Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Loo king for assistance with questions 7 through 9. PMPM is $38.96 In setting the specific premium rates, New England must ensure that the total





Loo

king for assistance with questions 7 through 9. PMPM is $38.96
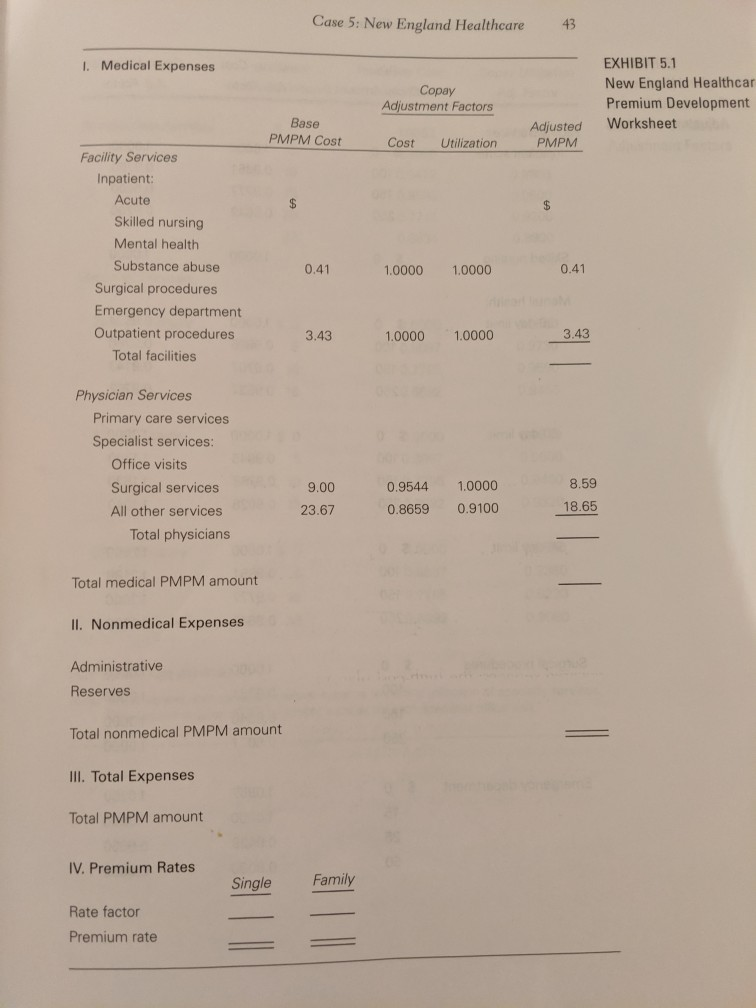
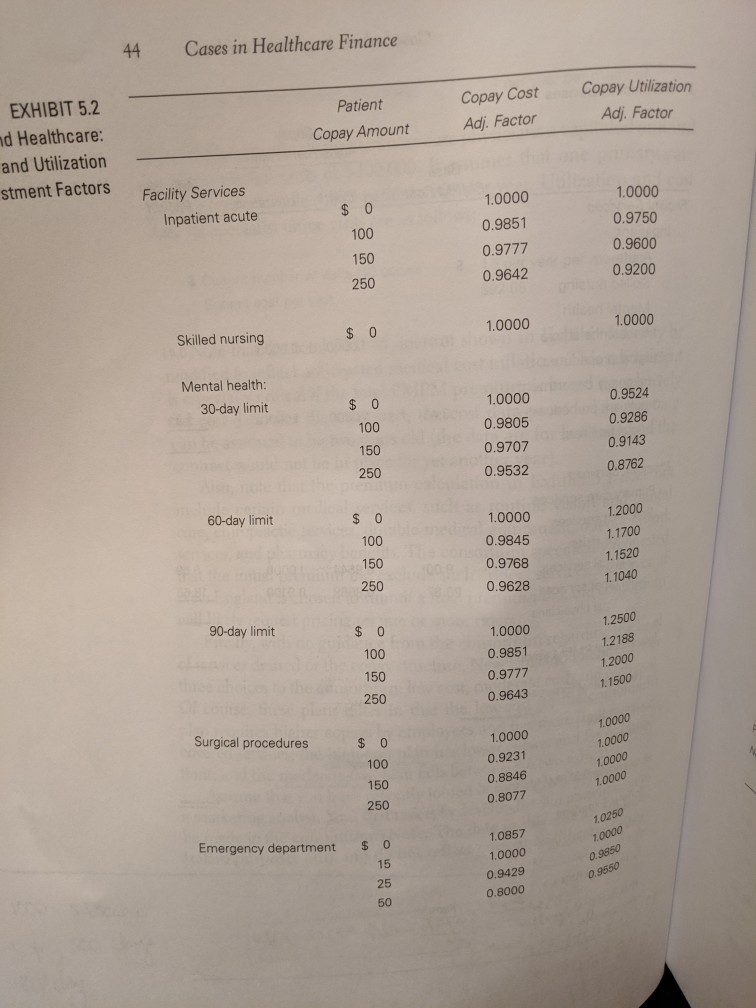
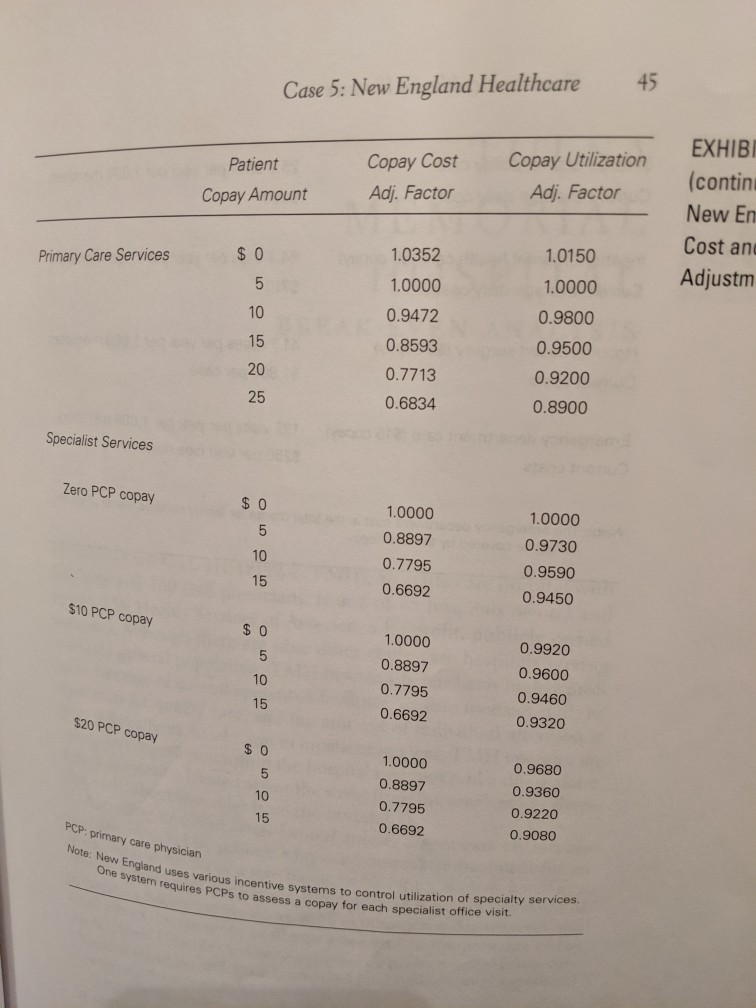
In setting the specific premium rates, New England must ensure that the total premiums collected, which would be paid by both the employer and employees, equal the estimated total calculated using the PMPM rate. The 75,000 population who would be served by the contract con- (roughly) of 12,000 individual members and 18,000 families. AThus, 75,000 x Total PMPM amount must equal (12,000 x Single premhium) + (18,000 x Family premium) Exhibit 5.1 is a partially completed copy of the worksheet that New England on any contract. The worksheet provides a relatively easy guide for implementing the procedures described above. Exhibit 5.2 contains the relevant cost and utilization adjustment factors for a variety of ser- vice and copayment options. Once the decision has been made on the appropriate service and copay structure, these adjustment factors feed into the calculations in Exhibit 5.1 for each service's medical PMPM sists uses to establish the total PMPM amount and premium rates amount. The consortium has furnished New England with a significant amount of data concerning its employees' current utilization of healthcare services. The inpatient cost and utilization data for con- sortium employees 91 are as follows: $1,400 Average daily fee-for-service charge Utilization ($100 copay) 500 days per year per 1,000 members Note, however, that a recent survey of New Hampshire hospitals indi- cates that most managed the range of $1,000 to $1,200. Additionally, New England's experi- ence with similar employee groups indicates that moderate utilization management would result in 400-450 inpatient days per 1,000 plan members. care contracts call for per diem payments in Exhibit 5.3 shows current cost and utilization data for other facility services, including skilled nursing hospital surgical services, and emergency department zation and cost data on primary care services for consortium employ- ees are as follows: care, inpatient mental health care care. The utili- Cases in Hea 42 3.4 per year per member Current number of visits ($5 copay) physicians a capitated amount New England routinely pays primary care based on annual costs of $200,000. It assumes that one primary care physician can handle 4,000 patient visits per year. Utilization and cost data for specialist office visits are as follows: 1.5 per year per member Current number of visits ($0 copay) $92.65 Current cost per visit Note that the total PMPM amount shown in Exhibit 5.1 may be modified to reflect anticipated medical cost inflation. This adjustment is especially critical if the total PMPM premium is based on old cost data. For the most part, the cost data provided in the case can be assumed to be two years old (the data are for last year, and the contract would not be in place for yet another year). Also, note that the premium calculation in Exhibit 5.l does not include certain medical services, such as routine vision and dental care, chiropractic services, durable medical equipment, out-of-network services, and pharmacy benefits. The consortium specifically requested that the initial premium bid exclude such "rider" services. However, if New England is chosen to submit a final premium bid, the consortium will likely request pricing Finally, with no of services desired or the copay structure, New England intends to offer three choices to the consortium: low cost, moderate cost, and high cost. Of course, these plans differ in that the low-cost (to the consortium) plan requires higher copays by employees and has more limitations on covered services; the high-cost plan has lower copays and fewer limita- tions; and the moderate-cost plan falls between the two extremes. relatively on one or more riders. guidance from the consortium regarding the level Assume that you have recently joined New England Healthcare as a marketing analyst. Your first task is to develop the bid presentation to be made to the consortium. (Note: The data in this case are for illus- trative purposes only and do not reflect current healthcare costs.) Case 5: New England Healthcare 43 I. Medical Expenses EXHIBIT 5.1 New England Healthcar Premium Development Copay Adjustment Factors Base PMPM Cost Worksheet Adjusted PMPM Cost Utilization Facility Services Inpatient: Acute Skilled nursing Mental health Substance abuse 0.41 0.41 1.0000 1.0000 Surgical procedures Emergency department Outpatient procedures 3.43 3.43 1.0000 1.0000 Total facilities Physician Services Primary care services Specialist services: Office visits 8.59 1.0000 Surgical services 9.00 0.9544 18.65 0.9100 All other services 0.8659 23.67 Total physicians Total medical PMPM amount 1I. Nonmedical Expenses Administrative Reserves Total nonmedical PMPM amount III. Total Expenses Total PMPM amount IV. Premium Rates Family Single Rate factor Premium rate 44 Cases in Healthcare Finance EXHIBIT 5.2 Copay Utilization Copay Cost Patient nd Healthcare: Adj. Factor Adj. Factor Copay Amount and Utilization stment Factors Facility Services 1.0000 1.0000 Inpatient acute $ 0 0.9750 0.9851 100 0.9777 0.9600 150 0.9642 0.9200 250 Skilled nursing $ 0 1.0000 1.0000 Mental health: 30-day limit $ 0 1.0000 0.9524 100 0.9805 0.9286 150 0.9707 0.9143 250 0.9532 0.8762 60-day limit $ 0 1.0000 1.2000 100 1.1700 0.9845 150 .1520 0.9768 250 .1040 0.9628 90-day limit $ 0 1.2500 1.0000 100 1.2188 0.9851 1.2000 150 0.9777 1.1500 250 0.9643 Surgical procedures 1.0000 $ 0 1,0000 1,0000 100 0.9231 10000 150 0.8846 1.0000 250 0.8077 1.0250 Emergency department 1.0857 1.0000 1.0000 15 9850 0.9429 25 2.9550 0.8000 50 45 Case 5: New England Healthcare Copay Utilization Copay Cost (contin Patient Adj. Factor Adj. Factor Copay Amount New En Cost an 1.0150 1.0352 0 Adjustm Primary Care Services 1.0000 1.0000 5 0.9800 0.9472 10 0.9500 0.8593 15 20 0.9200 0.7713 25 0.8900 0.6834 Specialist Services Zero PCP copay $ 0 1.0000 1.0000 0.8897 0.9730 10 0.7795 0.9590 15 0.6692 .9450 $10 PCP copay $ 0 1.0000 0.9920 5 0.8897 0.9600 10 0.7795 0.9460 15 0.6692 0.9320 $20 PCP copay $ 0 1.0000 0.9680 0.8897 0.9360 10 0.7795 0.9220 15 0.6692 0.9080 PCP: primary care physician Note: New England uses various incentive systems to control utilization of specialty services. One system requires PCPS to assess a cons pay for each specialist office visit 46 Cases in Healthcare Finance EXHIBIT 5.3 Skilled nursing facility care 25.2 days per year per 1,000 sortium Employee ion and Cost Data: Current average daily cost $650 er Facility Services Inpatient mental health care ($0 copay) 64.4 days per year per 1,000r Current average daily cost $740 Hospital-based surgery ($0 copay) 41.7 cases per year per 1,000 m Current costs $1,800 per case Emergency department care ($15 copay) 132 visits per vear per 1,000 men Current costs $250 per visit (see notel Note: The emergency department cost is the total charge for facility services, some of whs would be covered by the $15 copay gest Copays a 7. Which plan should the managed care company offer to the buyer consortium? ao a maleting anali or Assume that the consortium wants emplbyees to pay half of the final premium. Furthermor 8. assume that the consortium accepts your base case (moderate) bid. Finally, the consortiu wants to limit the family coverage premium to twice that of the individual coverage premiun What are the resulting premium costs to employees under single and family coverage? Expla why the premium costs to employees calculated for this question are not the same as th premium costs calculated in the model. In your opinion, what are three key learning points from this case? 9. What are the appropriate base PMPM costs for the remaining facilities services, including skilled nursing home, mental health, surgical, and emergency room utilization? 3. Now, focus your attention on physician services. What are the base PMPM costs for physician services, including primary care services and specialist office visits? Use the data developed in Questions 1 through 3, along with other required inputs, to complete the Exhibit 5.1 Premium Development Worksheet assuming that a moderate approach is taken regarding the delivery of health services. Consider this premium to be the base case. 4. 5 Now complete the worksheet for the high-cost plan. (Note: This plan will have the lowest copays and highest service thresholds.) 6. What is the premium for the low-cost plan? (Note: This plan will have the highest copays and lowest service thresholds.) 7. Which plan should the managed care company offer to the buyer consortium? ao a 8 mdleting analj or Assume that the consortium wants emplbyees to pay half of the final premium. Furthermore, assume that the consortium accepts your base case (moderate) bid. Finally, the consortium wants to limit the family coverage premium to twice that of the individual coverage premium. What are the resulting premium costs to employees under single and family coverage? Explain why the premium costs to employees calculated for this question are not the same as the premium costs calculated in the model. In your opinion, what are three key learning points from this case? 9. hoi ces Cost (highen copayeo, limitud Covued vreo 35 9/mo C h 1Ms bhw. th tuo restrictive most 01:Historical data indicate that the covered population uses 500 inpatient days of acute care services per 1,000 members Furthermore, the consortium's current average daily payment for inpatient services is $1,400. However, the managed care company's data (400+450)/2= 425 Average Days 425/1000 425 Average days utilized per member per year indicate that utilization management could reduce utilization into the 400-450 day range and that hospitals within the state currently have managed care plan contracts with per diem rates of $1,000 to $1,200. With this information in hand, calculate the appropriate base PMPM for inpatient services (1000+1200)/2 1100 Average per diem rate (425 X 1100)/12 $38.96 PMPM for inpatient services 02:What are the appropriate base PMPM costs for the remaining facilities services including skilled nursing home, mental health, surgical, and emergency room utilization? Skilled nursing home: (25.2/1,000) X (650/12) $1.365 PMPM Mental health: (64.4/1,000) X (740/12) $3.97 PMPM Surgical: (41.7/1000) X (1800/12) $6.25 PMPM Emergency services: (132/1000) X (235/12) = $2.59 PMPM In setting the specific premium rates, New England must ensure that the total premiums collected, which would be paid by both the employer and employees, equal the estimated total calculated using the PMPM rate. The 75,000 population who would be served by the contract con- (roughly) of 12,000 individual members and 18,000 families. AThus, 75,000 x Total PMPM amount must equal (12,000 x Single premhium) + (18,000 x Family premium) Exhibit 5.1 is a partially completed copy of the worksheet that New England on any contract. The worksheet provides a relatively easy guide for implementing the procedures described above. Exhibit 5.2 contains the relevant cost and utilization adjustment factors for a variety of ser- vice and copayment options. Once the decision has been made on the appropriate service and copay structure, these adjustment factors feed into the calculations in Exhibit 5.1 for each service's medical PMPM sists uses to establish the total PMPM amount and premium rates amount. The consortium has furnished New England with a significant amount of data concerning its employees' current utilization of healthcare services. The inpatient cost and utilization data for con- sortium employees 91 are as follows: $1,400 Average daily fee-for-service charge Utilization ($100 copay) 500 days per year per 1,000 members Note, however, that a recent survey of New Hampshire hospitals indi- cates that most managed the range of $1,000 to $1,200. Additionally, New England's experi- ence with similar employee groups indicates that moderate utilization management would result in 400-450 inpatient days per 1,000 plan members. care contracts call for per diem payments in Exhibit 5.3 shows current cost and utilization data for other facility services, including skilled nursing hospital surgical services, and emergency department zation and cost data on primary care services for consortium employ- ees are as follows: care, inpatient mental health care care. The utili- Cases in Hea 42 3.4 per year per member Current number of visits ($5 copay) physicians a capitated amount New England routinely pays primary care based on annual costs of $200,000. It assumes that one primary care physician can handle 4,000 patient visits per year. Utilization and cost data for specialist office visits are as follows: 1.5 per year per member Current number of visits ($0 copay) $92.65 Current cost per visit Note that the total PMPM amount shown in Exhibit 5.1 may be modified to reflect anticipated medical cost inflation. This adjustment is especially critical if the total PMPM premium is based on old cost data. For the most part, the cost data provided in the case can be assumed to be two years old (the data are for last year, and the contract would not be in place for yet another year). Also, note that the premium calculation in Exhibit 5.l does not include certain medical services, such as routine vision and dental care, chiropractic services, durable medical equipment, out-of-network services, and pharmacy benefits. The consortium specifically requested that the initial premium bid exclude such "rider" services. However, if New England is chosen to submit a final premium bid, the consortium will likely request pricing Finally, with no of services desired or the copay structure, New England intends to offer three choices to the consortium: low cost, moderate cost, and high cost. Of course, these plans differ in that the low-cost (to the consortium) plan requires higher copays by employees and has more limitations on covered services; the high-cost plan has lower copays and fewer limita- tions; and the moderate-cost plan falls between the two extremes. relatively on one or more riders. guidance from the consortium regarding the level Assume that you have recently joined New England Healthcare as a marketing analyst. Your first task is to develop the bid presentation to be made to the consortium. (Note: The data in this case are for illus- trative purposes only and do not reflect current healthcare costs.) Case 5: New England Healthcare 43 I. Medical Expenses EXHIBIT 5.1 New England Healthcar Premium Development Copay Adjustment Factors Base PMPM Cost Worksheet Adjusted PMPM Cost Utilization Facility Services Inpatient: Acute Skilled nursing Mental health Substance abuse 0.41 0.41 1.0000 1.0000 Surgical procedures Emergency department Outpatient procedures 3.43 3.43 1.0000 1.0000 Total facilities Physician Services Primary care services Specialist services: Office visits 8.59 1.0000 Surgical services 9.00 0.9544 18.65 0.9100 All other services 0.8659 23.67 Total physicians Total medical PMPM amount 1I. Nonmedical Expenses Administrative Reserves Total nonmedical PMPM amount III. Total Expenses Total PMPM amount IV. Premium Rates Family Single Rate factor Premium rate 44 Cases in Healthcare Finance EXHIBIT 5.2 Copay Utilization Copay Cost Patient nd Healthcare: Adj. Factor Adj. Factor Copay Amount and Utilization stment Factors Facility Services 1.0000 1.0000 Inpatient acute $ 0 0.9750 0.9851 100 0.9777 0.9600 150 0.9642 0.9200 250 Skilled nursing $ 0 1.0000 1.0000 Mental health: 30-day limit $ 0 1.0000 0.9524 100 0.9805 0.9286 150 0.9707 0.9143 250 0.9532 0.8762 60-day limit $ 0 1.0000 1.2000 100 1.1700 0.9845 150 .1520 0.9768 250 .1040 0.9628 90-day limit $ 0 1.2500 1.0000 100 1.2188 0.9851 1.2000 150 0.9777 1.1500 250 0.9643 Surgical procedures 1.0000 $ 0 1,0000 1,0000 100 0.9231 10000 150 0.8846 1.0000 250 0.8077 1.0250 Emergency department 1.0857 1.0000 1.0000 15 9850 0.9429 25 2.9550 0.8000 50 45 Case 5: New England Healthcare Copay Utilization Copay Cost (contin Patient Adj. Factor Adj. Factor Copay Amount New En Cost an 1.0150 1.0352 0 Adjustm Primary Care Services 1.0000 1.0000 5 0.9800 0.9472 10 0.9500 0.8593 15 20 0.9200 0.7713 25 0.8900 0.6834 Specialist Services Zero PCP copay $ 0 1.0000 1.0000 0.8897 0.9730 10 0.7795 0.9590 15 0.6692 .9450 $10 PCP copay $ 0 1.0000 0.9920 5 0.8897 0.9600 10 0.7795 0.9460 15 0.6692 0.9320 $20 PCP copay $ 0 1.0000 0.9680 0.8897 0.9360 10 0.7795 0.9220 15 0.6692 0.9080 PCP: primary care physician Note: New England uses various incentive systems to control utilization of specialty services. One system requires PCPS to assess a cons pay for each specialist office visit 46 Cases in Healthcare Finance EXHIBIT 5.3 Skilled nursing facility care 25.2 days per year per 1,000 sortium Employee ion and Cost Data: Current average daily cost $650 er Facility Services Inpatient mental health care ($0 copay) 64.4 days per year per 1,000r Current average daily cost $740 Hospital-based surgery ($0 copay) 41.7 cases per year per 1,000 m Current costs $1,800 per case Emergency department care ($15 copay) 132 visits per vear per 1,000 men Current costs $250 per visit (see notel Note: The emergency department cost is the total charge for facility services, some of whs would be covered by the $15 copay gest Copays a 7. Which plan should the managed care company offer to the buyer consortium? ao a maleting anali or Assume that the consortium wants emplbyees to pay half of the final premium. Furthermor 8. assume that the consortium accepts your base case (moderate) bid. Finally, the consortiu wants to limit the family coverage premium to twice that of the individual coverage premiun What are the resulting premium costs to employees under single and family coverage? Expla why the premium costs to employees calculated for this question are not the same as th premium costs calculated in the model. In your opinion, what are three key learning points from this case? 9. What are the appropriate base PMPM costs for the remaining facilities services, including skilled nursing home, mental health, surgical, and emergency room utilization? 3. Now, focus your attention on physician services. What are the base PMPM costs for physician services, including primary care services and specialist office visits? Use the data developed in Questions 1 through 3, along with other required inputs, to complete the Exhibit 5.1 Premium Development Worksheet assuming that a moderate approach is taken regarding the delivery of health services. Consider this premium to be the base case. 4. 5 Now complete the worksheet for the high-cost plan. (Note: This plan will have the lowest copays and highest service thresholds.) 6. What is the premium for the low-cost plan? (Note: This plan will have the highest copays and lowest service thresholds.) 7. Which plan should the managed care company offer to the buyer consortium? ao a 8 mdleting analj or Assume that the consortium wants emplbyees to pay half of the final premium. Furthermore, assume that the consortium accepts your base case (moderate) bid. Finally, the consortium wants to limit the family coverage premium to twice that of the individual coverage premium. What are the resulting premium costs to employees under single and family coverage? Explain why the premium costs to employees calculated for this question are not the same as the premium costs calculated in the model. In your opinion, what are three key learning points from this case? 9. hoi ces Cost (highen copayeo, limitud Covued vreo 35 9/mo C h 1Ms bhw. th tuo restrictive most 01:Historical data indicate that the covered population uses 500 inpatient days of acute care services per 1,000 members Furthermore, the consortium's current average daily payment for inpatient services is $1,400. However, the managed care company's data (400+450)/2= 425 Average Days 425/1000 425 Average days utilized per member per year indicate that utilization management could reduce utilization into the 400-450 day range and that hospitals within the state currently have managed care plan contracts with per diem rates of $1,000 to $1,200. With this information in hand, calculate the appropriate base PMPM for inpatient services (1000+1200)/2 1100 Average per diem rate (425 X 1100)/12 $38.96 PMPM for inpatient services 02:What are the appropriate base PMPM costs for the remaining facilities services including skilled nursing home, mental health, surgical, and emergency room utilization? Skilled nursing home: (25.2/1,000) X (650/12) $1.365 PMPM Mental health: (64.4/1,000) X (740/12) $3.97 PMPM Surgical: (41.7/1000) X (1800/12) $6.25 PMPM Emergency services: (132/1000) X (235/12) = $2.59 PMPMStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


