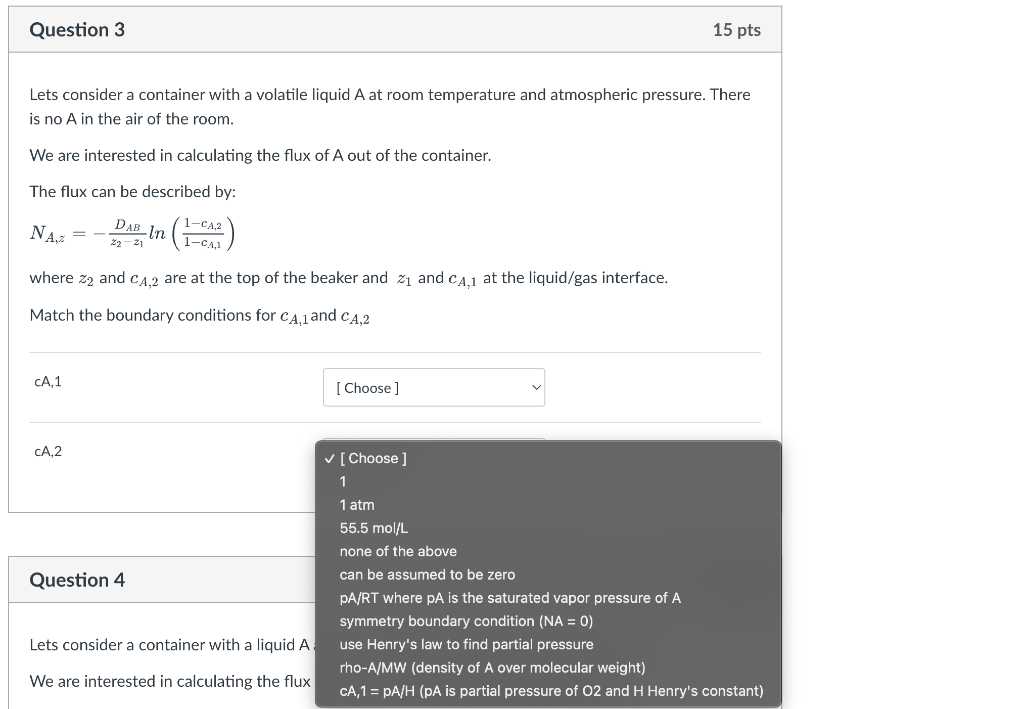
Lets consider a container with a volatile liquid A at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. There is no A in the air of the room. We are interested in calculating the flux of A out of the container. The flux can be described by: NA,z=z2z1DABln(1cA,11cA,2) where z2 and cA,2 are at the top of the beaker and z1 and cA,1 at the liquid/gas interface. Match the boundary conditions for cA,1 and cA,2 Lets consider a container with a volatile liquid A at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. There is no A in the air of the room. We are interested in calculating the flux of A out of the container. The flux can be described by: NA,z=z2z1DABln(1cA,11cA,2) where z2 and cA,2 are at the top of the beaker and z1 and cA,1 at the liquid/gas interface. Match the boundary conditions for cA,1 and cA,2 \begin{tabular}{ll} \hline cA,1 & [ Choose ] \\ & 1 \\ & 1atm \\ & 55.5mol/L,2 \\ & none of the above \\ & can be assumed to be zero \\ pA/RT where pA is the saturated vapor pressure of A \\ & symmetry boundary condition (NA = 0) \\ use Henry's law to find partial pressure \\ & rho-A/MW (density of A over molecular weight) \\ & CA,1=pA/H (pA is partial pressure of O2 and H Henry's constant) \end{tabular} Lets consider a container with a volatile liquid A at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. There is no A in the air of the room. We are interested in calculating the flux of A out of the container. The flux can be described by: NA,z=z2z1DABln(1cA,11cA,2) where z2 and cA,2 are at the top of the beaker and z1 and cA,1 at the liquid/gas interface. Match the boundary conditions for cA,1 and cA,2 cA,1 CA,2 [ Choose ] 1 1atm 55.5mol/L none of the above can be assumed to be zero pA/RT where pA is the saturated vapor pressure of A symmetry boundary condition ( NA=0 ) use Henry's law to find partial pressure rho-A/MW (density of A over molecular weight) CA,1=pA/H (pA is partial pressure of O2 and H Henry's constant) Lets consider a container with a liquid A : use Henry's law to find partial pressure We are interested in calculating the flux









